Abstract
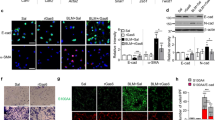
Wnt-1 inducible signalling pathway protein 1 (WISP-1/CCN4) is an extracellular matrix protein that belongs to the Cyr61 (cysteine-rich protein 61), CTGF (connective tissue growth factor) and NOV (CCN) family and plays a role in multiple cellular processes. No specific WISP-1 receptors have been identified but emerging evidence suggests WISP-1 mediates its downstream effects by binding to integrins. Here we describe a functional analysis of integrin receptor usage by WISP-1. Truncated WISP-1 proteins were produced using a baculovirus expression system. Full length WISP-1 and truncated proteins were evaluated for their ability to induce adhesion in A549 epithelial cells and β-catenin activation and CXCL3 secretion in fibroblasts (NRK49-F cells). Subsequent inhibition of these responses by neutralising integrin antibodies was evaluated. A549 cells demonstrated adhesion to full-length WISP-1 whilst truncated proteins containing VWC, TSP or CT domains also induced adhesion, with highest activity observed with proteins containing the C-terminal TSP and CT domains. Likewise the ability to induce β-catenin activation and CXCL3 secretion was retained in truncations containing C-terminal domains. Pre-treatment of A549s with either integrin αVβ5, αVβ3 or β1 neutralising antibodies partially inhibited full length WISP-1 induced adhesion whilst combining integrin αVβ5 and β1 antibodies increased the potency of this effect. Incubation of NRK49-F cells with integrin neutralising antibodies failed to effect β-catenin translocation or CXCL3 secretion. Analysis of natural WISP-1 derived from human lung tissue showed the native protein is a high order oligomer. Our data suggest that WISP-1 mediated adhesion of A549 cells is an integrin-driven event regulated by the C-terminal domains of the protein. Activation of β-catenin signalling and CXCL3 secretion also resides within the C-terminal domains of WISP-1 but are not regulated by integrins. The oligomeric nature of native WISP-1 may drive a high avidity interaction with these receptors in vivo.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carman CV, Springer TA (2003) Integrin avidity regulation: are changes in affinity and conformation underemphasized? Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:547–556
Cervello M, Giannitrapani L, Labbozzetta M, Notarbartolo M, D’Alessandro N, Lampiasi N, Azzolina A, Montalto G (2004) Expression of WISPs and of their novel alternative variants in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1028:432–439
Chen CC, Lau LF (2009) Functions and mechanisms of action of CCN matricellular proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:771–783
Chen PC, Cheng HC, Yang SF, Lin CW, Tang CH (2014) The CCN family proteins: modulators of bone development and novel targets in bone-associated tumors. Biomed Res Int 2014:437096
Chuang JY, Chang AC, Chiang IP, Tsai MH, Tang CH (2013) Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 is involved in WISP-1-promoted cell motility in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. PLoS One 8:e78022
Colston JT, de la Rosa SD, Koehler M, Gonzales K, Mestril R, Freeman GL, Bailey SR, Chandrasekar B (2007) Wnt-induced secreted protein-1 is a prohypertrophic and profibrotic growth factor. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H1839–H1846
Desnoyers L, Arnott D, Pennica D (2001) WISP-1 binds to decorin and biglycan. J Biol Chem 276:47599–47607
Holbourn KP, Acharya KR, Perbal B (2008) The CCN family of proteins: structure-function relationships. Trends Biochem Sci 33:461–473
Holbourn KP, Perbal B, Ravi AK (2009) Proteins on the catwalk: modelling the structural domains of the CCN family of proteins. J Cell Commun Signal 3:25–41
Hou CH, Tang CH, Hsu CJ, Hou SM, Liu JF (2013) CCN4 induces IL-6 production through alphavbeta5 receptor, PI3K, Akt, and NF-kappaB singling pathway in human synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 15:R19
Jiang F, Parsons CJ, Stefanovic B (2006) Gene expression profile of quiescent and activated rat hepatic stellate cells implicates Wnt signaling pathway in activation. J Hepatol 45:401–409
Konigshoff M, Kramer M, Balsara N, Wilhelm J, Amarie OV, Jahn A, Rose F, Fink L, Seeger W, Schaefer L, Gunther A, Eickelberg O (2009) WNT1-inducible signaling protein-1 mediates pulmonary fibrosis in mice and is upregulated in humans with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest 119:772–787
Liu JF, Hou SM, Tsai CH, Huang CY, Hsu CJ, Tang CH (2013) CCN4 induces vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human synovial fibroblasts and promotes monocyte adhesion. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:966–975
Ono M, Inkson CA, Kilts TM, Young MF (2011) WISP-1/CCN4 regulates osteogenesis by enhancing BMP-2 activity. J Bone Miner Res 26:193–208
Perbal B (2009) Alternative splicing of CCN mRNAs .... it has been upon us. J Cell Commun Signal 3:153–157
Shimo T, Nakanishi T, Nishida T, Asano M, Kanyama M, Kuboki T, Tamatani T, Tezuka K, Takemura M, Matsumura T, Takigawa M (1999) Connective tissue growth factor induces the proliferation, migration, and tube formation of vascular endothelial cells in vitro, and angiogenesis in vivo. J Biochem 126:137–145
Su F, Overholtzer M, Besser D, Levine AJ (2002) WISP-1 attenuates p53-mediated apoptosis in response to DNA damage through activation of the Akt kinase. Genes Dev 16:46–57
Wang H, Zhang R, Wen S, McCafferty DM, Beck PL, MacNaughton WK (2009) Nitric oxide increases Wnt-induced secreted protein-1 (WISP-1/CCN4) expression and function in colitis. J Mol Med (Berl) 87:435–445
Wang D, Dai C, Li Y, Liu Y (2011) Canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling mediates transforming growth factor-beta1-driven podocyte injury and proteinuria. Kidney Int 80:1159–1169
Yanagita T, Kubota S, Kawaki H, Kawata K, Kondo S, Takano-Yamamoto T, Tanaka S, Takigawa M (2007) Expression and physiological role of CCN4/Wnt-induced secreted protein 1 mRNA splicing variants in chondrocytes. FEBS J 274:1655–1665
Yang F, Tuxhorn JA, Ressler SJ, McAlhany SJ, Dang TD, Rowley DR (2005) Stromal expression of connective tissue growth factor promotes angiogenesis and prostate cancer tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 65:8887–8895
Zulato E, Favaretto F, Veronese C, Campanaro S, Marshall JD, Romano S, Cabrelle A, Collin GB, Zavan B, Belloni AS, Rampazzo E, Naggert JK, Abatangelo G, Sicolo N, Maffei P, Milan G, Vettor R (2011) ALMS1-deficient fibroblasts over-express extra-cellular matrix components, display cell cycle delay and are resistant to apoptosis. PLoS One 6:e19081
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephens, S., Palmer, J., Konstantinova, I. et al. A functional analysis of Wnt inducible signalling pathway protein −1 (WISP-1/CCN4). J. Cell Commun. Signal. 9, 63–72 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-015-0267-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-015-0267-9