Abstract
Introduction
Hypersensitivity reaction (HSR) to antineoplastic drugs can force doctors to stop treatment and seek other alternatives. These alternatives may be less effective, not as well tolerated and/or more expensive. Another option is to use desensitization protocols that induce a temporary state of tolerance by gradually administering small quantities of the antineoplastic drug until the therapeutic dosage is reached. The aim of this study is to assess the effectiveness of oxaliplatin desensitization protocols.
Materials and methods
A retrospective observational study was carried out between January 2006 and May 2011. The inclusion criteria were patients undergoing chemotherapy treatment with oxaliplatin who had developed an HSR to the drug and who were candidates for continuing the treatment using a desensitization protocol. The patients’ clinical records were reviewed and variables were gathered relating to the patient, the treatment, the HSR, and the desensitization protocol administered. The data were analysed using version 18.0 of the statistics program SPSS.
Results
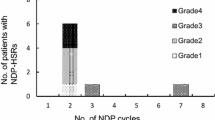
A total of 53 desensitization protocols were administered to 21 patients. In 89 % of these cases, no new reactions occurred while the drug was being administered. New reactions of mild severity only occurred in 11 % of cases, and none of these reactions were severe enough for treatment to be stopped. All patients were able to complete the desensitization protocol.
Conclusion
This study confirms that oxaliplatin desensitization protocols are safe and effective and allow patients to continue with the treatment that initially caused an HSR.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee C, Gianos M, Klaustermeyer WB (2009) Diagnosis and management of hypersensitivity reactions related to common cancer chemotherapy agents. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 102:179–187
Syrigou E, Syrigos K, Saif MW (2008) Hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin and other antineoplastic agents. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 8:56–62
Pagani M (2010) The complex clinical picture of presumably allergic side effects to cytostatic drugs: symptoms, pathomechanism, reexposure, and desensitization. Med Clin North Am 94:835–852
Polyzos A, Tsavaris N, Gogas H, Souglakos J, Vambakas L, Vardakas N et al (2008) Clinical features of hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: a 10-year experience. Oncology 76:36–41
Medioni J, Coulon MA, Morere JF, Hennebelle F, Piperno-Neumann S, Breau JL (1999) Anaphylaxis after oxaliplatin. Ann Oncol 10:610
De Vries RS, Mattijssen EJ, van Sorge AA (2006) Serious delayed hypersensitivity reaction to oxaliplatin. Ann Oncol 17:1723–1724
Potenza S, Nasti G, Alessandro O, Filippelli A, Rossi F, Capuano A (2010) Severe respiratory symptoms to oxaliplatin infusion: a case report of delayed hypersensitivity reaction. Investig New Drugs 28:185–186
Köhlmoos C, Marquardt GG, Brinkmann D, Meier K (2008) Allergic reactions to oxaliplatin therapy—an overview. Eur J Oncol Pharm 2:27–28
Siu S, Chan R, Au G (2006) Hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: experience in a single institute. Ann Oncol 17:259
Shao YY, Hu FC, Liang JT, Chiu WT, Cheng AL, Yang CH (2010) Characteristics and risk factors of oxaliplatin-related hypersensitivity reactions. J Formosan Med Assoc 109:362–368
Kim BH, Bradley T, Tai J, Budman DR (2009) Hypersensitivity to oxaliplatin: an investigation of incidence and risk factors, and literature review. Oncology 76:231–238
Mori Y, Nishimura T, Kitano T, Yoshimura K, Matsumoto S, Kanai M et al (2010) Oxaliplatin-free interval as a risk factor for hypersensitivity reaction among colorectal cancer patients treated with FOLFOX. Oncology 79:136–143
Bhargava P, Gammon D, McCormick MJ (2004) Hypersensitivity and idiosyncratic reactions to oxaliplatin. Cancer 100:211–212
Brandi G, Pantaleo M, Galli C, Falcone A, Antonuzzo A, Mordenti P et al (2003) Hypersensitivity reactions related to oxaliplatin (OHP). Br J Cancer 89:477–481
Kidera Y, Satoh T, Ueda S, Okamoto W, Okamoto I, Fumita S et al (2011) High-dose dexamethasone plus antihistamine prevents colorectal cancer patients treated with modified FOLFOX6 from hypersensitivity reactions induced by oxaliplatin. Int J Clin Oncol. doi:10.1007/s10147-010-0170-6:1-6
Maindrault-Goebel F, André T, Tournigand C, Louvet C, Perez-Staub N, Zeghib N et al (2005) Allergic-type reactions to oxaliplatin: retrospective analysis of 42 patients. Eur J Cancer 41:2262–2267
Thomas RR, Quinn MG, Schuler B, Grem JL (2003) Hypersensitivity and idiosyncratic reactions to oxaliplatin. Cancer 97:2301–2307
Tonini G, Santini D, Vincenzi B, Borzomati D, Dicuonzo G, La Cesa A et al (2002) Oxaliplatin may induce cytokine-release syndrome in colorectal cancer patients. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 16:105–109
Ulrich-Pur H, Fiebiger WCC, Schüll B, Kornek GV, Scheithauer W, Raderer M (2000) Oxaliplatin-induced fever and release of IL-6. Oncology 59:187–189
Wilson C, Purcell C, Seaton A, Oladipo O, Maxwell PJ, O’Sullivan JM, Wilson R, Johnston PG, Waugh D (2012) Chemotherapy-induced CXC-chemokine/CXC-chemokine Receptor signaling in metastatic prostate cancer cells confers resistance to oxaliplatin through potentiation of nuclear factor-kappaB transcription and evasion of apoptosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 327:746–759
Kast R, Scheuerle A, Wirtz C, Karpel-Massler G, Halatsch ME (2011) The rationale of targeting neutrophils with dapsone during glioblastoma treatment. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem 11:756–761
Edmondson DA, Gruling BJ, Urmanski AM, Wong SJ, Levy MB (2007) Oxaliplatin hypersensitivity: case report and successful repeat desensitization. Am J Ther 14:116–118
Gammon D, Bhargava P, McCormick MJ (2004) Hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin and the application of a desensitization protocol. Oncologist 9:546
Meyer L, Zuberbier T, Worm M, Oettle H, Riess H (2002) Hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: cross-reactivity to carboplatin and the introduction of a desensitization schedule. J Clin Oncol 20:1146
Castells MC, Tennant NM, Sloane DE, Ida Hsu F, Barrett NA, Hong DI et al (2008) Hypersensitivity reactions to chemotherapy: outcomes and safety of rapid desensitization in 413 cases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:574–580
Habert H, Castagne V (2009) Management of hypersensitivity to oxaliplatin at the Paul Brousse hospital pharmacy department: desensitization protocol and clinical impact. Pharm World Sci 31:96–97
Syrigou EI, Karapanagiotou EM, Alamara CV, Boura PG, Saif MW, Syrigos KN (2009) Hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: a retrospective study and the development of a desensitization protocol. Clin Colorectal Cancer 8:106–109
Gottlieb GR, Bordoni RE, Lawhead RA Jr, Feinberg BA (2010) Successful outpatient desensitization of cancer patients with hypersensitivity reactions to chemotherapy. Community Oncol 7:452–457
Herrero T, Tornero P, Infante S, Fuentes V, Sanchez M, De Barrio M et al (2006) Diagnosis and management of hypersensitivity reactions caused by oxaliplatin. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 16:327
Gastaminza G, de la Borbolla JM, Goikoetxea MJ, Escudero R, Antón J, Espinós J et al (2011) A new rapid desensitization protocol for chemotherapy agents. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 21:108–112
Garufi C, Cristaudo A, Vanni B, Bria E, Aschelter AM, Santucci B et al (2003) Skin testing and hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin. Ann Oncol 14:497–498
Rubbia-Brandt L, Tauzin S, Brezault C, Delucinge-Vivier C, Descombes P, Dousset B, Majno PE, Mentha G, Benoit T (2011) Gene expression profiling provides insights into pathways of oxaliplatin-related sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in humans. Mol Cancer Ther 10:687–696
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest relating to the publication of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cortijo-Cascajares, S., Nacle-López, I., García-Escobar, I. et al. Effectiveness of oxaliplatin desensitization protocols. Clin Transl Oncol 15, 219–225 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-012-0909-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-012-0909-9