Abstract
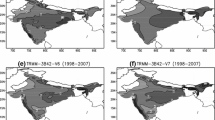
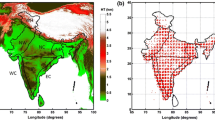
Objective analysis of daily rainfall at the resolution of 1° grid for the Indian monsoon region has been carried out merging dense land rainfall observations and INSAT derived precipitation estimates. This daily analysis, being based on high dense rain gauge observations was found to be very realistic and able to reproduce detailed features of Indian summer monsoon. The inter-comparison with the observations suggests that the new analysis could distinctly capture characteristic features of the summer monsoon such as north-south oriented belt of heavy rainfall along the Western Ghats with sharp gradient of rainfall between the west coast heavy rain region and the rain shadow region to the east, pockets of heavy rainfall along the location of monsoon trough/low, over the east central parts of the country, over north-east India, along the foothills of Himalayas and over the north Bay of Bengal. When this product was used to assess the quality of other available standard climate products (CMAP and ECMWF reanalysis) at the gird resolution of 2.5°, it was found that the orographic heavy rainfall along Western Ghats of India was poorly identified by them. However, the GPCC analysis (gauge only) at the resolution of 1° grid closely discerns the new analysis. This suggests that there is a need for a higher resolution analysis with adequate rain gauge observations to retain important aspects of the summer monsoon over India. The case studies illustrated show that the daily analysis is able to capture large-scale as well as mesoscale features of monsoon precipitation systems. This study with data of two seasons (2001 and 2003) has shown sufficiently promising results for operational application, particularly for the validation of NWP models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler R F, Huffman G J and Co-authors 2003 The version 2 Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) Monthly precipitation analysis (1979-present); J. Hydrometeorology 4 1147–1167.
Arkin P A, Rao A V R K and Kelkar R R 1989 Largescale precipitation and out-going long-wave radiation from INSAT-1B during 1986 southwest Monsoon season; J. Climate 2 619–628.
Cressman G P 1959 An operational objective analysis system; Mon. Wea. Rev. 87 367–374.
Ebert E and Marshall J L 1995 An evaluation of infrared satellite estimates techniques over Australia; Aust. Meteor. Mag. 44 177–190.
India Meteorological Department 2003 Climate Diagnostic Bulletin of India — June, July, August 2003; Rep. No. 88, 89 and 90, National Climate Centre, IMD, Pune.
Janowiak J E 1992 Tropical rainfall: A comparison of satellite derived rainfall estimates with model precipitation forecast, climatologies and observations; Mon. Wea. Rev. 120 448–462.
Janowiak J E and Xie P 1999 CMAPS-OPI: A global satellite rain gauge merge product for real time precipitation monitoring application; J. Climate 12 3335–3342.
Mitra A K, Das Gupta M, Singh S V and Krishnamurti T N 2003 Daily rainfall for the Indian Monsoon region from merged satellite and rain gauge values: Large scale analysis from the real-time data, J. Hydrometeorology 4 769–781.
Rajeevan M, Bhate J, Kale J D and Lal B 2005 Development of a high resolution daily gridded rainfall data for Indian region; Met. Monograph Climatology No. 22/2005, India Meteorological Department, Pune, pp 26.
Richard F and Arkin P 1981 On the relationship between satellite observed cloud cover and precipitation; Mon. Wea. Rev. 109 1081–1093.
Roy Bhowmik S K and Prasad K 2001 Some characteristics of Limited Area Model Precipitation Forecast of Indian Monsoon and evaluation of associated flow features; Meteor. Atmos. Phys. 76 223–236.
Roy Bhowmik S K, Joardar D and Das Ananda K 2005 Radius of rainfall influence over Indian monsoon region; Geofizika 22 131–141.
Roy Bhowmik S K and Sen Roy Soma 2006 Principal Component Analysis to study spatial variability of errors in the INSAT derived quantitative precipitation estimates over Indian monsoon region; Atmosfera 19 255–265.
Rudolf B, Hauschild H, Rueth W and Sucheider U 1994 Terrestrial precipitation analysis: operational method, required density of point measurements; Global precipitation and Climate change (eds) Desbais M and Desahmond F, Springer Verlag, 173–186.
Sen Zekia 1997 Objective Analysis by Cumulative Semivariogram technique and its application in Turkey; J. Appl. Meteor. 36 1712–1724.
Shepard D 1968 A two dimensional interpolation function for irregularly spaced data; Proc. 1968 ACM Nat. Conf. pp 517–524.
Thiebaux H J and Pedder M A 1987 Spatial Objective analysis: with Applications in Atmospheric Science (London: Academic Press) 299 pp.
Xie P and Arkin P A 1996 Analysis of global monthly precipitation using gauge observation, satellite estimates and numerical model precipitation; J. Climate 9 840–858.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy Bhowmik, S.K., Das, A.K. Rainfall analysis for Indian monsoon region using the merged rain gauge observations and satellite estimates: Evaluation of monsoon rainfall features. J Earth Syst Sci 116, 187–198 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0019-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0019-1