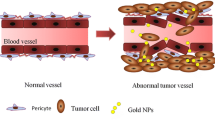
Abstract
Recent years brought increasing use of gold nano particles (GNP) as a model platform for interaction of irradiation and GNPs aiming radiosensitization. Endocytosis seems to be one of the major pathways for cellular uptake of GNPs. Internalization mechanism of GNPs is likely receptor-mediated endocytosis, influenced by GNP size, shape, its coating and surface charging. Many showed that DNA damage can occur as a consequence of metal-enhanced production of low energy electrons, Auger electrons and alike. Kilovoltage radiotherapy (RT) carries significantly higher dose enhancement factor (DEF) that is observed with megavoltage irradiations, the latter usually been at the order of 1.1–1.2. Higher gold concentrations seem to carry higher risk of toxicity, while with lower concentrations the DEF can be reduced. Adding a chemotherapeutic agent could increase level of enhancement. Clinical trials are eagerly awaited with a promise of gaining more knowledge deemed necessary for more successful transition to widespread clinical practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM International, E-2456-06 (2006) Terminology for nanotechnology. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Turkevich J, Hiller J, Stevenson PC (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss Faraday Soc 11:55–75
Boisselier E, Astruc D (2009) Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem Soc Rev 38:1759–1782
Shukla R, Bansal V, Chaudhary M et al (2005) Biocompatibility mod gold nanoparticles and their endocytic fate inside the cellular compartment: a microscopic overview. Langmuir 21:10644–10654
Hainfeld JF, Dilmanian FA, Slatkin DN et al (2008) Radiotherapy enhancement with gold nanoparticles. J Pharm Pharmacol 60:977–985
Hainfeld JF, Slatkin DN, Smilowitz HM (2004) The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice. Phys Med Biol 49:N309–N315
Kong T, Zeng J, Wang X et al (2008) Enhancement of radiation cytotoxicity in breast-cancer cells by localized attachment of gold nanoparticles. Small 4:1537–1543
Rahman WN, Bishara N, Ackerly T et al (2009) Enhancement of radiation effects by gold nanoparticles for superficial radiation therapy. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 5:136–142
Butterworth KT, Coulter JA, Jain S et al (2010) Evaluation of cytotoxicity and radiation enhancement using 1.9 nm gold particles: potential application for cancer therapy. Nanotechnology 21:295101
Chithrani BD, Ghazani AA, Chen WCW (2006) Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett 6:662–668
Chithrani BD, Stewart J, Allen C et al (2009) Intracellular uptake, transport, and processing of nanostructures in cancer cells. Nanomedicine 5:118–127
Mukherjee S, Ghosh RN, Maxfield FR (1997) Endocytosis. Physiol Rev 77:759–803
Jin H, Heller DA, Strano MS et al (2009) Size-dependent cellular uptake and expulsion of single-walled carbon nanotubes: single particle tracking and a generic uptake model for nanoparticles. ACS Nano 3:149–158
Xu X-HN, Brownlow WJ, Kyriacou SV et al (2004) Real-time probing of membrane transport in living microbial cells using single nanoparticle optics and living cell imaging. Biochem 43:10400–10413
Arnida, Malugin A, Ghandehari H (2009) Cellular uptake and toxicity of gold nanoparticles in prostate cancer cells: a comparative study of rods and spheres. J Appl Toxicol 30:212–217
Cartiera MS, Johnson KM, Rajendran V et al (2009) The uptake and intracellular fate of PLGA nanoparticles in epithelial cells. Biomaterials 30:2790–2798
Aoyama Y, Kanamori T, Nakai T et al (2003) Artificial viruses and their application to gene delivery. Size-controlled gene coating with glycocluster nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 125:3455–3457
Nakai T, Kanemori T, Sando S et al (2003) Remarkably size-regulated cell invasions by artificial viruses. Saccharide-dependent self-aggregation of glycoviruses and its consequences in glycoviral gene delivery. J Am Chem Soc 125:8465–8475
Osaki F, Kanemori T, Sando S et al (2004) A quantum dot conjugated sugar ball and its cellular uptake on the size effects of endocytosis in the subviral region. J Am Chem Soc 126:6520–6521
Gao H, Shi W, Freund LB (2005) Mechanics of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9469–9474
Shi W, Wang J, Fan X, Gao H (2008) Size and shape effects on diffusion and absorption of colloidal particles near a partially absorbing sphere: implications for uptake of nanoparticles in animal cells. Phy Rev E 78:061914–061925
Chithrani DB (2010) Intracellular uptake, transport, and processing of gold nanostructures. Mol Membr Biol 27:299–311
Cho EC, Xie J, Wurm PA et al (2009) Understanding the role of surface charge sin cellular adsorption versus internalization by selectively removing gold nanoparticles on the cell surface with a I2/KI etchant. Nano Lett 9:1080–1084
Vertegel AS, Siegel RW, Dordick JS (2004) Silica nanoparticle size influences the structure and enzymatic activity of adsorbed lysozyme. Langmuir 20:6800–6807
Aubin-Tam M-E, Hamad-Schifferli K (2005) Gold nanoparticle—cytochrome c complexes: the effect of nanoparticle ligand charge on protein structure. Langmuir 21:12080–12084
Yang Z, Leon J, Martin M et al (2009) Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of near-infrared fluorescence polymeric nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 20:165101
Ishida O, Maruyama K, Sasaki K et al (1999) Size-dependent extravasation and interstitial localization of polyethyleneglycol liposomes in solid tumor-bearing mice. Int J Pharm 190:49–56
Perrault SD, Walkey C, Jennings T et al (2009) Mediating tumor targeting efficiency of nanoparticles through design. Nano Lett 9:1909–1915
Chen J, Irudayaraj J (2009) Quantitative investigation of compartmentalized dynamics of erbB2 targeting gold nanorods in live cells by single molecule spectroscopy. ACS Nano 3:4071–4079
Lukacs GL, Haggie P, Seksek O et al (2000) Size-dependent DNA mobility in cytoplasm and nucleus. J Biol Chem 275:1625–1629
Goldstein JL, Anderson RGW, Brown MS (1979) Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature 279:679–685
See L, Free P, Cesbron Y et al (2009) Cathepsin L digestion of nanobioconjugates upon endocytosis. ACS Nano 3:2461–2468
Taylor U, Klein S, Petersen S et al (2010) Nonendosomal cellular uptake of ligand-free, positively charged nanoparticles. Cytometry A 77A:439–446
Panyam J, Zhou WZ, Prabhs S et al (2002) Rapid endo-lysosomal escape of poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles: implications for drug and gene delivery. FASEB J 16:1217–1226
Chithrani BD, Chan WCW (2007) Elucidating the mechanism of cellular uptake and removal of protein-coated gold nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes. Nano Lett 7:1542–1550
Nativo P, Prior IA, Brust M (2008) Uptake and intracellular fate of surface-modified gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2:1639–1644
Tkachenko AG, Xie H, Coleman D et al (2003) Multifunctional gold nanoparticle-peptide complexes for nuclear targeting. J Am Chem Soc 125:4700–4701
Tkachenko A, Xie H, Liu Y et al (2004) Cellular trajectories of peptide-modified gold particle complexes: comparison of nuclear localization signals and peptide transduction domains. Bioconjugate Chem 15:482–490
Connor EE, Mwamuka J, Gole A et al (2005) Gold nanoparticles are taken up by human cells but do not cause acute cytotoxicity. Small 1:325–327
Rayavarapu RJ, Petersen W, Ungureanu C et al (2007) Synthesis and bioconjugation of gold nanoparticles as potential probes for light-based imaging techniques. In J Biomed Imag 2007:1–10
Berry CC, de la Fuente JM, Mullin M et al (2007) Nuclear localization of HIV-1 tat functionalized gold nanoparticles. IEEE Trans Nano Biosci 6:262–269
Maeda H (2001) The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect in tumor vasculature: the key role of tumor-selective macromolecular drug targeting. Adv Enzyme Regul 41:189–207
Maki S, Konno T, Maeda H (1985) Image enhancement in computerised tomography for sensitive diagnosis of liver cancer and semiquantitation of tumor selective drug targeting with oily contrast medium. Cancer 56:751–757
Fang J, Nakamura H, Maeda H (2011) The EPR effect: unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv Drug Deliv Res 63:136–151
Kaul G, Amiji M (2002) Long-circulating poly(ethylene glycol)-modified gelating nanoparticles for intracellular delivery. Pharm Res 19:1061–1067
Cho SH (2005) Estimation of tumor dose enhancement due to gold nanoparticles during typical radiation treatments: a preliminary Monte Carlo study. Phys Med Biol 50:N163–N173
Roeske JC, Nunez L, Hoggarth M et al (2007) Characterization of the theoretical dose enhancement from nanoparticles. Technol Cancer Res Treat 6:395–401
McMahon SJ, Mendenhall MH, Jain S et al (2008) Radiotherapy in the presence of contrast agents: a general figure of merit and its application to gold nanoparticles. Phys Med Biol 53:5635–5651
Cho SH, Jones BL, Krishnan S (2009) The dosimetric feasibility of gold nanoparticle-aided radiation therapy (GNRT) via brachytherapy using low-energy gamma-/X-ray sources. Phys Med Biol 54:4889–4905
Carter JD, Cheng NN, Qu Y et al (2007) Nanoscale energy deposition by X-ray absorbing nanostructures. J Phys Chem 111:11622–11625
Boudaiffa B, Cloutier P, Hunting DJ et al (2000) Resonant formation of DNA strand breaks by low-energy (3–20 eV) electrons. [Report]. Science 287:1658–1660
Roa W, Zhang X, Guo L et al (2009) Gold nanoparticle sensitize radiotherapy of prostate cancer cells by regulation of cell cycle. Nanotechnology 20:375101
Chang M, Shiau A, Chen Y et al (2008) Increased apoptotic potential and dose-enhancing effects of gold nanoparticles in combination with single-dose clinical electron beams on tumor bearing mice. Cancer Sci 99:1479–1484
Chithrani DB, Jelveh S, Jalali F et al (2010) Gold nanoparticles as radiation sensitizers in cancer therapy. Radiat Res 173:719–728
Liu C-J, Wang C-H, Chien C–C et al (2008) Enhanced X-irradiation-induced cancer cell damage by gold nanoparticles treated by anew synthesis method of polyethylene glycol modification. Nanotechnology 19:295104–295109
Hainfeld JF, Dilmanian FA, Zhong Z et al (2010) Gold nanoparticles enhance the radiation therapy of a murine squamous cell carcinoma. Phys Med Biol 55:3045–3059
Kirschenbaum J, Riesz P (2009) Enhancement of 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced oxidative stress on two cancer cell lines by gold nanoparticles. Free Radic Res 43:1214–1224
Kassis AI (2004) The amazing world of Auger electrons. Int J Radiat Biol 11–12:789–803
Sanche L (2005) Low-energy electron-driven damage in biomolecules. Eur Phys J D 35:367–390
Hall EJ, Giaccia AJ (2006) Radiobiology for the radiologist, 6th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Leung MKK, Chow JCL, Chithrani BD et al (2011) Irradiation of gold nanoparticles by X-rays: Monte Carlo simulation of dose enhancements and the spatial properties of the secondary electron production. Med Phys 38:624–631
Jain S, Coulter JA, Hounsell AR et al (2011) Cell-specific radiosensitization by gold nanoparticles at megavoltage radiation energies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79:531–539
Patra HK, Banerjee S, Chaudhuri U et al (2007) Cell selective response to gold nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3:111–119
Cho WS, Cho M, Jeong J et al (2009) Acute toxicity and pharmacokinetics of 13 nm-sized PEG-coated gold nanoparticles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 236:16–24
McMahon SJ, Hyland WB, Muir MF et al (2011) Biological consequences of nanoscale energy deposition near irradiated heavy atom nanoparticles. Sci Rep 1:18
Lechtman E, Chattopadhyay N, Cai Z et al (2011) Implications on clinical scenario of gold nanoparticle radiosensitization in regards to photon energy, nanoparticle size, concentration and location. Phys Med Biol 56:4631–4647
Brun E, Sanche L, Sicard-Roselli C (2009) Parameters governing gold nanoparticles X-ray sensitization of DNA in solution. Colloids Surf B 72:128–134
Rahman WN, Wong CJ, Ackerly T et al (2012) Polymer gels impregnated with gold nanoparticles implemented for measurements of radiation dose enhancement in synchrotron and conventional radiotherapy type beams. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 35:301–309
Zhang C, Huang P, Bao L et al (2011) Enhancement of gastric cell radiation sensitivity by chitosan-modified gold nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11:9528–9535
Berbeco RI, Ngwa W, Makrigiorgios GM (2011) Localized dose enhancement to tumor blood vessel endothelial cells via megavoltage X-rays and targeted nanoparticles: new potential for external beam radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:270–276
Pan Y, Neuss S, Leifert A et al (2007) Size-dependent cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles. Small 3:1941–1949
Lewinski N, Colvin V, Drezek R (2008) Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Small 4:26–49
Herold DM, Das IJ, Stobe CC et al (2000) Gold microspheres: a selective technique for producing biologically effective dose enhancement. Int J Radiat Biol 76:1357–1364
Hainfeld JF, Foley CF, Shrivastava SC et al (1990) Radioactive gold cluster immunoconjugates: potential agents for cancer therapy. Nucl Med Biol 17:287–294
Niidome T, Nakashima H, Takahashi Y et al (2004) Preparation of primary amine-modified gold nanoparticles and their transfection ability into cultivated cells. Chem Commun 17:1978–1979
Dvorak HF, Nagy JA, Dvorak JT et al (1988) Identification and characterisation of the blood vessels of solid tumors that are leaky to circulating macromolecules. Am J Pathol 133:95–109
Gratton SEA, Ropp PA, Polhaus PD et al (2008) The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:11613–11618
Champion JA, Mitragotri S (2009) Shape induced inhibition of phagocytosis of polymer particles. Pharm Res 26:244–249
Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:662–667
Cho EC, Au L, Zhang Q et al (2009) The effects of size, shape, and surface functional group of gold nanoparticles on their adsorption and internalization by cells. Small 6:517–522
Sayes CM, Reed KL, Warheit DB (2007) Assessing toxicity of fine and nanoparticles: comparing in vitro measurements to in vivo pulmonary toxicity profiles. Toxicol Sci 97:163–180
Goodman CM, McCucker CD, Yilmaz T et al (2004) Toxicity of gold nanoparticles functionalized with cationic and anionic side chains. Bioconjug Chem 15:897–900
Pernodet N, Fang X, Sun Y et al (2006) Adverse effects of citrate/gold nanoparticles on human dermal fibroblasts. Small 2:766–773
Murphy CJ, Gole AM, Stone JW et al (2008) Gold nanoparticles in biology: beyond toxicity to cellular imaging. Acc Chem Res 41:1721–1730
Male KB, Lachance B, Hrapovic S et al (2008) Assessment of cytotoxicity of quantum dots and gold nanoparticles using cell-based impedance spectroscopy. Anal Chem 80:5487–5493
Zhang X-D, Wu HY, Wu D et al (2010) Toxicologic effects of gold nanoparticles in vivo by different administration routes. Int J Nanomed 5:771–781
de Jong WH, Hagens WI, Krystek P et al (2008) Particle size-dependent organ distribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Biomaterials 29:1912–1919
Sonavane G, Tomoda K, Makino K (2008) Biodistribution of colloidal gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration: effect of particle size. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 66:274–280
Chen YS, Hung YC, Liau I et al (2009) Assessment of the in vivo toxicity of gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett 4:858–864
Cho WS, Kim S, Han BS et al (2009) Comparison of gene expression profiles in mice liver following intravenous injection of 4 and 100 nm-sized PEG-coated gold nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 191:96–102
Semmler-Behnke M, Kreyling WG, Lipka J et al (2008) Biodistribution of 1.4- and 18-nm gold particles in rats. Small 4:2108–2111
Lipka J, Semmler-Behnke M, Sperling RA et al (2010) Biodistribution of PED-modified gold nanoparticles following intrathecal instillation and intravenous injection. Biomaterials 31:6574–6581
Cho WS, Cho M, Jeong J et al (2010) Size-dependent tissue-kinetics of PEG-coated gold nanoparticles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 245:116–123
Balasubramaniam SK, Jittiwat J, Manikandan J et al (2010) Biodistribution of gold nanoparticles and gene expression changes in the liver and spleen after intravenous administration in rats. Biomaterials 31:2034–2042
Balogh L, Nigavekar SS, Nair BM et al (2007) Significant effect of size on the in vivo biodistribution of gold composite nanodevices in mouse tumor models. Nanomedicine 3:281–296
Zhang X-D, Wu D, Shen X et al (2012) Size-dependent radiosensitization of PEG-coated gold nanoparticles for cancer radiation therapy. Biomaterials 33:6408–6419
Zhang X-D, Wu D, Shen X et al (2011) Size-dependent toxicity of PEG-coated gold nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed 6:2071–2081
Zhang X-D, Wu D, Shen X et al (2012) In vivo renal clearance, biodistribution, toxicity of gold nanoclusters. Biomaterials 33:4628–4638
Zheng Y, Hunting D, Ayotte P et al (2008) Role of secondary low energy electrons in the concomitant chemoradiation therapy of cancer. Phys Rev Lett 100:198101–198104
Pimblott SM, LaVerne JA (2007) Production of low energy electrons by ionizing irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 76:1244–1249
Zheng L, Sanche L (2009) Gold nanoparticles enhance DNA damage induced by anti-cancer drugs and irradiation. Radiat Res 172:114–119
Acknowledgments
This research was partly supported by Ministry of Education and Science in Serbia, ON174028 and III41007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeremic, B., Aguerri, A.R. & Filipovic, N. Radiosensitization by gold nanoparticles. Clin Transl Oncol 15, 593–601 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-013-1003-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-013-1003-7