Abstract
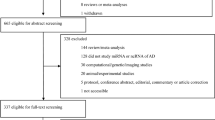
Late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD) is a high-occurrence neurological disorder but the difficulty in identifying precise and early biomarkers has complicated the understanding of the disease and the development of new treatments. In this sense, important knowledge is emerging regarding novel molecular and biological candidates with diagnostic potential, including microRNAs (miRNAs), which have a key role in gene repression. The aim of this systematic review was to define the role of miRNAs’ expression as biomarkers for LOAD both in brain tissues, which could help understand the biology of the disease, and circulating tissues, which could serve as non-invasive markers of the pathology. A systematic search was performed in Web of Science and PubMed using the keywords ((Alzheimer or Alzheimer’s) and (microRNA or microRNAs or miRNA or miRNAs or miR)) until August 2018 to retrieve all articles that presented independent original data evaluating the impact of miRNA expression on the development of LOAD in human population. A total of 90 studies investigating the role of miRNAs’ expression in the development of LOAD were identified. While other widely studied miRNAs such as hsa-miR-146a presented contradictory results among studies, deregulation in brain tissue of seven miRNAs, hsa-miR-16-5p, hsa-miR-34a-5p, hsa-miR-107, hsa-miR-125-5p, hsa-miR-132-3p, hsa-miR-181-3p, and hsa-miR-212-3p, was consistently identified in LOAD patients. Their role in the disease could be mediated through the regulation of key pathways, such as axon guidance, longevity, insulin, and MAPK signaling pathway. However, regarding their role as non-invasive biomarkers of LOAD in fluids, although the limited results available are promising, further studies are required.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan Y, Liu R, Terpstra E, Wang Y, Qiao F, Wang J et al (2016) Dysregulation and diagnostic potential of microRNA in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 49(1):1–12
Disease AAs (2018). Association Alzheimer’s Disease. https://www.alz.org/global/overview.asp. Accessed 2018.
Wattmo C, Wallin AK, Londos E, Minthon L (2011) Predictors of long-term cognitive outcome in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 3(4):23
Ossenkoppele R, Mattsson N, Teunissen CE, Barkhof F, Pijnenburg Y, Scheltens P et al (2015) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and cerebral atrophy in distinct clinical variants of probable Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 36(8):2340–2347
Cui L, Li Y, Ma G, Wang Y, Cai Y, Liu S et al (2014) A functional polymorphism in the promoter region of microRNA-146a is associated with the risk of Alzheimer disease and the rate of cognitive decline in patients. PLoS One 9(2):e89019
Mattsson N, Rosén E, Hansson O, Andreasen N, Parnetti L, Jonsson M et al (2012) Age and diagnostic performance of Alzheimer disease CSF biomarkers. Neurology. 78(7):468–476
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116(2):281–297
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19(1):92–105. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.082701.108
Johanson TM, Skinner JP, Kumar A, Zhan Y, Lew AM, Chong MM (2014) The role of microRNAs in lymphopoiesis. Int J Hematol 100(3):246–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-014-1606-y
Shah SZA, Zhao D, Hussain T, Sabir N, Yang L (2018) Regulation of microRNAs-mediated autophagic flux: a new regulatory avenue for neurodegenerative diseases with focus on prion diseases. Front Aging Neurosci 10:139
Gilad S, Meiri E, Yogev Y, Benjamin S, Lebanony D, Yerushalmi N et al (2008) Serum microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS One 3(9):e3148
Edsbagge M, Andreasson U, Ambarki K, Wikkelsø C, Eklund A, Blennow K et al (2017) Alzheimer’s disease-associated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers do not correlate with CSF volumes or CSF production rate. J Alzheimers Dis 58(3):821–828. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-161257
Web, Science o. Web of Science core collection. https://apps.webofknowledge.com/WOS_GeneralSearch_input.do?product=WOS&SID=F3C19V4ITCwyVekjgNr&search_mode=GeneralSearch. Accessed 2019.
PubMed. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Accessed 2018.
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P, Gretz N (2011) miRWalk--database: prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by “walking” the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform 44(5):839–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2011.05.002
Kamburov A, Wierling C, Lehrach H, Herwig R (2009) ConsensusPathDB--a database for integrating human functional interaction networks. Nucleic Acids Res 37(Database issue):D623–D628. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn698
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):27–30
Croft D, O'Kelly G, Wu G, Haw R, Gillespie M, Matthews L et al (2011) Reactome: a database of reactions, pathways and biological processes. Nucleic Acids Res 39(Database issue):D691–D697. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq1018
Biocarta. http://cgap.nci.nih.gov/Pathways/BioCarta_Pathways Accessed 2019.
Heberle H, Meirelles GV, da Silva FR, Telles GP, Minghim R (2015) InteractiVenn: a web-based tool for the analysis of sets through Venn diagrams. BMC Bioinformatics 16:169. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-015-0611-3
Lam F, Lalansingh CM, Babaran HE, Wang Z, Prokopec SD, Fox NS et al (2016) VennDiagramWeb: a web application for the generation of highly customizable Venn and Euler diagrams. BMC Bioinformatics. 17(1):401. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-016-1281-5
Akhter R, Shao Y, Shaw M, Formica S, Khrestian M, Leverenz JB et al (2018) Regulation of ADAM10 by miR-140-5p and potential relevance for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 63:110–119
Annese A, Manzari C, Lionetti C, Picardi E, Horner DS, Chiara M et al (2018) Whole transcriptome profiling of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease patients provides insights into the molecular changes involved in the disease. Sci Rep 8(1):4282–018-22701-2
Kumar S, Reddy PH (2018) MicroRNA-455-3p as a potential biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: an update. Front Aging Neurosci 10:41
Pogue AI, Lukiw WJ (2018) Up-regulated pro-inflammatory microRNAs (miRNAs) in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Cell Mol Neurobiol 38(5):1021–1031
Zumkehr J, Rodriguez-Ortiz CJ, Medeiros R, Kitazawa M (2018) Inflammatory cytokine, IL-1beta, regulates glial glutamate transporter via microRNA-181a in vitro. J Alzheimers Dis 63(3):965–975
Hara N, Kikuchi M, Miyashita A, Hatsuta H, Saito Y, Kasuga K et al (2017) Serum microRNA miR-501-3p as a potential biomarker related to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun 5(1):10-017-0414-z
Kumar S, Vijayan M, Reddy PH (2017) MicroRNA-455-3p as a potential peripheral biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 26(19):3808–3822
Ma X, Liu L, Meng J (2017) MicroRNA-125b promotes neurons cell apoptosis and tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 661:57–62
Moncini S, Lunghi M, Valmadre A, Grasso M, Vescovo VD, Riva P et al (2017) The miR-15/107 family of microRNA genes regulates CDK5R1/p35 with implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Mol Neurobiol 54(6):4329–4342
Pichler S, Gu W, Hartl D, Gasparoni G, Leidinger P, Keller A et al (2017) The miRNome of Alzheimer’s disease: consistent downregulation of the miR-132/212 cluster. Neurobiol Aging 50(167):e1–e10
Jesko H, Wilkaniec A, Cieslik M, Hilgier W, Gassowska M, Lukiw WJ et al (2016) Altered arginine metabolism in cells transfected with human wild-type beta amyloid precursor protein (beta APP). Curr Alzheimer Res 13(9):1030–1039
Moon J, Lee ST, Kong IG, Byun JI, Sunwoo JS, Shin JW et al (2016) Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease from elevated olfactory mucosal miR-206 level. Sci Rep 6:20364
Zhao Y, Alexandrov PN, Jaber V, Lukiw WJ (2016) Deficiency in the ubiquitin conjugating enzyme UBE2A in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is linked to deficits in a natural circular miRNA-7 sponge (circRNA; ciRS-7). Genes. 7:12. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7120116
Zhu QB, Unmehopa U, Bossers K, Hu YT, Verwer R, Balesar R et al (2016) MicroRNA-132 and early growth response-1 in nucleus basalis of Meynert during the course of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 139(Pt 3):908–921
Lei X, Lei L, Zhang Z, Cheng Y (2015) Downregulated miR-29c correlates with increased BACE1 expression in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(2):1565–1574
Santa-Maria I, Alaniz ME, Renwick N, Cela C, Fulga TA, Vactor DV et al (2015) Dysregulation of microRNA-219 promotes neurodegeneration through post-transcriptional regulation of tau. J Clin Invest 125(2):681–686
Smith PY, Hernandez-Rapp J, Jolivette F, Lecours C, Bisht K, Goupil C et al (2015) miR-132/212 deficiency impairs tau metabolism and promotes pathological aggregation in vivo. Hum Mol Genet 24(23):6721–6735
Weinberg RB, Mufson EJ, Counts SE (2015) Evidence for a neuroprotective microRNA pathway in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Front Neurosci 9:430
Banzhaf-Strathmann J, Benito E, May S, Arzberger T, Tahirovic S, Kretzschmar H et al (2014) MicroRNA-125b induces tau hyperphosphorylation and cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO J 33(15):1667–1680
Long JM, Ray B, Lahiri DK (2014) MicroRNA-339-5p down-regulates protein expression of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) in human primary brain cultures and is reduced in brain tissue specimens of Alzheimer disease subjects. J Biol Chem 289(8):5184–5198
Muller M, Kuiperij HB, Claassen JA, Kusters B, Verbeek MM (2014) MicroRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease: differential expression in hippocampus and cell-free cerebrospinal fluid. Neurobiol Aging 35(1):152–158
Absalon S, Kochanek DM, Raghavan V, Krichevsky AM (2013) MiR-26b, upregulated in Alzheimer’s disease, activates cell cycle entry, tau-phosphorylation, and apoptosis in postmitotic neurons. J Neurosci 33(37):14645–14659
Hebert SS, Wang W-X, Zhu Q, Nelson PT (2013) A study of small RNAs from cerebral neocortex of pathology-verified Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, hippocampal sclerosis, frontotemporal lobar dementia, and non-demented human controls. J Alzheimers Dis 35(2):335–348
Lau P, Bossers K, Janky RS, Salta E, Frigerio CS, Barbash S et al (2013) Alteration of the microRNA network during the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol Med 5(10):1613–1634
Wong HK, Veremeyko T, Patel N, Lemere CA, Walsh DM, Esau C et al (2013) De-repression of FOXO3a death axis by microRNA-132 and -212 causes neuronal apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 22(15):3077–3092. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt164
Yan H, Xu T, Zhao H, Lee KC, Wang HY, Zhang Y (2013) Isoflurane increases neuronal cell death vulnerability by downregulating miR-214. PLoS One 8(2):e55276
Zhao Y, Bhattacharjee S, Jones BM, Dua P, Alexandrov PN, Hill JM et al (2013) Regulation of TREM2 expression by an NF-small ka, CyrillicB-sensitive miRNA-34a. Neuroreport. 24(6):318–323
Alexandrov PN, Dua P, Hill JM, Bhattacharjee S, Zhao Y, Lukiw WJ (2012) MicroRNA (miRNA) speciation in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and extracellular fluid (ECF). Int J Biochem Mol Biol 3(4):365–373
Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, Kim JH, Huh JY, Yoon H et al (2012) miR-206 regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Alzheimer disease model. Ann Neurol 72(2):269–277
Lukiw WJ, Alexandrov PN, Zhao Y, Hill JM, Bhattacharjee S (2012) Spreading of Alzheimer’s disease inflammatory signaling through soluble micro-RNA. Neuroreport. 23(10):621–626
Agostini M, Tucci P, Killick R, Candi E, Sayan BS, di Val Cervo PR et al (2011) Neuronal differentiation by TAp73 is mediated by microRNA-34a regulation of synaptic protein targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(52):21093–21098
Culpan D, Kehoe PG, Love S (2011) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and miRNA expression in frontal and temporal neocortex in Alzheimer’s disease and the effect of TNF-alpha on miRNA expression in vitro. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet 2(2):156–162
Geekiyanage H, Chan C (2011) MicroRNA-137/181c regulates serine palmitoyltransferase and in turn amyloid beta, novel targets in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 31(41):14820–14830
Zovoilis A, Agbemenyah HY, Agis-Balboa RC, Stilling RM, Edbauer D, Rao P et al (2011) microRNA-34c is a novel target to treat dementias. EMBO J 30(20):4299–4308
Cui JG, Li YY, Zhao Y, Bhattacharjee S, Lukiw WJ (2010) Differential regulation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1) and IRAK-2 by microRNA-146a and NF-kappaB in stressed human astroglial cells and in Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 285(50):38951–38960
Faghihi MA, Zhang M, Huang J, Modarresi F, der Brug MPV, Nalls MA et al (2010) Evidence for natural antisense transcript-mediated inhibition of microRNA function. Genome Biol 11(5) R56–2010-11-5-r56
Nunez-Iglesias J, Liu CC, Morgan TE, Finch CE, Zhou XJ (2010) Joint genome-wide profiling of miRNA and mRNA expression in Alzheimer’s disease cortex reveals altered miRNA regulation. PLoS One 5(2):e8898
Sethi P, Lukiw WJ (2009) Micro-RNA abundance and stability in human brain: specific alterations in Alzheimer’s disease temporal lobe neocortex. Neurosci Lett 459(2):100–104
Cogswell JP, Ward J, Taylor IA, Waters M, Shi Y, Cannon B et al (2008) Identification of miRNA changes in Alzheimer’s disease brain and CSF yields putative biomarkers and insights into disease pathways. J Alzheimers Dis 14(1):27–41
Lukiw WJ, Zhao Y, Cui JG (2008) An NF-kappaB-sensitive micro RNA-146a-mediated inflammatory circuit in Alzheimer disease and in stressed human brain cells. J Biol Chem 283(46):31315–31322
Wang WX, Rajeev BW, Stromberg AJ, Ren N, Tang G, Huang Q et al (2008) The expression of microRNA miR-107 decreases early in Alzheimer’s disease and may accelerate disease progression through regulation of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1. J Neurosci 28(5):1213–1223
Lukiw WJ (2007) Micro-RNA speciation in fetal, adult and Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus. Neuroreport. 18(3):297–300
Geekiyanage H, Jicha GA, Nelson PT, Chan C (2012) Blood serum miRNA: non-invasive biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 235(2):491–496
Denk J, Oberhauser F, Kornhuber J, Wiltfang J, Fassbender K, Schroeter ML et al (2018) Specific serum and CSF microRNA profiles distinguish sporadic behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia compared with Alzheimer patients and cognitively healthy controls. PLoS One 13(5):e0197329
Derkow K, Rossling R, Schipke C, Kruger C, Bauer J, Fahling M et al (2018) Distinct expression of the neurotoxic microRNA family let-7 in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 13(7):e0200602
Dias IHK, Brown CL, Shabir K, Polidori MC, Griffiths HR (2018) miRNA 933 expression by endothelial cells is increased by 27-hydroxycholesterol and is more prevalent in plasma from dementia patients. J Alzheimers Dis 64(3):1009–1017
Manzine PR, Pelucchi S, Horst MA, Vale FAC, Pavarini SCI, Audano M et al (2018) MicroRNA 221 targets ADAM10 mRNA and is downregulated in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 61(1):113–123
McKeever PM, Schneider R, Taghdiri F, Weichert A, Multani N, Brown RA et al (2018) MicroRNA expression levels are altered in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with young-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol
Piscopo P, Grasso M, Puopolo M, D'Acunto E, Talarico G, Crestini A et al (2018) Circulating miR-127-3p as a potential biomarker for differential diagnosis in frontotemporal dementia. J Alzheimers Dis
Yang TT, Liu CG, Gao SC, Zhang Y, Wang PC (2018) The serum exosome derived microRNA-135a, −193b, and −384 were potential Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Biomed Environ Sci 31(2):87–96
Cosin-Tomas M, Antonell A, Llado A, Alcolea D, Fortea J, Ezquerra M et al (2017) Plasma miR-34a-5p and miR-545-3p as early biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: potential and limitations. Mol Neurobiol 54(7):5550–5562
Dangla-Valls A, Molinuevo JL, Altirriba J, Sanchez-Valle R, Alcolea D, Fortea J et al (2017) CSF microRNA profiling in Alzheimer’s disease: a screening and validation study. Mol Neurobiol 54(9):6647–6654
Guo R, Fan G, Zhang J, Wu C, Du Y, Ye H et al (2017) A 9-microRNA signature in serum serves as a noninvasive biomarker in early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 60(4):1365–1377
Lusardi TA, Phillips JI, Wiedrick JT, Harrington CA, Lind B, Lapidus JA et al (2017) MicroRNAs in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 55(3):1223–1233
Nagaraj S, Laskowska-Kaszub K, Debski KJ, Wojsiat J, Dabrowski M, Gabryelewicz T et al (2017) Profile of 6 microRNA in blood plasma distinguish early stage Alzheimer’s disease patients from non-demented subjects. Oncotarget. 8(10):16122–16143
Riancho J, Vazquez-Higuera JL, Pozueta A, Lage C, Kazimierczak M, Bravo M et al (2017) MicroRNA profile in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: analysis of miR-9-5p and miR-598 in raw and exosome enriched cerebrospinal fluid samples. J Alzheimers Dis 57(2):483–491
Wu Y, Xu J, Cheng J, Jiao D, Zhou C, Dai Y et al (2017) Lower serum levels of miR-29c-3p and miR-19b-3p as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Tohoku J Exp Med 242(2):129–136
Jia LH, Liu YN (2016) Downregulated serum miR-223 servers as biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Biochem Funct 34(4):233–237
Keller A, Backes C, Haas J, Leidinger P, Maetzler W, Deuschle C et al (2016) Validating Alzheimer’s disease micro RNAs using next-generation sequencing. Alzheimers Dement 12(5):565–576
Muller M, Jakel L, Bruinsma IB, Claassen JA, Kuiperij HB, Verbeek MM (2016) MicroRNA-29a is a candidate biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease in cell-free cerebrospinal fluid. Mol Neurobiol 53(5):2894–2899
Muller M, Kuiperij HB, Versleijen AA, Chiasserini D, Farotti L, Baschieri F et al (2016) Validation of microRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers for different forms of dementia in a multicenter study. J Alzheimers Dis 52(4):1321–1333
Ragusa M, Bosco P, Tamburello L, Barbagallo C, Condorelli AG, Tornitore M et al (2016) miRNAs plasma profiles in vascular dementia: biomolecular data and biomedical implications. Front Cell Neurosci 10:51
Ren RJ, Zhang YF, Dammer EB, Zhou Y, Wang LL, Liu XH et al (2016) Peripheral blood microRNA expression profiles in Alzheimer’s disease: screening, validation, association with clinical phenotype and implications for molecular mechanism. Mol Neurobiol 53(8):5772–5781
Xing H, Guo S, Zhang Y, Zheng Z, Wang H (2016) Upregulation of microRNA-206 enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and release of amyloid-beta by targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 in microglia. Mol Med Rep 14(2):1357–1364
Yilmaz SG, Erdal ME, Ozge AA, Sungur MA (2016) Can peripheral microRNA expression data serve as epigenomic (upstream) biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease? OMICS 20(8):456–461
Zhang Y, Liu C, Wang J, Li Q, Ping H, Gao S et al (2016) MiR-299-5p regulates apoptosis through autophagy in neurons and ameliorates cognitive capacity in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. Sci Rep 6:24566
Zhang Y, Xing H, Guo S, Zheng Z, Wang H, Xu D (2016) MicroRNA-135b has a neuroprotective role via targeting of beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1. Exp Ther Med 12(2):809–814
Cheng L, Doecke JD, Sharples RA, Villemagne VL, Fowler CJ, Rembach A et al (2015) Prognostic serum miRNA biomarkers associated with Alzheimer’s disease shows concordance with neuropsychological and neuroimaging assessment. Mol Psychiatry 20(10):1188–1196
Denk J, Boelmans K, Siegismund C, Lassner D, Arlt S, Jahn H (2015) MicroRNA profiling of CSF reveals potential biomarkers to detect Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 10(5):e0126423
Dong H, Li J, Huang L, Chen X, Li D, Wang T et al (2015) Serum microRNA profiles serve as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Dis Markers 2015:625659
Guedes JR, Santana I, Cunha C, Duro D, Almeida MR, Cardoso AM et al (2015) MicroRNA deregulation and chemotaxis and phagocytosis impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement (Amst) 3:7–17
Gui Y, Liu H, Zhang L, Lv W, Hu X (2015) Altered microRNA profiles in cerebrospinal fluid exosome in Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease. Oncotarget. 6(35):37043–37053
van Harten AC, Mulders J, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM, Oudejans CB (2015) Differential expression of microRNA in cerebrospinal fluid as a potential novel biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 47(1):243–252
Wang T, Chen K, Li H, Dong S, Su N, Liu Y et al (2015) The feasibility of utilizing plasma MiRNA107 and BACE1 messenger RNA gene expression for clinical diagnosis of amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J Clin Psychiatry 76(2):135–141
Yang G, Song Y, Zhou X, Deng Y, Liu T, Weng G et al (2015) MicroRNA-29c targets beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 and has a neuroprotective role in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep 12(2):3081–3088
Zhu Y, Li C, Sun A, Wang Y, Zhou S (2015) Quantification of microRNA-210 in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Ther Med 9(3):1013–1017
Bhatnagar S, Chertkow H, Schipper HM, Yuan Z, Shetty V, Jenkins S et al (2014) Increased microRNA-34c abundance in Alzheimer’s disease circulating blood plasma. Front Mol Neurosci 7:2
Burgos K, Malenica I, Metpally R, Courtright A, Rakela B, Beach T et al (2014) Profiles of extracellular miRNA in cerebrospinal fluid and serum from patients with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases correlate with disease status and features of pathology. PLoS One 9(5):e94839
Kiko T, Nakagawa K, Tsuduki T, Furukawa K, Arai H, Miyazawa T (2014) MicroRNAs in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid as potential markers for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 39(2):253–259
geng Liu C, ling Wang J, Li L, xiang Xue L, qi Zhang Y, chang Wang P (2014) MicroRNA-135a and-200b, potential biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease, regulate beta secretase and amyloid precursor protein. Brain Res 1583:55–64
Tan L, Yu JT, Liu QY, Tan MS, Zhang W, Hu N et al (2014) Circulating miR-125b as a biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 336(1–2):52–56
Tan L, Yu JT, Tan MS, Liu QY, Wang HF, Zhang W et al (2014) Genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling identifies serum biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 40(4):1017–1027
Tiribuzi R, Crispoltoni L, Porcellati S, Lullo MD, Florenzano F, Pirro M et al (2014) miR128 up-regulation correlates with impaired amyloid beta(1-42) degradation in monocytes from patients with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 35(2):345–356
Bekris LM, Lutz F, Montine TJ, Yu CE, Tsuang D, Peskind ER et al (2013) MicroRNA in Alzheimer’s disease: an exploratory study in brain, cerebrospinal fluid and plasma. Biomarkers. 18(5):455–466. https://doi.org/10.3109/1354750X.2013.814073
Frigerio CS, Lau P, Salta E, Tournoy J, Bossers K, Vandenberghe R et al (2013) Reduced expression of hsa-miR-27a-3p in CSF of patients with Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 81(24):2103–2106
Kumar P, Dezso Z, MacKenzie C, Oestreicher J, Agoulnik S, Byrne M et al (2013) Circulating miRNA biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 8(7):e69807
Leidinger P, Backes C, Deutscher S, Schmitt K, Mueller SC, Frese K et al (2013) A blood based 12-miRNA signature of Alzheimer disease patients. Genome Biol 14(7):R78
Lehmann SM, Kruger C, Park B, Derkow K, Rosenberger K, Baumgart J et al (2012) An unconventional role for miRNA: let-7 activates toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci 15(6):827–835
Villa C, Fenoglio C, Riz MD, Clerici F, Marcone A, Benussi L et al (2011) Role of hnRNP-A1 and miR-590-3p in neuronal death: genetics and expression analysis in patients with Alzheimer disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Rejuvenation Res 14(3):275–281
Schipper HM, Maes OC, Chertkow HM, Wang E (2007) MicroRNA expression in Alzheimer blood mononuclear cells. Gene Regul Syst Biol 1:263–274
Sheinerman KS, Tsivinsky VG, Abdullah L, Crawford F, Umansky SR (2013) Plasma microRNA biomarkers for detection of mild cognitive impairment: biomarker validation study. Aging (Albany NY) 5(12):925–938. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100624
Swarbrick S, Wragg N, Ghosh S, Stolzing A (2019) Systematic review of miRNA as biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1500-y
Fransquet PD, Ryan J (2018) Micro RNA as a potential blood-based epigenetic biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Biochem 58:5–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.05.020
Dickson JR, Kruse C, Montagna DR, Finsen B, Wolfe MS (2013) Alternative polyadenylation and miR-34 family members regulate tau expression. J Neurochem 127(6):739–749. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12437
Pogue AI, Cui JG, Li YY, Zhao Y, Culicchia F, Lukiw WJ (2010) Micro RNA-125b (miRNA-125b) function in astrogliosis and glial cell proliferation. Neurosci Lett 476(1):18–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.03.054
Basavaraju M, de Lencastre A (2016) Alzheimer’s disease: presence and role of microRNAs. Biomol Concepts 7(4):241–252. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmc-2016-0014
Lukiw WJ, Andreeva TV, Grigorenko AP, Rogaev EI (2012) Studying micro RNA function and dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Genet 3:327. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2012.00327
Selkoe DJ (2008) Biochemistry and molecular biology of amyloid beta-protein and the mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease. Handb Clin Neurol 89:245–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0072-9752(07)01223-7
Goedert M (2004) Tau protein and neurodegeneration. Semin Cell Dev Biol 15(1):45–49
Slota JA, Booth SA (2019) MicroRNAs in neuroinflammation: implications in disease pathogenesis, biomarker discovery and therapeutic applications. Noncoding RNA 5:2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5020035
Gaudet AD, Fonken LK, Watkins LR, Nelson RJ, Popovich PG (2018) MicroRNAs: roles in regulating neuroinflammation. Neuroscientist. 24(3):221–245. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858417721150
Nelson PT, Alafuzoff I, Bigio EH, Bouras C, Braak H, Cairns NJ et al (2012) Correlation of Alzheimer disease neuropathologic changes with cognitive status: a review of the literature. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 71(5):362–381. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e31825018f7
Spittaels K, Van den Haute C, Van Dorpe J, Geerts H, Mercken M, Bruynseels K et al (2000) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta phosphorylates protein tau and rescues the axonopathy in the central nervous system of human four-repeat tau transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 275(52):41340–41349. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M006219200
Shal B, Ding W, Ali H, Kim YS, Khan S (2018) Anti-neuroinflammatory potential of natural products in attenuation of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Pharmacol 9:548. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00548
Piedrahita D, Hernández I, López-Tobón A, Fedorov D, Obara B, Manjunath BS et al (2010) Silencing of CDK5 reduces neurofibrillary tangles in transgenic Alzheimer's mice. J Neurosci 30(42):13966–13976
Masliah E (1995) Mechanisms of synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Histol Histopathol 10(2):509–519
Masliah E, Mallory M, Hansen L, DeTeresa R, Terry RD (1993) Quantitative synaptic alterations in the human neocortex during normal aging. Neurology. 43(1):192–197
Nunomura A, Castellani RJ, Zhu X, Moreira PI, Perry G, Smith MA (2006) Involvement of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65(7):631–641
Arriagada PV, Growdon JH, Hedley-Whyte ET, Hyman BT (1992) Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 42(3 Pt 1):631–639
Stanley M, Macauley SL, Holtzman DM (2016) Changes in insulin and insulin signaling in Alzheimer’s disease: cause or consequence? J Exp Med 213(8):1375–1385. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20160493
de la Monte SM, Tong M, Daiello LA, Ott BR (2019) Early-stage Alzheimer’s disease is associated with simultaneous systemic and central nervous system dysregulation of insulin-linked metabolic pathways. J Alzheimers Dis. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-180906
Talbot K, Wang HY, Kazi H, Han LY, Bakshi KP, Stucky A et al (2012) Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease patients is associated with IGF-1 resistance, IRS-1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline. J Clin Invest 122(4):1316–1338. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI59903
de la Monte SM (2012) Contributions of brain insulin resistance and deficiency in amyloid-related neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Drugs. 72(1):49–66. https://doi.org/10.2165/11597760-000000000-00000
Rivera EJ, Goldin A, Fulmer N, Tavares R, Wands JR, de la Monte SM (2005) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and function deteriorate with progression of Alzheimer’s disease: link to brain reductions in acetylcholine. J Alzheimers Dis 8(3):247–268
Schubert M, Gautam D, Surjo D, Ueki K, Baudler S, Schubert D et al (2004) Role for neuronal insulin resistance in neurodegenerative diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(9):3100–3105. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308724101
Craft S (2007) Insulin resistance and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: potential mechanisms and implications for treatment. Curr Alzheimer Res 4(2):147–152
de la Monte SM (2014) Type 3 diabetes is sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: mini-review. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 24(12):1954–1960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2014.06.008
Luchsinger JA (2010) Type 2 diabetes, related conditions, in relation and dementia: an opportunity for prevention? J Alzheimers Dis 20(3):723–736. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2010-091687
Newsholme P, Morgan D, Rebelato E, Oliveira-Emilio HC, Procopio J, Curi R et al (2009) Insights into the critical role of NADPH oxidase(s) in the normal and dysregulated pancreatic beta cell. Diabetologia. 52(12):2489–2498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-009-1536-z
Ho L, Qin W, Pompl PN, Xiang Z, Wang J, Zhao Z et al (2004) Diet-induced insulin resistance promotes amyloidosis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J 18(7):902–904. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.03-0978fje
Kitazawa M, Cheng D, Tsukamoto MR, Koike MA, Wes PD, Vasilevko V et al (2011) Blocking IL-1 signaling rescues cognition, attenuates tau pathology, and restores neuronal β-catenin pathway function in an Alzheimer’s disease model. J Immunol 187(12):6539–6549. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1100620
Kempuraj D, Thangavel R, Natteru PA, Selvakumar GP, Saeed D, Zahoor H et al (2016) Neuroinflammation induces neurodegeneration. J Neurol Neurosurg Spine 1:1
Kirouac L, Rajic AJ, Cribbs DH, Padmanabhan J (2017) Activation of Ras-ERK signaling and GSK-3 by amyloid precursor protein and amyloid beta facilitates neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. eNeuro. 4(2). https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0149-16.2017
Bassani TB, Vital MA, Rauh LK (2015) Neuroinflammation in the pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease and therapeutic evidence of anti-inflammatory drugs. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 73(7):616–623. https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282X20150057
Longpré F, Garneau P, Christen Y, Ramassamy C (2006) Protection by EGb 761 against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity: involvement of NF-kappaB, SIRT1, and MAPKs pathways and inhibition of amyloid fibril formation. Free Radic Biol Med 41(12):1781–1794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.08.015
O’Neill LA, Kaltschmidt C (1997) NF-kappa B: a crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. Trends Neurosci 20(6):252–258
Marchegiani F, Matacchione G, Ramini D, Marcheselli F, Recchioni R, Casoli T et al (2019) Diagnostic performance of new and classic CSF biomarkers in age-related dementias. Aging (Albany NY) 11(8):2420–2429. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101925
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82(4):239–259
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12(3):189–198
Nelson-Gray RO (1991) DSM-IV: empirical guidelines from psychometrics. J Abnorm Psychol 100(3):308–315
Kopkova A, Sana J, Fadrus P, Slaby O (2018) Cerebrospinal fluid microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers in brain tumors. Clin Chem Lab Med 56(6):869–879. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2017-0958
Funding
This study was funded by the Basque Government (IT989-16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Soraya Herrera-Espejo and Borja Santos-Zorrozua share first authorship
Elixabet Lopez-Lopez and África Garcia-Orad share last authorship
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 856 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(XLSX 41.4 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(XLSX 15.6 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
(XLSX 34.9 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
(XLSX 63.1 kb)
Supplementary Table 5
(XLSX 80 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrera-Espejo, S., Santos-Zorrozua, B., Álvarez-González, P. et al. A Systematic Review of MicroRNA Expression as Biomarker of Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 56, 8376–8391 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01676-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01676-9