Abstract
Introduction
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation related to tyrosine kinase inhibitors’ (TKIs) responsiveness in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has become an important issue for therapeutic decision-making in NSCLC patients.
Material and methods
Sixty-nine Caucasian NSCLC patients were screened for mutations in the tyrosine kinase (TK) domain of EGFR by direct sequencing from December 2005 to September 2010.
Results
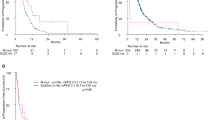
Activating mutations in the EGFR TK domain were found in 8 of 69 (11.6%) (7 deletions in exon 19 and one L858R mutation in exon 21). Seven of those mutations were found in adenocarcinoma and one mutation in bronchiolo-alveolar carcinoma; five of them in females (one smoker) and three of them in males (one smoker). All patients carrying activating mutations in the TK domain of EGFR were treated with TKIs. Ten patients not carrying an activating mutation in EGFR, who progressed after chemotherapy, were also treated with compassionate use of EGFR-specific TKIs (gefitinib or erlotinib). An objective response (partial response) was observed in all patients carrying an activating mutation in EGFR that received TKIs. Median overall survival for these patients has not been reached, however mean survival has been estimated at 39.5 months (95% CI, 22–57).
Conclusions
As previously reported, EGFR TK mutational analysis was a predictive test for response to targeted therapy with EGFR TKIs. The early identification of these patients consistently attains disease response and clearly improves outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R et al (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–2139
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC et al (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M et al (2004) EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13306–13311
Huang SF, Liu HP, Li LH et al (2004) High frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations with complex patterns in non-small cell lung cancers related to gefitinib responsiveness in Taiwan. Clin Cancer Res 10:8195–8203
Cortes-Funes H, Gomez C, Rosell R et al (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor activating mutations in Spanish gefitinib-treated non small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol 16:1081–1086
Paz-Ares L, Sanchez JM, García-Velasco A et al (2006) A prospective phase II trial of erlotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (p) with mutations in the tyrosine kinase (TK) domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). J Clin Oncol ASCO Proceedings I 24[18 Suppl]:7020
Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C et al (2009) Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N Engl J Med 3:958–967
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Gonzalez-Manzano R, Martínez-Navarro EM, Evgenyeva E et al (2008) A novel EGFR nonsense mutation in a non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patient who did not derive any clinical benefit with combination chemotherapy and erlotinib. Clin Transl Oncol 10:242–244
Cho D, Kocher O, Tenen DG et al (2005) Unusual cases in multiple myeloma and a dramatic response in metastatic lung cancer. Case 4: mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in an elderly man with advanced, gefitinib-responsive, non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:235–237
Maomondo M, Inoue A, Kobayshi K et al (2010) Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362:2380–2388
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA et al (2005) Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Med 2:e73
Pao W, Wang TY, Riely GJ et al (2005) KRAS mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib. PLoS Med 2:e17
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H et al (2006) Analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and acquired resistance to gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res 12:5764–5769
Mueller KL, Yang ZQ, Haddad R et al (2010) EGFR/Met association regulates EGFR TKI resistance in breast cancer. J Mol Signal 5:8
Wong DW, Leung EL, So KK et al (2009) The EML4-ALK fusion gene is involved in various histologic types of lung cancers from non smokers with wild-type EGFR and KRAS. Cancer 115:1723–1733
Shaw AT, Yeap BY, Mino-Kenudson M et al (2009) Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who harbour EML4_ALK. J Clin Oncol 27:4247–4253
Koivunen JP, Mermel C, Zejnullahu K et al (2008) EML4-ALK fusion gene and efficacy of an ALK kinase ihibitor in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:4275–4283
Chen YR, Fu YN, Lin CH et al (2006) Distinctive activation patterns in constitutively active and gefitinib-sensitive EGFR mutants. Oncogene 25:1205–1215
Asahina K, Yamazaki I, Kinoshita H et al (2006) Non-responsiveness to gefitinib in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma having rare EGFR mutations S768I and V769L. Lung Cancer 54:419–422
Wu SG, Chang Yl, Hsu YC et al (2008) Good response to gefitinib in lung adenocarcinoma of complex epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations with the classical mutation pattern. Oncologist 13:1276–1284
Zhang W, Stabile LP, Keohavong P et al (2006) Mutation and polymorphism in the EGFR-TK domain associated with lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 1:635–647
Yokoyama T, Kondo M, Goto Y et al (2006) EGFR point mutation in non-small cell lung cancer is occasionally accompanied by a second mutation or amplification. Cancer Sci 97:753–759
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Navarro, E.M., Rebollo, J., González-Manzano, R. et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in a series of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and response rate to EGFR-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Clin Transl Oncol 13, 812–818 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-011-0739-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-011-0739-1