Abstract
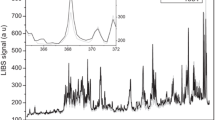
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is an emerging technique for simultaneous multi-elemental analysis of solids, liquids and gases with minute or no sample preparation and thus revolutionized the area of on-line analysis technologies. The foundation for LIBS is a solid state, short-pulsed laser that is focused on a sample to generate a high-temperature plasma, and the emitted radiation from the excited atomic and ionic fragments produced within the plasma is characteristic of the elemental composition of the sample that can be detected and analyzed using a suitable optical spectrograph. In the present paper, the applicability of LIBS for different solid samples having homogeneous (silver ornament, aluminum plate) or heterogeneous composition (soil) using nanosecond laser pulses is discussed. Nanosecond pulse laser makes plasma at the sample surface even at very low pulse energies and also allows for precise ablation of the substrate material with little damage to the surrounding area. We have also studied the penetration of different heavy metals inside the soil surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Z Martin, S D Wullschleger, C T Garten Jr and A V Palumbo, Appl. Opt. 42(12), 2072 (2003)
M Corsi, G Cristoforetti, V Palleschi, A Salvetti and E Tognoni, Euro. Phys. J. D13, 373 (2001)
R Barbini, F Calao, R Fantoni, A Palucci and F Capitelli, Appl. Phys. A69(Suppl.) S175 (1999)
S Koch, W Garen, M Muller and W Neu, Appl. Phys. A79, 1071 (2004)
A Kumar, F-Y Yueh and J P Singh, Appl. Opt. 42(30), 6047 (2003)
A K Rai, V N Rai, F-Y Yueh and J P Singh, Trends in Appl. Spectro. 4, 165 (2002)
Maria Greger, in: Heavy metals stress in plants — from biomolecules to ecosystem 2nd edition, edited by M N V Prasad (Springer, New York, 2003) Chap. 1, p. 2
H Lokeshwari and G T Chandrappa, Curr. Sci. 91(5), 622 (2006)
A V Palumbo, L S Fisher, M Z Martin, Z K Yang, J R Tarver, S D Wullschleger and W L Danies, Environ. Manage. 33, S518 (2004)
F Y Yueh, J P Singh and H Zhang, Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy: Elemental analysis in encyclopedia of analytical chemistry (Wiley, New York, 2000) pp. 3662–3669
F C De Lucia Jr, R S Harmon, K L Mcnesby, R J Winkel Jr and A W Miziolek, Appl. Opt. 42(30), 6148 (2003)
Shiwani Pandhija and A K Rai, in: Proceedings of National Laser Symposium (NLS), CAT Indore, India, 2006, p. 250
W R Brode, Chemical spectroscopy, 2nd edition (John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York, 1958)
S Pandhija and A K Rai, Calibration-free LIBS approach for quantitative measurement of constituents in environmental sample, in Proceedings of NASLIBS2007 (2007) p. 14, 60
H M Selim and M C Amacher, Reactivity and transport of heavy metals in soils (CRC Press, Lewis Publishers, USA, 1996)
M Sabsabi and P Cielo, Appl. Spectrosc. 49(4), 499 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandhija, S., Rai, A.K. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: A versatile tool for monitoring traces in materials. Pramana - J Phys 70, 553–563 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-008-0070-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-008-0070-8