Abstract
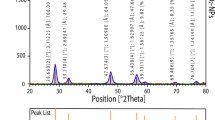
In this study, zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) were synthesized using the extract of Hyssops officinalis L. via green method and confirmed by transmission electron microscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray powder diffraction and Fourier transforms infrared spectroscopy techniques. In the in vivo section, the anti-angiogenesis and anti-inflammatory properties of the NPs were evaluated by the chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay and mouse paw edema test (induced by carrageenan), respectively. In the in vitro section, changes in the expression of angiogenesis genes (VEGF and VEGFR) and inflammatory genes (IL-1B and IL-10) were investigated by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction technique. In order to evaluate the cytotoxicity of ZnO-NPs, 3-5, 4-dimethylthiazol-2-yl) -5, 2-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) test was used on MDA-MB231 breast adenocarcinoma cell line. The results of the CAM assay showed that the ZnO-NPs significantly reduced the number and length of blood vessels, as well as the size and weight of the embryos. Evaluation of mouse paw edema showed that the NPs are able to decrease inflammation. Changes in the expression pattern of VEGF and VEGFR genes in MCF7 cells showed that the NPs have inhibitory effect on the expression of both genes. Expression levels of IL-10 and IL-1B genes also increased and decreased, respectively. The MTT test showed that the NP have the ability to decrease breast cancer cells. In conclusion, our results confirm that the ZnO-NPs synthesized by green method have promising anti-cancer properties.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar MJ, Ahamed M, Kumar S, Khan MM, Ahmad J and Alrokayan SA 2012 Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species. Int. J. Nanomed. 7 845
Bhattacharya R and Mukherjee P 2008 Biological properties of “naked” metal nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60 1289–1306
Choi HS, Ashitate Y, Lee JH, Kim SH, Matsui A, Insin N and Tsuda A 2010 Rapid translocation of nanoparticles from the lung airspaces to the body. Nat. Biotechnol. 28 1300
Folkman J 1971 Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. New Engl. J. Med. 285 1182–1186
Gamallo JPM, Espere G, Carillo DMC, Blanes DN, Abuda FG, Labarda HJ and Jumawan JC 2016 Evaluation of antiangiogenic property of Ocimum basilica ethanolic leaf extract by using duck embryo chorioallantoic membrane (cam) assay and its morphometric analysis. Int. J. Herbal Med. 4 22–26
Gojova A, Guo B, Kota RS, Rutledge JC, Kennedy IM and Barakat AI 2007 Induction of inflammation in vascular endothelial cells by metal oxide nanoparticles: effect of particle composition. Environ. Health Perspect. 115 403
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA 2011 Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 144 646–674
Henriques MG, Silva PM, Martins MA, Flores CA, Cunha FQ, Assreuy-Filho J and Cordeiro RS 1987 Mouse paw edema. A new model for inflammation? Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 20 243–249
Kawata K, Osawa M and Okabe S 2009 In vitro toxicity of silver nanoparticles at noncytotoxic doses to HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43 6046–6051
Kizil S, Hasimi N, Tolan V and Karatas H 2010 Chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of hyssop (Hyssopus officinalis L.) essential oil. Not. Bot. Hort. Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 38 99
Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N and Mitchell RN 2003 Robbins. Basic Pathology (general Pathilogy). 6th ed. (USA: Saundres Company) 147–158
Moro A, Zalacain A, Hurtado de Mendoza J and Carmona M 2011 Effects of agronomic practices on volatile composition of Hyssopus officinalis L. essential oils. Molecules 16 4131–4139
Mukhtar M, Arshad M, Ahmad M, Pomerantz RJ, Wigdahl B and Parveen Z 2008 Antiviral potentials of medicinal plants. Virus Res. 131 111–120
Nagajyothi P, Cha SJ, Yang IJ, Sreekanth T, Kim KJ and Shin HM 2015 Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using Polygala tenuifolia root extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 146 10–17
Narayanan KB and Sakthivel N 2010 Biological synthesis of metal nanoparticles by microbes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 156 1–13
Roy R, Parashar V, Chauhan L, Shanker R, Das M, Tripathi A and Dwivedi PD 2014 Mechanism of uptake of ZnO nanoparticles and inflammatory responses in macrophages require PI3K mediated MAPKs signaling. Toxicol. In Vitro 28 457–467
Ruhrberg C 2001 Endogenous inhibitors of angiogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 114 3215–3216
Senapati S, Syed A, Moeez S, Kumar A and Ahmad A 2012 Intracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles using alga Tetraselmis kochinensis. Mater. Lett. 79 116–118
Tada-Oikawa S, Ichihara G, Suzuki Y, Izuoka K, Wu W, Yamada Y and Ichihara S 2015 Zn (II) released from zinc oxide nano/micro particles suppresses vasculogenesis in human endothelial colony-forming cells. Toxicol. Rep. 2 692–701
Vaseghi Z, Nematollahzadeh A and Tavakoli O 2018 Green methods for the synthesis of metal nanoparticles using biogenic reducing agents: a review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 34 529–559
Wahab R, Siddiqui MA, Saquib Q, Dwivedi S, Ahmad J, Musarrat J and Shin H-S 2014 ZnO nanoparticles induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 cancer cells and their antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 117 267–276
Wei L-H, Kuo M-L, Chen C-A, Chou C-H, Lai K-B, Lee C-N and Hsieh C-Y 2003 Interleukin-6 promotes cervical tumor growth by VEGF-dependent angiogenesis via a STAT3 pathway. Oncogene 22 1517
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua P, Allred EN, Moore DH and Gasparini G 1992 Tumor angiogenesis: A new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. JNCI: J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 84 1875–1887
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by BJ Rao.
Corresponding editor: BJ Rao
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahimi Kalateh Shah Mohammad, G., Homayouni Tabrizi, M., Ardalan, T. et al. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of anti-angiogenesis, anti-inflammatory and cytotoxicity properties. J Biosci 44, 30 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-019-9845-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-019-9845-y