Abstract
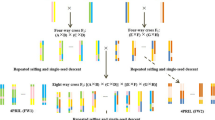
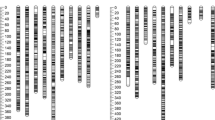
In this paper, we report the construction of the first composite map of cacao from linkage data of one F2 and two F1 mapping populations with a high number of codominant markers in common. The combination of linkage information from all three maps results in the currently most precise estimates of marker locations and distances between markers, especially in densely marked areas. JoinMap®V4 software was used for all marker quality assessment and mapping. Individual (sub-composite) maps and the composite map contained 10 major linkage groups, corresponding to the number of cacao chromosomes. Homogeneity of marker placement was very high among sub-composite maps, the composite map, and the designated “reference” map. Care was exercised in the re-creation of sub-composite maps and the composite map to include only markers with acceptable mapping quality parameters. The composite map places more markers with higher precision than any individual map. This research clearly demonstrates for the first time a very high level of marker homogeneity among commercial cacao clones compared to other species. The observed homogeneity between different maps, including the composite one, is probably due to a narrow genetic base of commercial cacao clones. Markers linked to identified quantitative trait loci (QTLs) are more likely to retain linkage in other commercial clones, rendering the QTLs in cacao potentially more stable than in other species.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFLP:
-
amplified fragment length polymorphism
- CATIE:
-
Tropical Agricultural Research and Higher Education Center
- CIRAD:
-
Centre de Cooperation Internaionale en Recherche Agronomique pour le Développement
- LG:
-
linkage group
- LOD:
-
log likelihood score
- QTL:
-
quantitative trait locus (loci)
- RAPD:
-
random amplified polymorphic DNA
- RFLP:
-
restriction fragment length polymorphism(s)
- RGH:
-
resistance gene homologue
- SCL:
-
strongest crosslink
- SHRS:
-
Subtropical Horticulture Research Station
- SSR:
-
simple sequence repeat
References
Aime MC, Phillips-Mora W (2005) The causal agents of witches’ broom and frosty pod rot of cacao (chocolate, Theobroma cacao) from a new lineage of Marasmiacaea. Mycologia 97:1012–1022
Beavis WD, Grant D (1991) A linkage map based on information from four F2 populations of maize (Zea maize L.). Theor Appl Genet 82:636–644
Borrone JW, Kuhn DN, Schnell RJ (2004) Isolation, characterization, and development of WRKY genes as useful genetic markers in Theobroma cacao. Theor Appl Genet 109(3):495–507
Brown JS, Phillips-Mora W, Power EJ et al (2007) Mapping QTLs for resistance to frosty pod and black pod diseases and horticultural traits in Theobroma cacao L. Crop Sci 47:1851–1858
Brown JS, Schnell RJ, Motamayor JC et al (2005) Resistance gene mapping for witches’ broom disease in Theobroma cacao L. in a F2 population using SSR markers and candidate genes. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 130(3):366–373
Clément D, Risterucci AM, Motamayor JC et al (2003a) Mapping quantitative trait loci for bean traits and ovule number in Theobroma cacao L. Genome 46:103–111
Clément D, Risterucci AM, Motamayor JC et al (2003b) Mapping QTL for yield components, vigor, and resistance to Phytophthora palmivora in Theobroma cacao L. Genome 46:204–212
Jansen J, de Jong AG, van Ooijen JW (2001) Constructing dense genetic linkage maps. Theor Appl Genet 102:1113–1122
Kuhn DN, Heath M, Wisser RJ et al (2003) Resistance Gene Homologues in Theobroma cacao as useful genetic markers. Theor Appl Genet 107:191–202
Lalouel JM (1977) Linkage mapping from pair-wise recombination data. Heredity 38:61–77
Lanaud C, Risterucci AM, N’Goran JAK et al (1995) A genetic linkage map of Theobroma cacao L. Theor Appl Genet 9:987–993
Maliepaard C, Jansen J, Van Ooijen JW (1997) Linkage analysis in a full-sib family of an outbreeding plant species: overview and consequences for applications. Genet Res 70:237–250
Motamayor JC, Risterucci AM, Heath M et al (2003) Cacao domestication II: progenitor germplasm of the Trinitario cacao cultivar. Heredity 91:322–330
Pelgas B, Bousquet J, Beauseigle S et al (2005) A composite linkage map from two crosses for the species complex Picea mariana x Picea rubens and analysis of syunteny with other Pinaceae. Theor Appl Genet 111:1466–1488
Pereira TNS, Yamada MM (1999) Hibridação em cacao. In: Borem A (ed) Hibridação artificial de plantas. Editora UFV, Viçosa, Brazil
Pugh T, Fouet AM, Brottier P et al (2004) A new cacao linkage map based on codominant markers: development and integration of 201 new microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 108:1151–1161
Risterucci AM, Grivet L, N’Goran JAK et al (2000) A high-density linkage map of Theobroma cacao L. Theor Appl Genet 101:948–855
Schnell RJ, Brown JS, Kuhn DN et al (2007) Development of a marker assisted selection program for cacao. Phytopathology 97(12):1664–1669
Sewell MM, Sherman BK, Neale DB (1999) A consensus map for loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) I. Construction and integration of individual linkage maps from two outbred three-generation pedigrees. Genetics 151:321–330
Shepard M, Cross M, Dieters MJ et al (2003) Genetic maps for Pinus elliottii and P. carubaea var. honurensis using AFLP and microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 106:1409–1419
Stam P (1993) Construction of integrated genetic linkage maps by means of a new computer package: JoinMap. Plant J 3(5):739–744
Weir BS (2007) Impact of dense genetic marker maps on plant population genetic studies. Euphytica 154:355–364
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap® 4, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma® B. V., Wageningen, The Netherlands
Wu R, Ma CX, Painter I et al (2002) Simultaneous maximum likelihood estimation of linkage and linkage phases in outcrossing species. Theor Popul Biol 61:349–363
Zhang D, Arevaldo-Gardini E, Miksche S et al (2006) Genetic diversity and structure of managed and semi-natural populations of cocoa (Theobroma cacao) in the Hullaga and Ucallali valleys of Peru. Ann Bot 98:647–655
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Claire Lanaud of CIRAD, Montpellier, France, as well as other researchers at or related to CIRAD, for the development of the population and molecular marker data mentioned above from their research. We would also like to acknowledge Dr. Wilbert Phillips of CATIE, Turrialba, Costa Rica, and other researchers involved in the production of the population mentioned above from their location. We also acknowledge Dr. Uilson Lopes of CEPLAC, Itabuna, Bahía, Brazil, for the F2 cacao population used for mapping, as mentioned in the text. In addition, we acknowledge the helpful suggestions concerning mapping technique of Dr. Johan van Ooijen of Kyazma, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, J.S., Sautter, R.T., Olano, C.T. et al. A Composite Linkage Map from Three Crosses Between Commercial Clones of Cacao, Theobroma cacao L.. Tropical Plant Biol. 1, 120–130 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-008-9011-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-008-9011-4