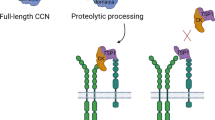
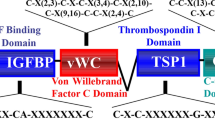
Abstract
The CCN family (CYR61; CTGF; NOV; CCN1–6; WISP1–3) of matricellular proteins in mammals is comprised of six homologous members that play important roles in development, inflammation, tissue repair, and a broad range of pathological processes including fibrosis and cancer. Despite considerable effort to search for a high affinity CCN-specific receptor akin to growth factor receptors, no such receptor has been found. Rather, CCNs bind several groups of multi-ligand receptors as characteristic of other matricellular proteins. The most extensively documented among CCN-binding receptors are integrins, including αvβ3, αvβ5, α5β1, α6β1, αIIbβ3, αMβ2, and αDβ2, which mediate diverse CCN functions in various cell types. CCNs also bind cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs), low density liproprotein receptor-related proteins (LRPs), and the cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate (M6P) receptor, which are endocytic receptors that may also serve as co-receptors in cooperation with other cell surface receptors. CCNs have also been reported to bind FGFR-2, Notch, RANK, and TrkA, potentially altering the affinities of these receptors for their ligands. The ability of CCNs to bind a multitude of receptors in various cell types may account for the remarkable versatility of their functions, and underscore the diverse signaling pathways that mediate their activities.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyama E, Kubota S, Takigawa M (2012) CCN2/CTGF binds to fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 and modulates its signaling. FEBS Lett 586:4270–4275
Aoyama E, Kubota S, Khattab HM, Nishida T, Takigawa M (2015) CCN2 enhances RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation via direct binding to RANK and OPG. Bone 73:242–248
Babic AM, Kireeva ML, Kolesnikova TV, Lau LF (1998) CYR61, product of a growth factor-inducible immediate-early gene, promotes angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:6355–6360
Babic AM, Chen C-C, Lau LF (1999) Fisp12/mouse connective tissue growth factor mediates endothelial cell adhesion and migration through integrin αvβ3, promotes endothelial cell survival, and induces angiogenesis in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 19:2958–2966
Bai T, Chen C-C, Lau LF (2010) The matricellular protein CCN1 activates a pro-inflammatory genetic program in murine macrophages. J Immunol 184:3223–3232
Batmunkh R, Nishioka Y, Aono Y, Azuma M, Kinoshita K, Kishi J, Makino H, Kishi M, Takezaki A, Sone S (2011) CCN6 as a profibrotic mediator that stimulates the proliferation of lung fibroblasts via the integrin beta1/focal adhesion kinase pathway. J Med Investig 58:188–196
Blalock TD, Gibson DJ, Duncan MR, Tuli SS, Grotendorst GR, Schultz GS (2012) A connective tissue growth factor signaling receptor in corneal fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:3387–3394
Bork P (1993) The modular architecture of a new family of growth regulators related to connective tissue growth factor. FEBS Lett 327:125–130
Bornstein P (1995) Diversity of function is inherent in matricellular proteins: an appraisal of thrombospondin 1. J Cell Biol 130:503–506
Bradham DM, Igarashi A, Potter RL, Grotendorst GR (1991) Connective tissue growth factor: a cysteine-rich mitogen secreted by human vascular endothelial cells is related to the SRC-induced immediate early gene product CEF-10. J Cell Biol 114:1285–1294
Chen C-C, Lau LF (2009) Functions and mechanisms of action of CCN matricellular proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:771–783
Chen N, Chen CC, Lau LF (2000) Adhesion of human skin fibroblasts to Cyr61 is mediated through integrin α6β1 and cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J Biol Chem 275:24953–24961
Chen C-C, Chen N, Lau LF (2001) The angiogenic factors Cyr61 and CTGF induce adhesive signaling in primary human skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 276:10443–10452
Chen N, Leu S-J, Todorovic V, Lam SC-T, Lau LF (2004a) Identification of a novel integrin αvβ3 binding site in CCN1 (CYR61) critical for pro-angiogenic activities in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 279:44166–44176
Chen Y, Abraham DJ, Shi-wen X, Pearson JD, Black CM, Lyons KM, Leask A (2004b) CCN2 (connective tissue growth factor) promotes fibroblast adhesion to fibronectin. Mol Biol Cell 15:5635–5646
Chen CC, Young JL, Monzon RI, Chen N, Todorovic V, Lau LF (2007a) Cytotoxicity of TNFalpha is regulated by integrin-mediated matrix signaling. EMBO J 26:1257–1267
Chen PS, Wang MY, Wu SN, Su JL, Hong CC, Chuang SE, Chen MW, Hua KT, Wu YL, Cha ST, Babu MS, Chen CN, Lee PH, Chang KJ, Kuo ML (2007b) CTGF enhances the motility of breast cancer cells via an integrin-alphavbeta3-ERK1/2-dependent S100 A4-upregulated pathway. J Cell Sci 120:2053–2065
Chen CC, Kim KH, Lau LF (2016) The matricellular protein CCN1 suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis by inhibiting compensatory proliferation. Oncogene 35:1314–1323. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.190
Chuang JY, Chen PC, Tsao CW, Chang AC, Lein MY, Lin CC, Wang SW, Lin CW, Tang CH (2015) WISP-1 a novel angiogenic regulator of the CCN family promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma angiogenesis through VEGF-A expression. Oncotarget 6:4239–4252
Cicha I, Garlichs CD, Daniel WG, Goppelt-Struebe M (2004) Activated human platelets release connective tissue growth factor. Thromb Haemost 91:755–760
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA (2010) Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 10:9–22
Edwards LA, Woolard K, Son MJ, Li A, Lee J, Ene C, Mantey SA, Maric D, Song H, Belova G, Jensen RT, Zhang W, Fine HA (2011) Effect of brain- and tumor-derived connective tissue growth factor on glioma invasion. J Natl Cancer Inst 103:1162–1178
Ellis PD, Metcalfe JC, Hyvonen M, Kemp PR (2003) Adhesion of endothelial cells to NOV is mediated by the integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha5beta1. J Vasc Res 40:234–243
El-Shewy HM, Luttrell LM (2009) Insulin-like growth factor-2/mannose-6 phosphate receptors. Vitam Horm 80:667–697
Gao R, Brigstock DR (2004) Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) induces adhesion of rat activated hepatic stellate cells by binding of its C-terminal domain to integrin alpha (v)beta(3) and heparan sulfate proteoglycan. J Biol Chem 279:8848–8855
Gao R, Brigstock DR (2005) Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) in rat pancreatic stellate cell function: integrin alpha5beta1 as a novel CCN2 receptor. Gastroenterology 129:1019–1030
Graness A, Cicha I, Goppelt-Struebe M (2006) Contribution of Src-FAK signaling to the induction of connective tissue growth factor in renal fibroblasts. Kidney Int 69:1341–1349
Guo F, Carter DE, Leask A (2011) Mechanical tension increases CCN2/CTGF expression and proliferation in gingival fibroblasts via a TGFbeta-dependent mechanism. PLoS One 6:e19756
Holbourn KP, Acharya KR, Perbal B (2008) The CCN family of proteins: structure-function relationships. Trends Biochem Sci 33:461–473
Hou CH, Tang CH, Hsu CJ, Hou SM, Liu JF (2013) CCN4 induces IL-6 production through alphavbeta5 receptor, PI3K, Akt, and NF-kappaB singling pathway in human synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 15:R19. doi:10.1186/ar4151.
Hynes RO (2002) Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 110:673–687
Iyer VR, Eisen MB, Ross DT, Schuler G, Moore T, Lee JC, Trent JM, Staudt LM, Hudson J, Boguski MS, Lashkari D, Shalon D, Botstein D, Brown PO (1999) The transcriptional program in the response of human fibroblasts to serum. Science 283:83–87
Jedsadayanmata A, Chen CC, Kireeva ML, Lau LF, Lam SC (1999) Activation-dependent adhesion of human platelets to Cyr61 and Fisp12/mouse connective tissue growth factor is mediated through integrin αIIbβ3. J Biol Chem 274:24321–24327
Joiner DM, Tayim RJ, Kadado A, Goldstein SA (2012) Bone marrow stromal cells from aged male rats have delayed mineralization and reduced response to mechanical stimulation through nitric oxide and ERK1/2 signaling during osteogenic differentiation. Biogerontology 13:467–478
Joliot V, Martinerie C, Dambrine G, Plassiart G, Brisac M, Crochet J, Perbal B (1992) Proviral rearrangements and overexpression of a new cellular gene (nov) in myeloblastosis-associated virus type 1-induced nephroblastomas. Mol Cell Biol 12:10–21
Jones JI, Gockerman A, Busby WH Jr, Camacho-Hubner C, Clemmons DR (1993) Extracellular matrix contains insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5: potentiation of the effects of IGF-I. J Cell Biol 121:679–687
Jun JI, Lau LF (2010) The matricellular protein CCN1 induces fibroblast senescence and restricts fibrosis in cutaneous wound healing. Nat Cell Biol 12:676–685
Jun JI and Lau LF (2011). Taking aim at the extracellular matrix: CCN proteins as emerging therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10: 945–963.
Jun JI, Kim KH, Lau LF (2015) The matricellular protein CCN1 mediates neutrophil efferocytosis in cutaneous wound Healing. Nat Commun 6:7386. doi:10.1038/ncomms8386
Juric V, Chen CC, Lau LF (2009) Fas-mediated apoptosis is regulated by the extracellular matrix protein CCN1 (CYR61) in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 29:3266–3279
Juric V, Chen CC, Lau LF (2012) TNFalpha-induced apoptosis enabled by CCN1/CYR61: pathways of reactive oxygen species generation and cytochrome c release. PLoS One 7:e31303
Kennedy L, Liu S, Shi-wen X, Chen Y, Eastwood M, Sabetkar M, Carter DE, Lyons KM, Black CM, Abraham DJ, Leask A (2007) CCN2 is necessary for the function of mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 313:952–964
Kim KH, Chen CC, Alpini G, Lau LF (2015) CCN1 induces hepatic ductular reaction through integrin αvβ5-mediated activation of NF-κB. J Clin Invest 125:1886–1900
Kireeva ML, Mo FE, Yang GP, Lau LF (1996) Cyr61, a product of a growth factor-inducible immediate-early gene, promotes cell proliferation, migration, and adhesion. Mol Cell Biol 16:1326–1334
Kireeva ML, Latinkic BV, Kolesnikova TV, Chen C-C, Yang GP, Abler AS, Lau LF (1997) Cyr61 and Fisp12 are both signaling cell adhesion molecules: comparison of activities, metablism, and localization during development. Exp Cell Res 233:63–77
Kireeva ML, Lam SCT, Lau LF (1998) Adhesion of human umbilical vein endothelial cells to the immediate-early gene product Cyr61 is mediated through integrin αvβ3. J Biol Chem 273:3090–3096
Kiwanuka E, Andersson L, Caterson EJ, Junker JP, Gerdin B, Eriksson E (2013) CCN2 promotes keratinocyte adhesion and migration via integrin alpha5beta1. Exp Cell Res 319:2938–2946
Kubota S, Takigawa M (2013) The CCN family acting throughout the body: recent research developments. Biomol Concepts 4:477–494
Kubota S, Kawata K, Yanagita T, Doi H, Kitoh T, Takigawa M (2004) Abundant retention and release of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) by platelets. J Biochem (Tokyo) 136:279–282
Latinkic BV, Mercurio S, Bennett B, Hirst EM, Xu Q, Lau LF, Mohun TJ, Smith JC (2003) Xenopus Cyr61 regulates gastrulation movements and modulates Wnt signalling. Development 130:2429–2441
Lau LF (2011) CCN1/CYR61: the very model of a modern matricellular protein. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:3149–3163
Lau LF, Lam SC (1999) The CCN family of angiogenic regulators: the integrin connection. Exp Cell Res 248:44–57
Leask A, Abraham DJ (2006) All in the CCN family: essential matricellular signaling modulators emerge from the bunker. J Cell Sci 119:4803–4810
Leu S-J, Lam SC-T, Lau LF (2002) Proangiogenic activities of CYR61 (CCN1) mediated through integrins αvβ3 and α6β1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 277:46248–46255
Leu S-J, Liu Y, Chen N, Chen CC, Lam SC, Lau LF (2003) Identification of a novel integrin α6β1 binding site in the angiogenic inducer CCN1 (CYR61). J Biol Chem 278:33801–33808
Leu S-J, Chen N, Chen C-C, Todorovic V, Bai T, Juric V, Liu Y, Yan G, Lam SC-T, Lau LF (2004) Targeted mutagenesis of the matricellular protein CCN1 (CYR61): selective inactivation of integrin α6β1-heparan sulfate proteoglycan coreceptor-mediated cellular activities. J Biol Chem 279:44177–44187
Lillis AP, Mikhailenko I, Strickland DK (2005) Beyond endocytosis: LRP function in cell migration, proliferation and vascular permeability. J Thromb Haemost 3:1884–1893
Lin CG, Leu SJ, Chen N, Tebeau CM, Lin SX, Yeung CY, Lau LF (2003) CCN3 (NOV) is a novel angiogenic regulator of the CCN protein family. J Biol Chem 278:24200–24208
Lipson KE, Wong C, Teng Y, Spong S (2012) CTGF is a central mediator of tissue remodeling and fibrosis and its inhibition can reverse the process of fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 5:S24
Liu SC, Hsu CJ, Chen HT, Tsou HK, Chuang SM, Tang CH (2012) CTGF increases IL-6 expression in human synovial fibroblasts through integrin-dependent signaling pathway. PLoS One 7:e51097
Liu SC, Lee HP, Hung CY, Tsai CH, Li TM, Tang CH (2015) Berberine attenuates CCN2-induced IL-1beta expression and prevents cartilage degradation in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 289:20–29
Mercurio S, Latinkic BV, Itasaki N, Krumlauf R, Smith JC (2004) Connective-tissue growth factor modulates WNT signalling and interacts with the WNT receptor complex. Development 131:2137–2147
Miranti CK, Brugge JS (2002) Sensing the environment: a historical perspective on integrin signal transduction. Nat Cell Biol 4:E83–E90
Murphy-Ullrich JE, Sage EH (2014) Revisiting the matricellular concept. Matrix Biol 37:1–14
Myers RB, Wei L, Castellot JJ Jr (2014) The matricellular protein CCN5 regulates podosome function via interaction with integrin alphavbeta 3. J Cell Commun Signal 8:135–146
Nishida T, Nakanishi T, Shimo T, Asano M, Hattori T, Tamatani T, Tezuka K, Takigawa M (1998) Demonstration of receptors specific for connective tissue growth factor on a human chondrocytic cell line (HCS-2/8). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 247:905–909
Nishida T, Emura K, Kubota S, Lyons KM, Takigawa M (2011) CCN family 2/connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) promotes osteoclastogenesis via induction of and interaction with dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP). J Bone Miner Res 26:351–363
O’Brien TP, Yang GP, Sanders L, Lau LF (1990) Expression of cyr61, a growth factor-inducible immediate-early gene. Mol Cell Biol 10:3569–3577
Parada C, Li J, Iwata J, Suzuki A, Chai Y (2013) CTGF mediates Smad-dependent transforming growth factor beta signaling to regulate mesenchymal cell proliferation during palate development. Mol Cell Biol 33:3482–3493
Riley KG, Pasek RC, Maulis MF, Peek J, Thorel F, Brigstock DR, Herrera PL and Gannon M (2015). Connective tissue growth factor modulates adult beta-cell maturity and proliferation to promote beta-cell regeneration in mice. Diabetes 64:1284–1298
Sakamoto K, Yamaguchi S, Ando R, Miyawaki A, Kabasawa Y, Takagi M, Li CL, Perbal B, Katsube K (2002) The nephroblastoma overexpressed gene (NOV/ccn3) protein associates with Notch1 extracellular domain and inhibits myoblast differentiation via notch signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 277:29399–29405
Sarrazin S, Lamanna WC and Esko JD (2011). Heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3, pii: a004952. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a004952
Schober JM, Chen N, Grzeszkiewicz TM, Emeson EE, Ugarova TP, Ye RD, Lau LF, Lam SC-T (2002) Identification of integrin αMβ2 as an adhesion receptor on peripheral blood moncytes for Cyr61 (CCN1) and connective tissue growth factor (CCN2), immediate-early gene products expressed in atherosclerotic lesions. Blood 99:4457–4465
Segarini PR, Nesbitt JE, Li D, Hayes LG, Yates JR III, Carmichael DF (2001) The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/α2-macroglobulin receptor is a receptor for connective tissue growth factor (CTGF). J Biol Chem 276:40659–40667
Shimoyama T, Hiraoka S, Takemoto M, Koshizaka M, Tokuyama H, Tokuyama T, Watanabe A, Fujimoto M, Kawamura H, Sato S, Tsurutani Y, Saito Y, Perbal B, Koseki H, Yokote K (2010) CCN3 inhibits neointimal hyperplasia through modulation of smooth muscle cell growth and migration. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:675–682
Shi-wen X, Stanton LA, Kennedy L, Pala D, Chen Y, Howat SL, Renzoni EA, Carter DE, Bou-Gharios G, Stratton RJ, Pearson JD, Beier F, Lyons KM, Black CM, Abraham DJ, Leask A (2006) CCN2 is necessary for adhesive responses to transforming growth factor-beta1 in embryonic fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 281:10715–10726
Stephens S, Palmer J, Konstantinova I, Pearce A, Jarai G, Day E (2015) A functional analysis of Wnt inducible signalling pathway protein −1 (WISP-1/CCN4). J Cell Commun Signal 9:63–72
Todorovic V, Chen C-C, Hay N, Lau LF (2005) The matrix protein CCN1 (CYR61) induces apoptosis in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 171:559–568
Tran CM, Schoepflin ZR, Markova DZ, Kepler CK, Anderson DG, Shapiro IM, Risbud MV (2014) CCN2 suppresses catabolic effects of interleukin-1beta through alpha5beta1 and alphaVbeta3 integrins in nucleus pulposus cells: implications in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Biol Chem 289:7374–7387
Ventresca EM, Lecht S, Jakubowski P, Chiaverelli RA, Weaver M, Del Valle L, Ettinger K, Gincberg G, Priel A, Braiman A, Lazarovici P, Lelkes PI, Marcinkiewicz C (2015) Association of p75(NTR) and alpha9beta1 integrin modulates NGF-dependent cellular responses. Cell Signal 27:1225–1236
Wahab NA, Weston BS, Mason RM (2005) Connective tissue growth factor CCN2 interacts with and activates the tyrosine kinase receptor TrkA. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:340–351
Wang X, McLennan SV, Allen TJ, Tsoutsman T, Semsarian C, Twigg SM (2009) Adverse effects of high glucose and free fatty acid on cardiomyocytes are mediated by connective tissue growth factor. Am J Phys Cell Physiol 297:C1490–C1500
Wang X, MCLennan SV, Allen TJ, Twigg SM (2010) Regulation of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic factors by CCN2/CTGF in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. J Cell Commun Signal 4:15–23
Wells JE, Howlett M, Cheung LC, Kees UR (2015) The role of CCN family genes in haematological malignancies. J Cell Commun Signal 9:267–278
Xu H, Li P, Liu M, Liu C, Sun Z, Guo X, Zhang Y (2015) CCN2 and CCN5 exerts opposing effect on fibroblast proliferation and transdifferentiation induced by TGF-beta. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 42:1207–1219
Yang GP, Lau LF (1991) Cyr61, product of a growth factor-inducible immediate early gene, is associated with the extracellular matrix and the cell surface. Cell Growth Differ 2:351–357
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to Drs. Karen Lyons and David Brigstock for helpful suggestions. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01 AR061791 and R01 GM078492).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lau, L.F. Cell surface receptors for CCN proteins. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 10, 121–127 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-016-0324-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-016-0324-z