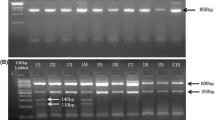
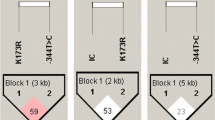
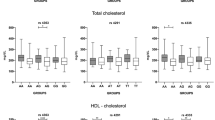
Abstract
Essential hypertension which accounts 90–95% of the total hypertension cases is affected by both genetic and environmental factors. This study was undertaken to investigate the association of aldosterone synthase C-344T, angiotensin II type I receptor A1166C and 11- β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 G534A polymorphisms with essential hypertension in the population of Odisha, India. A total of 246 hypertensive subjects (males, 159; females, 87) and 274 normal healthy individuals (males, 158; females, 116) were enrolled in this study based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Analysis of genetic and biochemical data revealed that in this population the CT and TT genotypes of aldosterone synthase C-344T polymorphism, frequency of alcohol consumption and aldosterone levels were significantly high among the total as well as male hypertensives, while the AC and CC genotypes of angiotensin II type I receptor A1166C polymorphism were significantly high among the total as well as female hypertensives. High density lipoprotein levels were higher in male hypertensives.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agachan B., Isbir T., Yilmaz H., and Akoglu E. 2003 Angiotensin converting enzyme I/D, angiotensinogen T174M-M235T and angiotensin II type 1 receptor A1166C gene polymorphisms in Turkish hypertensive patients. Exp. Mol. Med. 35, 545–549.
Alavi-Shahri J., Behravan J., Hassany M., Tatari F., Kasaian J., Ganjali R., et al. 2010 Association between angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphism and metabolic syndrome in a young female Iranian population. Arch. Med. Res. 41, 343–349.
Araújo M. A., Menezes B S., Lourenço C, Cordeiro E. R., Gatti R. R., and Goulart L. R. 2004 The A1166C polymorphism of the angiotensin II type-1 receptor in acute myocardial infarction. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 83, 409–413, 404–408.
Bonnardeaux A., Davies E., Jeunemaitre X., Féry I., Charru A., Clauser E., et al. 1994 Angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphisms in human essential hypertension. Hypertens 24, 63–69.
Brand E., Schorr U., Ringel J., Beige J., Distler A., and Sharma A. M. 1999 Aldosterone synthase gene (CYP11B2) C-344T polymorphism in Caucasians from the Berlin Salt-Sensitivity Trial (BeSST). J. Hypertens. 17, 1563–1567.
Campino C., Quinteros H., Owen G. I., Carvajal C. A., Morales M., Olivieri O., et al. 2012 11 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 polymorphisms and activity in a Chilean essential hypertensive and normotensive cohort. Am. J. Hypertens. 25, 597–603.
Castellano M., Muiesan M. L., Beschi M, Rizzoni D., Cinelli A., Salvetti M., et al. 1996 Angiotensin II type 1 receptor A/C1166 polymorphism. Relationships with blood pressure and cardiovascular structure. Hypertens 28, 1076–1080.
Chobanian A., Bakris G., Black H., Cushman W., Green L., Izzo J. J., et al. 2003 The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 289, 2560–2572.
Clyne C. D., Zhang Y, Slutsker L, Mathis J. M., White P. C., and Rainey W. E. 1997 Angiotensin II and potassium regulate human CYP11B2 transcription through common cis-elements. Mol. Endocrinol. 11, 638–649.
Davies E., Holloway C. D., Ingram M. C., Inglis G. C., Friel E. C., Morrison C., et al. 1999 Aldosterone excretion rate and blood pressure in essential hypertension are related to polymorphic differences in the aldosterone synthase gene CYP11B2. Hypertens 33, 703–707.
Freel E. M. and Connel J. M. C. 2004 Mechanisms of hypertension: the expanding role of aldosterone. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 15, 1993–2001.
Funder J. W., Pearce P. T., Smith R., and Smith A. I. 1988 Mineralocorticoid action: target tissue specificity is enzyme, not receptor, mediated. Science 242, 583–585.
Hu B. C., Chu S. L., Wang J. G., Wang Z. H., Wang G. L., Gao P. J., et al. 2006 Association of aldosterone synthase gene −344T/C polymorphism with plasma aldosterone and angiotensin II concentration in hypertensive patients. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 86, 1144–1147.
Iverson C., Christiansen S., Flanagin A., Fontanarosa P. B., Glass R. M., Gregoline B. et al. 2007. AMA manual of style. A guide for authors and editors 10th edition. Oxford University Press, New York, USA.
Jíra M., Závodná E., Honzíková N., Nováková Z., Vasku̇ A., Izakovicová Hollá L., et al. 2010 Association of A1166C polymorphism in AT(1) receptor gene with baroreflex sensitivity. Physiol. Res. 59, 517–528.
Kaur R., Das R., Ahluwalia J., Kumar R. M., and Talwar K. K. 2012 Synergistic effect of angiotensin II type-1 receptor 1166A/C with angiotensin-converting enzyme polymorphism on risk of acute myocardial infarction in north Indians. J. Renin. Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 13, 440–445.
Lifton R. P., Gharavi A. G., and Geller D. S. 2001 Molecular mechanisms of human hypertension. Cell 104, 545–546.
Liu Y., Shan G. L., Cui C. Y., Hou S. Q., Zhuoma C., Cen W. J., et al. 2003 A1166C polymorphism of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene and essential hypertension in Han, Tibetan and Yi populations. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 20, 220– 224.
Mariniello B., Ronconi V., Sardu C., Pagliericcio A., Galletti F., Strazzullo P., et al. 2005 Analysis of the 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 gene (HSD11B2) in human essential hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 18, 1091–1098.
Martin M. M., Buckenberger J. A., Jiang J, Malana G. E., Nuovo G. J., Chotani M., et al. 2007 The human angiotensin II type 1 receptor + 1166 A/C polymorphism attenuates microRNA-155 binding. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 24262–24269.
Melander O., Orho-Melander M., Bengtsson K., Lindblad U., Råstam L., Groop L., et al. 2000 Association between a variant in the 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 gene and primary hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 14, 819–823.
Mune T., Rogerson F. M., Nikkilä H., Agarwal A. K., and White P. C. 1995 Human hypertension caused by mutations in the kidney isozyme of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Nat. Genet. 10, 394–399.
National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection E., and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) 2002 Third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation 106, 3143–3421.
Odermatt A., Dick B., Arnold P., Zaehner T., Plueschke V., Deregibus M. N., et al. 2001 A mutation in the cofactor-binding domain of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 associated with mineralocorticoid hypertension. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 1247–1252.
Pickering T. G., Hall J. E., Appel L J., Falkner B. E., Graves J, Hill M. N., et al. 2005 Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of professional and public education of the American Heart Association Council on high blood pressure research. Circulation 111, 697–716.
Pojoga L., Gautier S., Blanc H., Guyene T -T., Poirier O., Cambien F., et al. 1998 Genetic determination of plasma aldosterone levels in essential hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 11, 856– 860.
Pullareddy B. R., Babu B M. V. S., Karunakar K. V., Yasovanthi J, Kumar P. S., Annam Sharath A., et al. 2009 Angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphism in myocardial infarction patients. J. Renin. Angiotensin. Aldosterone. Syst. 10, 174–178.
Rajan S, Ramu P., Umamaheswaran G. and Adithan C. 2010 Association of aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2 C-344T) gene polymorphism and susceptibility to essential hypertension in a south Indian Tamil population. Ind. J. Med. Res. 132, 379–385.
Sambrook J. and Russell D. W. 2001 Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, vol. 1, 3rd edition, pp. 6.4–6.11. Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York, USA.
Schmidt S., Beige J., Walla-Friedel M., Michel M. C., Sharma A. M., and Ritz E. 1997 A polymorphism in the gene for the angiotensin II type 1 receptor is not associated with hypertension. J. Hypertens. 15, 1385–1388.
Smolenicka Z., Bach E., Schaer A., Liechti-Gallati S., Frey B. M., Frey F. J., et al. 1998 A new polymorphic restriction site in the human 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 gene. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83, 1814–1817.
Staessen J. A., Li Y., and Thijs L. 2007 Meta-analysis of blood pressure and the CYP11B2 polymorphism highlights the need for better designed studies. J. Hypertens. 25, 37–39.
Stanković A., Zivkovic M., Glisić S., and Alavantić D. 2003 Angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphism and essential hypertension in Serbian population. Clin. Chim. Acta 327, 181–185.
Strazzullo P., Galletti F., and Barba G. 2003 Altered renal handling of sodium in human hypertension: short review of the evidence. Hypertens 41, 1000–1005.
Szombathy T., Szalai C., Katalin B., Palicz T., Romics L., and Császár A. 1998 Association of angiotensin II type 1 receptor polymorphism with resistant essential hypertension. Clin. Chim. Acta 269, 91–100.
Tsai C. T., Fallin D, Chiang F. T., Hwang J. J., Lai L. P., Hsu K. L., et al. 2003 Angiotensinogen gene haplotype and hypertension: interaction with ACE gene I allele. Hypertens 41, 9–15.
Tsukada K., Ishimitsu T., Teranishi M., Saitoh M., Yoshii M., Inada H. et al. 2002 Positive association of CYP11B2 gene polymorphism with genetic predisposition to essential hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 16, 789–793.
Vasudevan R., Ali A. B. T., Mansoor M. S., Zulkifli N. F., and Ismail P. 2011 Analysis of C344T genetic polymorphism of CYP11B2 gene in Malaysian end stage renal disease patients. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 6, 213–218.
WHO Consultation on Obesity 2000. obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. WHO technical report series 894. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
Xu X. J., Wang S. Z., Lin R. Y., Wang X. F., Liang X. H., Wen H., et al. 2004 Association of the T(-344)C polymorphism of aldosterone synthase gene CYP11B2 with essential hypertension in Xinjiang Kazakh isolated group. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 21, 622–624.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, for providing fellowship to Manisha Patnaik to carry out the research (sanction number: 09/547(0004)2009-EMR-I). We also acknowledge the School of Biotechnology, Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology, Bhubaneswar for registering Mrs Manisha Patnaik as a Ph.D. student (registration number: 11396621439), Dr S. K. Kar, Director of Regional Medical Research Centre, Bhubaneswar, for providing necessary laboratory facilities for the study, the Regional Medical Research Centre, Indian Council of Medical Research, Bhubaneswar, for additional intramural financial help, and the patients who participated in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
[Patnaik M., Pati P., Swain S. N., Mohapatra M. K., Dwibedi B., Kar S. K. and Ranjit M. 2014 Aldosterone synthase C-344T, angiotensin II type 1 receptor A1166C and 11-β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase G534A gene polymorphisms and essential hypertension in the population of Odisha, India. J. Genet. 93, xx–xx]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PATNAIK, M., PATI, P., SWAIN, S.N. et al. Aldosterone synthase C-344T, angiotensin II type 1 receptor A1166C and 11-β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase G534A gene polymorphisms and essential hypertension in the population of Odisha, India. J Genet 93, 799–808 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-014-0464-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-014-0464-y