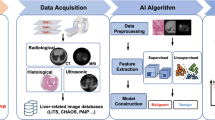
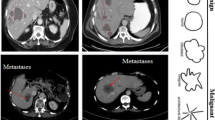
Abstract
Deep learning (DL) is a recently developed artificial intelligent method that can be integrated into numerous fields. For the imaging diagnosis of liver disease, several remarkable outcomes have been achieved with the application of DL currently. This advanced algorithm takes part in various sections of imaging processing such as liver segmentation, lesion delineation, disease classification, process optimization, etc. The DL optimized imaging diagnosis shows a broad prospect instead of the pathological biopsy for the advantages of convenience, safety, and inexpensiveness. In this paper, we reviewed the published representative DL-related hepatic imaging works, described the general situation of this new-rising technology in medical liver imaging and explored the future direction of DL development.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Trefts E, Gannon M, Wasserman DH. The liver. Curr Biol 2017;27(21):R1147–R1151
Di Tommaso L, et al. Role of liver biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2019;25(40):6041–6052
Ayuso C, et al. Diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): current guidelines. Eur J Radiol 2018;101:72–81
Sertorio F, et al. Ultrasonography as first line imaging for the diagnosis of positional plagiocephaly: our experience and literature review. Minerva Pediatr 2019. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0026-4946.19.05424-0
Nishida N, et al. Current status and perspectives for computer-aided ultrasonic diagnosis of liver lesions using deep learning technology. Hepatol Int 2019;13(4):416–421
Choi KJ, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning system for staging liver fibrosis by using contrast agent-enhanced CT images in the liver. Radiology 2018;289(3):688–697
Han X. MR-based synthetic CT generation using a deep convolutional neural network method. Med Phys 2017;44(4):1408–1419
Ben-Cohen A, Greenspan H. Liver lesion detection in CT using deep learning techniques. In: Handbook of Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, 2020; p. 65–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-816176-0.00008-9
Waite S, et al. Interpretive error in radiology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2017;208(4):739–749
Chan HP, Samala RK, Hadjiiski LM. CAD and AI for breast cancer-recent development and challenges. Br J Radiol 2020;93(1108):20190580
Suzuki K. Overview of deep learning in medical imaging. Radiol Phys Technol 2017;10(3):257–273
Sapkota M, Shi X, Xing F, Yang L. Deep convolutional hashing for low-dimensional binary embedding of histopathological images. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 2019;23(2):805–816
Le EPV, et al. Artificial intelligence in breast imaging. Clin Radiol 2019;74(5):357–366
Sahiner B, et al. Deep learning in medical imaging and radiation therapy. Med Phys 2019;46(1):e1–36
Lundervold AS, Lundervold A. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Z Med Phys 2019;29(2):102–127
Sarıgül M, Ozyildirim BM, Avci M. Differential convolutional neural network. Neural Netw 2019;116:279–287
Karim AM, et al. A novel framework using deep auto-encoders based linear model for data classification. Sensors (Basel) 2020;20(21):6378
Movahedi F, Coyle JL, Sejdic E. deep belief networks for electroencephalography: a review of recent contributions and future outlooks. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf. 2018;22(3):642–652
Barak O. Recurrent neural networks as versatile tools of neuroscience research. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2017;46:1–6
Pons E, Braun LM, Hunink MG, Kors JA. Natural language processing in radiology: a systematic review. Radiology 2016;279(2):329–343
Min S, Lee B, Yoon S. Deep learning in bioinformatics. Brief Bioinform 2017;18(5):851–869
Huan EY, Wen GH. Multilevel and multiscale feature aggregation in deep networks for facial constitution classification. Comput Math Methods Med 2019;2019:1258782
Yamashita R, Nishio M, Do RKG, Togashi K. Convolutional neural networks: an overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018;9(4):611–629
Biswas M, et al. Symtosis: A liver ultrasound tissue characterization and risk stratification in optimized deep learning paradigm. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2018;155:165–177
Ohn I, Kim Y. Smooth function approximation by deep neural networks with general activation functions. Entropy (Basel) 2019;21(7):627
Soffer S, et al. Convolutional neural networks for radiologic images: a radiologist’s guide. Radiology 2019;290(3):590–606
Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2017;39(4):640–651
Falk T, et al. U-Net: deep learning for cell counting, detection, and morphometry. Nat Methods 2019;16(1):67–70
Clancy K, et al. Deep learning pre-training strategy for mammogram image classification: an evaluation study. J Digit Imaging 2020;33(5):1257–1265
Jansen MJA, et al. Patient-specific fine-tuning of convolutional neural networks for follow-up lesion quantification. J Med Imaging (Bellingham) 2020;7(6):064003
Ben-Cohen A, et al. Fully convolutional network for liver segmentation and lesions detection. Deep Learn Data Label Med Appl 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46976-8_9
Zhang Y, et al. Deep learning initialized and gradient enhanced Level-Set based segmentation for liver tumor from CT images. IEEE Access 2020;8:76056–76068
Fang X, Xu S, Wood BJ, Yan P. Deep learning-based liver segmentation for fusion-guided intervention. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2020;15(6):963–972
Tang X, et al. Whole liver segmentation based on deep learning and manual adjustment for clinical use in SIRT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2020;47(12):2742–2752
Hu P, et al. Automatic 3D liver segmentation based on deep learning and globally optimized surface evolution. Phys Med Biol 2016;61(24):8676–8698
Winkel DJ, et al. Validation of a fully automated liver segmentation algorithm using multi-scale deep reinforcement learning and comparison versus manual segmentation. Eur J Radiol 2020;126:108918
Marinelli B, et al. Combination of active transfer learning and natural language processing to improve liver volumetry using surrogate metrics with deep learning. Radiol Artif Intell 2019. https://doi.org/10.1148/ryai.2019180019
Ghoniem RM. A novel bio-inspired deep learning approach for liver cancer diagnosis. Information 2020;11(2):80
Halder A, Dey D, Sadhu AK. lung nodule detection from feature engineering to deep learning in thoracic CT images: a comprehensive review. J Digit Imaging 2020;33(3):655–677
Yamakawa M, Shiina T, Nishida N, Kudo M. Computer aided diagnosis system developed for ultrasound diagnosis of liver lesions using deep learning. In: 2019 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), 2019; p. 2330–2333. https://doi.org/10.1109/ULTSYM.2019.8925698
Schmauch B, et al. Diagnosis of focal liver lesions from ultrasound using deep learning. Diagn Interv Imaging 2019;100(4):227–233
Hassan TM, Elmogy M, Sallam ES. Diagnosis of focal liver diseases based on deep learning technique for ultrasound images. Arab J Sci Eng 2017;42:3127–3140
Durot I, Wilson SR, Willmann JK. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of malignant liver lesions. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2018;43(4):819–847
Jaspers N, Pfister R, Kinkel H, Michels G. Kontrastmittelsonographie [Contrast-enhanced ultrasound]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 2012;137(45):2336–2339
Guo L, et al. CEUS-based classification of liver tumors with deep canonical correlation analysis and multi-kernel learning. In: 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2017; p. 1748–1751. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2017.8037181
Wu K, Chen X, Ding MY. Deep learning based classification of focal liver lesions with contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Optik 2014;125(15):4057–4063
Das A, et al. Deep learning based liver cancer detection using watershed transform and Gaussian mixture model techniques. Cogn Syst Res 2019;54:165–175
Xu X, et al. Radiomic analysis of contrast-enhanced CT predicts microvascular invasion and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2019;70(6):1133–1144
Wang W, et al. Classification of focal liver lesions using deep learning with fine-tuning. In: Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on digital medicine and image processing 2018; p. 56–60. https://doi.org/10.1145/3299852.3299860
Shi W, et al. Deep learning assisted differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma from focal liver lesions: choice of four-phase and three-phase CT imaging protocol. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2020;45(9):2688–2697
Hamm CA, et al. Deep learning for liver tumor diagnosis part I: development of a convolutional neural network classifier for multi-phasic MRI. Eur Radiol 2019;29(7):3338–3347
Wang C, et al. Deep learning for liver tumor diagnosis part II: convolutional neural network interpretation using radiologic imaging features. Eur Radiol 2019;29(7):3348–3357
Trivizakis E, et al. Extending 2-D convolutional neural networks to 3-D for advancing deep learning cancer classification with application to mri liver tumor differentiation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 2019;23(3):923–930
Xiao G, et al. Comparison of laboratory tests, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance elastography to detect fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017;66(5):1486–1501
Reddy DS, Bharath R, Rajalakshmi P. A novel computer-aided diagnosis framework using deep learning for classification of fatty liver disease in ultrasound imaging. In: IEEE 20th International Conference on e-health networking, applications and services 2018; p. 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/HealthCom.2018.8531118
Byra M, et al. Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network for liver steatosis assessment in ultrasound images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2018;13(12):1895–1903
Cao W, et al. Application of deep learning in quantitative analysis of 2-dimensional ultrasound imaging of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Ultrasound Med 2020;39(1):51–59
Lee JH, et al. Deep learning with ultrasonography: automated classification of liver fibrosis using a deep convolutional neural network. Eur Radiol 2020;30(2):1264–1273
Sigrist RMS, et al. Ultrasound elastography: review of techniques and clinical applications. Theranostics 2017;7(5):1303–1329
Colombo S, et al. Head-to-head comparison of transient elastography (TE), real-time tissue elastography (RTE), and acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis. J Gastroenterol 2012;47(4):461–469
Gatos I, et al. Temporal stability assessment in shear wave elasticity images validated by deep learning neural network for chronic liver disease fibrosis stage assessment. Med Phys 2019;46(5):2298–2309
Wang K, et al. Deep learning Radiomics of shear wave elastography significantly improved diagnostic performance for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: a prospective multicentre study. Gut 2019;68(4):729–741
Li Y, et al. A deep learning trial on transient elastography for assessment of liver fibrosis. In: IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium. 2018; p. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/ULTSYM.2018.8579992
Yip SS, Aerts HJ. Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys Med Biol 2016;61(13):R150–R166
Liu Y, et al. MRI-based treatment planning for proton radiotherapy: dosimetric validation of a deep learning-based liver synthetic CT generation method. Phys Med Bio. 2019;64(14):145015
Ibragimov B, et al. Combining deep learning with anatomical analysis for segmentation of the portal vein for liver SBRT planning. Phys Med Biol 2017;62(23):8943–8958
Ibragimov B, et al. Automated hepatobiliary toxicity prediction after liver stereotactic body radiation therapy with deep learning-based portal vein segmentation. Neurocomputing 2020;392:181–188
Esses SJ, et al. Automated image quality evaluation of T2 -weighted liver MRI utilizing deep learning architecture. J Magn Reson Imaging 2018;47(3):723–728
Cho BJ, et al. Automated classification of gastric neoplasms in endoscopic images using a convolutional neural network. Endoscopy 2019;51(12):1121–1129
Le Berre C, et al. Application of artificial intelligence to gastroenterology and hepatology. Gastroenterology 2020;158(1):76-94.e2
Cho BJ, et al. Prediction of submucosal invasion for gastric neoplasms in endoscopic images using deep-learning. J Clin Med 2020;9(6):1858
Sbeit W, et al. A comprehensive narrative review on the evolving role of endoscopic ultrasound in focal solid liver lesions diagnosis and management. Diagnostics (Basel) 2020;10(9):688
Lisotti A, et al. EUS liver assessment using contrast agents and elastography. Endosc Ultrasound 2018;7(4):252–256
Zhang WY, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided ethanol ablation therapy for tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2013;19(22):3397–3403
Chua T, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided ablation of liver tumors. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2019;29(2):369–379
ASGE Technology Committee, Trikudanathan G, et al. EUS-guided portal vein interventions. Gastrointest Endosc 2017;85(5):883–888
Bhatia V, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound description of liver segmentation and anatomy. Dig Endosc 2014;26(3):482–490
Li YD, et al. Intelligent detection endoscopic assistant: an artificial intelligence-based system for monitoring blind spots during esophagogastroduodenoscopy in real-time. Dig Liver Dis 2021;53(2):216–223
Ramalhinho J, et al. A pre-operative planning framework for global registration of laparoscopic ultrasound to CT images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2018;13(8):1177–1186
Short RG, Bralich J, Bogaty D, Befera NT. Comprehensive word-level classification of screening mammography reports using a neural network sequence labeling approach. J Digit Imaging 2019;32(5):685–692
Xiong J, Xiong Z, Chen K, Jiang H, Zheng M. Graph neural networks for automated de novo drug design. Drug Discov Today 2021;26(6):1382–1393
Li W, Liu K, Zhang L, Cheng F. Object detection based on an adaptive attention mechanism. Sci Rep 2020;10(1):11307
Fourment M, Darling AE. Evaluating probabilistic programming and fast variational Bayesian inference in phylogenetics. PeerJ 2019;7:e8272
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFE0195200), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81873156), The Leading Talent of Hundred, Thousand and Ten Thousand Project of Liaoning Province (XLYC1905013).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFE0195200), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81873156), The Leading Talent of Hundred, Thousand and Ten Thousand Project of Liaoning Province (XLYC1905013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to this paper. Material preparation and article collection were performed by Kailai Xiang and Baihui Jiang. Reviewing and editing was performed by Dong Shang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Kailai Xiang and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
Kailai Xiang, Baihui Jiang, and Dong Shang have declared that they have no competing interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, K., Jiang, B. & Shang, D. The overview of the deep learning integrated into the medical imaging of liver: a review. Hepatol Int 15, 868–880 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-021-10229-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-021-10229-z