Abstract
Purpose
To summarize the outcomes of stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT), with or without whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT), in the treatment of multiple brain metastasis and to explore the status of WBRT and SRT in the management of multiple brain metastasis.
Methods
From May 1995 to April 2010, 98 patients with newly diagnosed, multiple brain metastasis were treated in our center. Forty-four patients were treated with SRT alone for the initial treatment, and 54 were treated with SRT + WBRT. Kaplan–Meier and Cox proportional hazards regression analyses were used for the survival analysis.
Results
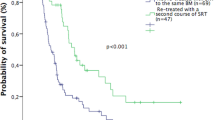
The median survival time (MST) was 13.5 months. No difference was observed in MST between the SRT and the SRT + WBRT groups (p = 0.578). The Karnofsky Performance Score at the time of treatment (p = 0.025), the interval time between diagnosis of primary tumor and brain metastasis (P = 0.012) and the situation of extracranial disease (p = 0.018) were significant predictors of survival. The crude distant intracranial recurrence (DIR) rates were 47.7 % in the SRT group and 24.1 % in the SRT + WBRT group (p = 0.018). In addition, 52.3 % patients in the SRT group were free from DIR and did not require WBRT in their whole lives.
Conclusions
Our data suggest that use of SRT as the initial treatment while reserving WBRT as the salvage therapy in case of distant intracranial recurrence made about 50 % of the patients avoid WBRT throughout the course of their lives and may be another optional treatment modality for multiple brain metastases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Posner JB (1992) Management of brain metastases. Rev Neurol (Paris) 148:477–487
Nussbaum ES, Djalilian HR, Cho KH et al (1996) Brain metastases. Histology, multiplicity, surgery, and survival. Cancer 78:1781–1788
Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT et al (1988) Distribution of brain metastases. Arch Neurol 45:741–744
Komarnicky LT, Phillips TL, Martz K et al (1991) A randomized phase III protocol for the evaluation of misonidazole combined with radiation in the treatment of patients with brain metastases (RTOG 79–16). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 20:53–58
Sause WT, Scott C, Kirsch R et al (1993) Phase I/II trial of accelerated fractionation in brainmetastases, RTOG 85-28. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 26:653–657
Phillips TL, Scott CB, Leibel S et al (1995) Results of a randomized comparison of radiotherapy and bromodeoxyuridine to radiotherapy alone for brain metastases: report of RTOG trial89-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 33:339–348
Murray KJ, Scott C, Greenberg HM et al (1997) A randomized phase III study of accelerated hyperfractionation versus standard in patients with unresected brain metastasis: a report of RTOG9104. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 39:571–574
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW et al (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672
Frazier JL, Batra S, Kapor S et al (2010) Stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of brain metastases: an institutional retrospective analysis of survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(5):1486–1492
Bhatnagar AK, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery for four or more intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64(3):898–903
Kim SH, Weil RJ, Chao ST et al (2008) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of brain metastases in older patients. Cancer 113:834–840
Flannery TW, Suntharalingam M, Regine WF et al (2008) Long-term survival in patients with synchronous, solitary brain metastasis from non–small-cell lung cancer treated with radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72:19–23
Sanghavi SN, Miranpuri SS, Chappell R, Buatti JM, Sneed PK, Suh JH et al (2001) Radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis, stratified by the RTOG recursive partitioning analysis method. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51(2):426–434
Lagerwaard FJ, Levendag PC, Nowak PJ, Eijkenboom WM, Hanssens PE, Schmitz PI (1999) Identification of prognostic factors in patients with brain metastases: a review of 1292 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43:795–803
Lorenzoni J, Devriendt D, Massager N, David P, Ruiz S, Vanderlinden B, Van Houtte P, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2004) Radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases: estimation of patient eligibility using three stratification systems. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60:218–224
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Rades D, Dziggel L, Haatanen T et al (2011) Scoring system to estimate intracranial control and survival rates of patients irradiated for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 80(4):1122–1127
Kim EY, Maciunas RJ, Williams JM et al (2006) 153 tumor volume is a predictor of overall survival for patients with brain metastases who undergo gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 66(3 Suppl):S86
Bhatnagar AK, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery for four or more intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:898–903
Jawahar A, Shaya M, Campbell P et al (2005) Role of stereotactic radiosurgery as a primary treatment option in the management ofnewly diagnosed multiple (3–6) intracranial metastases. Surg Neurol 64:207–212
Sheehan J, Kondziolka D, Flickinger J, Lunsford LD (2005) Radiosurgery for patients with recurrent small cell lung carcinoma metastatic to the brain: outcomes and prognostic factors. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl.):247–254
Selek U, Chang EL, Hassenbusch SJ III et al (2004) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment in 103 patients for 153 cerebral melanoma metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:1097–1106
Shaw Edward, Scott Charles, Souhami Luis et al (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain Metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90–05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Kim YJ, Cho KH, Kim JY et al (2010) Single-dose versus fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.05.033
Shehata MK, Young B, Reid B et al (2004) Stereotactic radiosurgery of 468 brain metastases < or =2 cm: implications for SRS dose and whole brain radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:87–93
Chidel MA, Suh JH, Reddy CA et al (2000) Application of recursive partitioning analysis and evaluation of the use of whole brain radiation among patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery for newly diagnosed brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:993–999
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR et al (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044
Aoyama H, Tago M, Katoh N et al (2007) Neurocognitive function of patients with brain metastasis who received either whole brain radiotherapy plus stereotactic radiosurgery or radiosurgery alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:1388–1395
Martin K, Riccardo S, Ufuk A et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29(2):134–141
Alexander S, Kyounghwa B, Elizabeth MG et al (2010) Phase III trial of prophylactic cranial irradiation compared with observation in patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: neurocognitive and quality-of-life analysis. J Clin Oncol. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.29.1609
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Xiao, J., Li, X. et al. Fifty percent patients avoid whole brain radiotherapy: stereotactic radiotherapy for multiple brain metastases. A retrospective analysis of a single center. Clin Transl Oncol 14, 599–605 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-012-0849-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-012-0849-4