Abstract
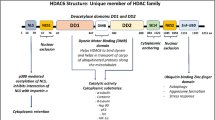
Cancer is a disease that develops when cells begin to divide uncontrollably and spreads to other parts of the body. Proliferation and invasion of cancerous cells are generally known to be influenced by cell cycle-related proteins in human malignancies. Therefore, in this review, we have emphasized on the serine/threonine kinase named NEK6. NEK6 is been deliberated to play a critical role in mitosis progression that includes mitotic spindle formation, metaphase to anaphase transition, and centrosome separation. Moreover, it has a mechanistic role in DNA repair and can cause apoptosis when inhibited. Past studies have connected NEK6 protein expression to cancer cell senescence. Besides, there are reports relating NEK6 to a range of malignancies including breast, lung, ovarian, prostate, kidney, liver, and others. Given its significance, this review attempts to describe the structural and functional aspects of NEK6 in various cellular processes, as well as how it is linked to different forms of cancer. Lastly, we have accentuated, on some of the plausible inhibitors that have been explored against NEK6 overexpression.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yin M-J, Shao L, Voehringer D, Smeal T, Jallal B. The serine/threonine kinase Nek6 is required for cell cycle progression through mitosis. J Biol Chemis United States. 2003;278:52454–60.
Pu RT, Osmani SA. Mitotic destruction of the cell cycle regulated NIMA protein kinase of Aspergillus nidulans is required for mitotic exit. EMBO J. 1995;14:995–1003.
Letwin K, Mizzen L, Motro B, Ben-David Y, Bernstein A, Pawson T. A mammalian dual specificity protein kinase, Nek1, is related to the NIMA cell cycle regulator and highly expressed in meiotic germ cells. EMBO J. 1992;11:3521–31.
Schultz SJ, Nigg EA. Identification of 21 novel human protein kinases, including 3 members of a family related to the cell cycle regulator nimA of Aspergillus nidulans. Cell Growth Differ Mol Biol J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 1993;4:821–30.
Pavan ICB, Peres de Oliveira A, Dias PRF, Basei FL, Issayama LK, de Ferezin C, C, et al. On Broken Ne(c)ks and broken DNA: the role of human NEKs in the DNA damage response. Cells. 2021;10:1–25.
Panchal NK, Evan PS. The NEK family of serine/threonine kinases as a biomarker for cancer. Clin Exp Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-021-00782-0.
Belham C, Roig J, Caldwell JA, Aoyama Y, Kemp BE, Comb M, et al. A mitotic cascade of NIMA family kinases: Nercc1/Nek9 activates the Nek6 and Nek7 kinases. J Biol Chemis. 2003;278:34897–909. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M303663200.
Hames RS, Wattam SL, Yamano H, Bacchieri R, Fry AM. Cell cycle regulation by the NEK family of protein kinases. J Cell Sci. 2001;125(19):4423–33.
O’Regan L, Fry AM. The Nek6 and Nek7 protein kinases are required for robust mitotic spindle formation and cytokinesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:3975–90.
Meirelles GV, Silva JC, de Mendonça Y, A, Ramos CHI, Torriani IL, Kobarg J. Human Nek6 is a monomeric mostly globular kinase with an unfolded short N-terminal domain. BMC Struct Biol. 2011;11(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6807-11-12.
Wu L, Osmani SA, Mirabito PM. A role for NIMA in the nuclear localization of cyclin B in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1998;141:1575–87.
De Souza CP, Osmani AH, Wu LP, Spotts JL, Osmani SA. Mitotic histone H3 phosphorylation by the NIMA kinase in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell United States. 2000;102:293–302.
Govindaraghavan M, Anglin SL, Osmani AH, Osmani SA. The Set1/COMPASS histone H3 methyltransferase helps regulate mitosis with the CDK1 and NIMA mitotic kinases in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 2014;197:1225–36.
Fry AM, O’Regan L, Sabir SR, Bayliss R. Cell cycle regulation by the NEK family of protein kinases. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:4423–33.
Fry AM, Bayliss R, Roig J. Mitotic regulation by NEK kinase networks. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017;5:1–13.
Bertran MT, Sdelci S, Regué L, Avruch J, Caelles C, Roig J. Nek9 is a Plk1-activated kinase that controls early centrosome separation through Nek6/7 and Eg5. EMBO J. 2011;30:2634–47.
Lizcano JM, Deak M, Morrice N, Kieloch A, James Hastie C, Dong L, et al. Molecular basis for the substrate specificity of NIMA-related kinase-6 (NEK6). Evidence that NEK6 does not phosphorylate the hydrophobic motif of ribosomal S6 protein kinase and serum- and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase in vivo. J Biol Chemis. 2002;277:27839–49. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M202042200.
Lee M-Y, Kim H-J, Kim M-A, Jee HJ, Kim AJ, Bae Y-S, et al. Nek6 is involved in G2/M phase cell cycle arrest through DNA damage-induced phosphorylation. Cell Cycle (Georgetown Tex). 2008;7:2705–9.
Rapley J, Nicolàs M, Groen A, Regué L, Bertran MT, Caelles C, et al. The NIMA-family kinase Nek6 phosphorylates the kinesin Eg5 at a novel site necessary for mitotic spindle formation. J cell Sci. 2008;121:3912–21.
Goshima G, Kimura A. New look inside the spindle: microtubule-dependent microtubule generation within the spindle. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010;22:44–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2009.11.012.
Leung CO, Wong CC, Fan DN, Kai AK, Tung EK, Xu IM, et al. PIM1 regulates glycolysis and promotes tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6:10880–92.
Panchal NK, Sabina EP. A serine/threonine protein PIM kinase as a biomarker of cancer and a target for anti-tumor therapy. Life Sci. 2020;255:117866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117866.
He Z, Ni X, Xia L, Shao Z. Overexpression of NIMA-related kinase 6 (NEK6) contributes to malignant growth and dismal prognosis in human breast cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2018;214:1648–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2018.07.030.
Jee HJ, Kim AJ, Song N, Kim H-J, Kim M, Koh H, et al. Nek6 overexpression antagonizes p53-induced senescence in human cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:4703–10. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.9.23.14059.
Li MZ, Yu L, Liu Q, Chu JY, Zhao SY. Assignment of NEK6, a NIMA-related gene, to human chromosome 9q33. 3–>q34.11 by radiation hybrid mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genetic. 1999;87:271–2.
Hashimoto Y, Akita H, Hibino M, Kohri K, Nakanishi M. Identification and characterization of Nek6 protein kinase, a potential human homolog of NIMA histone H3 kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;293:753–8.
Meirelles GV, Silva JC, Mendonça YDA, Ramos CHI, Torriani IL, Kobarg J. Human Nek6 is a monomeric mostly globular kinase with an unfolded short N-terminal domain. BMC Struct Biol BioMed. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6807-11-12.
Kandli M, Feige E, Chen A, Kilfin G, Motro B. Isolation and characterization of two evolutionarily conserved murine kinases (Nek6 and nek7) related to the fungal mitotic regulator. NIMA Genom U S. 2000;68:187–96.
O’Connell MJ, Krien MJE, Hunter T. Never say never The NIMA-related protein kinases in mitotic control. Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:221–8.
Johnson LN, Noble ME, Owen DJ. Active and inactive protein kinases: structural basis for regulation. Cell U S. 1996;85:149–58.
O’Regan L, Blot J, Fry AM. Mitotic regulation by NIMA-related kinases. Cell Div. 2007;2:1–12.
Vaz Meirelles G, Ferreira Lanza DC, da Silva JC, Santana Bernachi J, Paes Leme AF, Kobarg J. Characterization of hNek6 interactome reveals an important role for its short N-terminal domain and colocalization with proteins at the centrosome. J Proteom Res U S. 2010;9:6298–316.
Björn H, A. HJR, Otto H, Maria N, Jonathan R, M. SM, et al. Systematic phosphorylation analysis of human mitotic protein complexes. Sci Sig. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2001993.
Lee EJ, Hyun SH, Chun J, Kang SS. Human NIMA-related kinase 6 is one of the Fe65 WW domain binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;358:783–8.
Waitzman JS, Rice SE. Mechanism and regulation of kinesin-5, an essential motor for the mitotic spindle. Biol Cell. 2014;106:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/boc.201300054.
Kapoor T, Mitchison T. Eg5 is static in bipolar spindles relative to tubulin: evidence for a static spindle matrix. J Cell Biol. 2001;154:1125–33.
Ong JY, Bradley MC, Torres JZ. Phospho-regulation of mitotic spindle assembly. Cytoskeleton. 2020;77:558–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/cm.21649.
Mardin BR, Schiebel E. Breaking the ties that bind: new advances in centrosome biology. J Cell Biol. 2012;197:11–8. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201108006.
Pavan ICB, Peres de Oliveira A, Dias PRF, Basei FL, Issayama LK, de Ferezin C, C, et al. Won broken Ne(C)ks and broken DNA: the role of human neks in the DNA damage response. Cells. 2021;10:1–25.
Smith J, Tho LM, Xu N, Gillespie DA. The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and cancer. Adv Cancer Res U S. 2010;108:73–112.
He L, Chen M, Liang Q, Wang Y, Tan W. Current advances in coptidis rhizoma for gastrointestinal and other cancers. Front Pharmacol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.775084.
Kang J, Goodman B, Zheng Y, Tantin D. Dynamic regulation of Oct1 during mitosis by phosphorylation and ubiquitination. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e23872.
Skoblov M, Marakhonov A, Marakasova E, Guskova A, Chandhoke V, Birerdinc A, et al. Protein partners of KCTD proteins provide insights about their functional roles in cell differentiation and vertebrate development. BioEssays. 2013;35:586–96.
Hirai Y, Tamura M, Otani J, Ishikawa F. NEK6-mediated phosphorylation of human TPP1 regulates telomere length through telomerase recruitment. Genes Cells. 2016;21:874–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/gtc.12391.
Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, et al. Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry. Molecular systems biology. 2007;3:89.
Adib R, Montgomery JM, Atherton J, O’Regan L, Richards MW, Straatman KR, et al. Mitotic phosphorylation by NEK6 and NEK7 reduces the microtubule affinity of EML4 to promote chromosome congression. Sci Sig. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aaw2939.
Yu Y, Shen T, Zhong X, Wang L-L, Tai W, Zou Y, et al. NEK6 is an injury-responsive kinase cooperating with STAT3 in regulation of reactive astrogliosis. Glia U S. 2022;70:273–86.
Jeon YJ, Lee KY, Cho Y-Y, Pugliese A, Kim HG, Jeong C-H, et al. Role of NEK6 in tumor promoter-induced transformation in JB6 C141 mouse skin epidermal cells. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:28126–33.
Takeno A, Takemasa I, Doki Y, Yamasaki M, Miyata H, Takiguchi S, et al. Integrative approach for differentially overexpressed genes in gastric cancer by combining large-scale gene expression profiling and network analysis. British J Cancer. 2008;99:1307–15.
Tolomeo M, Cascio A. The multifaced role of STAT3 in cancer and its implication for anticancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):603.
Zuo J, Ma H, Cai H, Wu Y, Jiang W, Yu L. An inhibitory role of NEK6 in TGFβ/Smad signaling pathway. BMB Rep. 2015;48:473–8.
O’Regan L, Sampson J, Richards MW, Knebel A, Roth D, Hood FE, et al. Hsp72 is targeted to the mitotic spindle by Nek6 to promote K-fiber assembly and mitotic progression. J Cell Biol. 2015;209:349–58.
Sampson J, O’Regan L, Dyer MJS, Bayliss R, Fry AM. Hsp72 and Nek6 cooperate to cluster amplified centrosomes in cancer cells. Cancer Res U S. 2017;77:4785–96.
Mbita Z, Hull R, Mokoena F, Lai C-H, Dlamini Z. RBBP6 interactome: RBBP6 isoform 3/DWNN and Nek6 interaction is critical for cell cycle regulation and may play a role in carcinogenesis. Inform Med. 2021;23:100522.
Chen J, Li L, Zhang Y, Yang H, Wei Y, Zhang L, et al. Interaction of Pin1 with Nek6 and characterization of their expression correlation in Chinese hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 2006;341:1059–65.
Zhang B, Zhang H, Wang D, Han S, Wang K, Yao A, et al. Never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 6 promotes cell proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma via cyclin B modulation. Oncol Letter. 2014;8:1163–8.
Jee HJ, Kim H-J, Kim AJ, Song N, Kim M, Yun J. Nek6 suppresses the premature senescence of human cancer cells induced by camptothecin and doxorubicin treatment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;408:669–73.
Kasap E, Gerceker E, Boyacıoglu SÖ, Yuceyar H, Yıldırm H, Ayhan S, et al. The potential role of the NEK6, AURKA, AURKB, and PAK1 genes in adenomatous colorectal polyps and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2016;37:3071–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4131-6.
De DM, Fanelli M, Mariani M, Raspaglio G, Pandya D, He S, et al. Nek6 and Hif-1α cooperate with the cytoskeletal gateway of drug resistance to drive outcome in serous ovarian cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5:1862–77.
Li X, Lian L, Zhang D, Qu L, Yang N. gga-miR-26a targets NEK6 and suppresses Marek’s disease lymphoma cell proliferation. Poultry Sci. 2014;93:1097–105.
Hong Z, Chen Z, Pan J, Shi Z, Wang C, Qiu C. 2022 MicroRNA-323a-3p negatively regulates NEK6 in colon adenocarcinoma cells. J Oncol. 2022;1:11.
Atish DC, Anna CS, Maura BC, Rosina TL, Katherine L, Ying JL, et al. Castration resistance in prostate cancer is mediated by the kinase NEK6. Cancer Res. 2017;77:753–65.
Choudhury AD, Schinzel AC, Cotter MB, Lis RT, Labella K, Lock YJ, et al. Castration resistance in prostate cancer is mediated by the kinase NEK6. Cancer Res. 2017;77:753–65.
Xu J, He Q, He X, Shao Q, Tao H, Ye Z. Expression of NEK-6 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Zhonghua wei chang wai ke za zhi Chinese J Gastroint Surg. 2015;18:1036–40.
Cao F, Wu X, Shan Y, Zhang B, Wang H, Liu H, et al. Circular RNA NEK6 contributes to the development of non-small-cell lung cancer by competitively binding with miR-382-5p to elevate BCAS2 expression at post-transcriptional level. BMC Pulm Med. 2021;21:325.
Yang M, Guo Y, Guo X, Mao Y, Zhu S, Wang N, et al. Analysis of the effect of NEKs on the prognosis of patients with non-small-cell lung carcinoma based on bioinformatics. Sci Rep. 2022;12:1705. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05728-4.
Wang XJ, Li S, Fang J, Yan ZJ, Luo GC. LncRNA FAM13A-AS1 promotes renal carcinoma tumorigenesis through sponging miR-141-3p to upregulate NEK6 expression. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:738711.
Li C-Q, Huang G-W, Wu Z-Y, Xu Y-J, Li X-C, Xue Y-J, et al. Integrative analyses of transcriptome sequencing identify novel functional lncRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogenesis. 2017;6:e297.
Wu L, Chen Z, Xing Y. MiR-506-3p inhibits cell proliferation, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in retinoblastoma by directly targeting NEK6. Cell Biol Int. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11041.
Smith AJ, Sompel KM, Elango A, Tennis MA. Non-coding RNA and frizzled receptors in cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:1–9.
Chen F, Feng Z, Zhu J, Liu P, Yang C, Huang R, et al. Emerging roles of circRNA_NEK6 targeting miR-370-3p in the proliferation and invasion of thyroid cancer via Wnt signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19:1139–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2018.1480888.
Gerçeker E, Boyacioglu SO, Kasap E, Baykan A, Yuceyar H, Yildirim H, et al. Never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 6 and aurora kinase a: new gene biomarkers in the conversion from ulcerative colitis to colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2015;34:1905–14.
Kasap E, Boyacioglu SÖ, Korkmaz M, Yuksel ES, Ünsal B, Kahraman E, et al. Aurora kinase A (AURKA) and never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 6 (NEK6) genes are upregulated in erosive esophagitis and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 2012;4:33–42.
Liu Y, Fu W, Yin F, Xia L, Zhang Y, Wang B, et al. miR-141-3p suppresses development of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by regulating NEK6. Anti Cancer Drugs Eng. 2022;33:e125–33.
Jee HJ, Kim H-J, Kim AJ, Song N, Kim M, Lee H-J, et al. The inhibition of Nek6 function sensitizes human cancer cells to premature senescence upon serum reduction or anticancer drug treatment. Cancer Lett. 2013;335:175–82.
De Donato M, Righino B, Filippetti F, Battaglia A, Petrillo M, Pirolli D, et al. Identification and antitumor activity of a novel inhibitor of the NIMA-related kinase NEK6. Sci Rep. 2018;8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34471-y.
Mutlu P. Bulletin of Biotechnology NEK6 gene silencing using siRNA for overcome multidrug resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Bull Biotechnol. 2022;3:1–6.
Kedhari Sundaram M, Hussain A, Haque S, Raina R, Afroze N. Quercetin modifies 5’CpG promoter methylation and reactivates various tumor suppressor genes by modulating epigenetic marks in human cervical cancer cells. J Cell Biochem U S. 2019;120:18357–69.
Moraes EC, Meirelles GV, Honorato RV, de Souza T, de ACB, de Souza EE, Murakami MT, et al. Kinase inhibitor profile for human nek1, nek6, and nek7 and analysis of the structural basis for inhibitor specificity. Molecules. 2015;20:1176–91.
Srinivasan P, Chella Perumal P, Sudha A. Discovery of novel inhibitors for Nek6 protein through homology model Assisted structure based virtual screening and molecular docking approaches. Sci World J. 2014;2014:1–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, India for providing the necessary facilities to carry out this work.
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NKP conceptualization, literature survey, writing–original draft. SM conceptualization, literature survey, writing–original draft. SEP conceptualization, supervision, writing–original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare no conflict of interest for this work.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable: no human/animal subjects were involved in the study.
Consent to publish
Not applicable: no human/animal subjects were involved in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Panchal, N.K., Mohanty, S. & Prince, S.E. NIMA-related kinase-6 (NEK6) as an executable target in cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 25, 66–77 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02926-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02926-4