Abstract
Objective
To develop a height and weight based equation to estimate total body water (TBW) in Sri Lankan children.
Methods
Cross sectional descriptive study done involving 5–15 year old healthy children. Height and weight were measured. TBW was assessed using isotope dilution method (D2O) and fat free mass (FFM) calculated. Multiple regression analysis was used to develop prediction equation and validated using PRESS statistical technique. Height, weight and sex code (male=1; female=0) were used as prediction variables.
Results
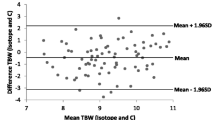
This study provides height and weight equation for the prediction of TBW in Sri Lankan children. To the best of our knowledge there are no published height weight prediction equations validated on South Asian populations.
Conclusion
Results of this study need to be affirmed by more studies on other closely related populations by using multicomponent body composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mellitus ED, Cheek DB. The assessment of body water and fatness from infancy to adulthood. Monograph of the society for research in child development 1970; 5: 12–26.
Deurenberg P, Weststrate JA, Seidell JC. Body mass index as a measure of body fatness: age- and sex-specific prediction formulas. Br J Nutr 1991; 65: 105–114.
Harsha DW, Voors AW, Berenson GS. Racial differences in subcutaneous fat patterns in children aged 7–15 years. Amer J Physi Anthropol 1980; 53: 333–337.
Wickramasinghe VP, Cleghorn GJ, Edmiston KA, Davies PSW. Impact of ethnicity upon body composition assessment in Sri Lankan Australian Children. J Pediatr Child Health 2005; 41:101–106.
Bell NA, McClure PD, Hill RJ et al. Assessment of foot-tofoot bioelectrical impedance for the prediction of total body water. Eur J Clin Nutr 1998; 52:856–859.
Lohman TG. Assessment of body composition in children. Pediatr Exerc Science 1989; 1:19–30.
Guo SS, Chumlea Wm C. Statistical methods for the development and testing of predictive equations. In Roche AF, Heymsfield SB, Lohman TG, eds. Human body composition. Champaign IL: Human Kinetics, 1996; 191–202.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986; 1:307–310.
Sun SS, Chumlea WC, Heymsfield SB, Lukaski HC, Schoeller D, Friell K et al. Development of bioelectrical impedance analysis prediction equations for body composition with the use of a multi-component model for use in epidemiological surveys. Amer J Clinic Nutr 2003; 77: 331–340.
Wickramasinghe VP, Lamabadusuriya SP, Atapattu N, Sathyadas G, Kuruparanantha S, Karunarathne P. Nutritional status of schoolchildren in an urban area of Sri Lanka. Ceylon Med J 2004; 49: 114–118.
WHO Technical Report Series-894. Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic. WHO, Geneva, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wickramasinghe, V.P., Laabadusuriya, S.P., Cleghorn, G.J. et al. Development of height-weight based equation for assessment of body composition in Sri Lankan children. Indian J Pediatr 77, 155–160 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-009-0333-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-009-0333-5