Abstract
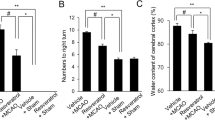
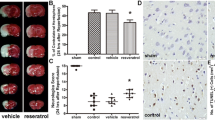
Resveratrol has neuroprotective effects for ischemic cerebral stroke. However, its neuroprotective mechanism for stroke is less well understood. Beneficial actions of the activated Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway in stroke, such as improving neurological function, promoting neurogenesis, anti-oxidative, anti-apoptotic, and pro-angiogenic effects, have been noted, but relatively little is known about the role of Shh signaling in resveratrol-reduced cerebral ischemic injury after stroke. The present study tests whether the Shh pathway mediates resveratrol to decrease cerebral ischemic injury and improve neurological function after stroke. We observed that resveratrol pretreatment significantly improved neurological function, decreased infarct volume, enhanced vitality, and reduced apoptosis of neurons in vivo and vitro after stroke. Meanwhile, expression levels of Shh, Ptc-1, Smo, and Gli-1 mRNAs were significantly upregulated and Gli-1 was relocated to the nucleus. Intriguingly, in vivo and in vitro inhibition of the Shh signaling pathway with cyclopamine, a Smo inhibitor, completely reversed the above effects of resveratrol. These results suggest that decreased cerebral ischemic injury and improved neurological function by resveratrol may be mediated by the Shh signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walle T (2011) Bioavailability of resveratrol. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1215:9–15
Baur JA, Sinclair DA (2006) Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:493–506
Lin HY, Tang HY, Davis FB, Davis PJ (2011) Resveratrol and apoptosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1215:79–88
Sinha K, Chaudhary G, Gupta YK (2002) Protective effect of resveratrol against oxidative stress in middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke in rats. Life Sci 71:655–665
Jin F, Wu Q, Lu YF, Gong QH, Shi JS (2008) Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol on 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 600:78–82
Li F, Gong Q, Dong H, Shi J (2012) Resveratrol, a neuroprotective supplement for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 18:27–33
Ren JW, Fan CC, Chen N, Huang J, Yang Q (2011) Resveratrol pretreatment attenuates cerebral ischemic injury by upregulating expression of transcription factor Nrf2 and HO-1 in rats. Neurochem Res 36:2352–2362
Washington SI, Byrd NA, Abu-Issa R, Goddeeris MM, Anderson R, Morris J et al (2005) Sonic hedgehog is required for cardiac outflow tract and neural crest cell development. Dev Biol 283:357–372
Palma V, Lim DA, Dahmane N, Sánchez P, Brionne TC, Herzberg CD et al (2005) Sonic hedgehog controls stem cell behavior in the postnatal and adult brain. Development 132:335–344
Choy SW, Cheng SH (2012) Hedgehog signaling. Vitam Horm 88:1–23
Zhang L, Chopp M, Meier DH, Winter S, Wang L, Szalad A et al (2013) Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway mediates cerebrolysin-improved neurological function after stroke. Stroke 44:1965–1972
Ding X, Li Y, Liu Z, Zhang J, Cui Y, Chen X et al (2013) The sonic hedgehog pathway mediates brain plasticity and subsequent functional recovery after bone marrow stromal cell treatment of stroke in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33(7):1015–24
Jin Y, Raviv N, Barnett A, Bambakidis NC, Filichia E, Luo Y (2015) The shh signaling pathway is upregulated in multiple cell types in cortical ischemia and influences the outcome of stroke in an animal model. PLoS One 10(4):e0124657
Chechneva OV, Mayrhofer F, Daugherty DJ, Krishnamurty RG, Bannerman P, Pleasure DE et al (2014) A Smoothened receptor agonist is neuroprotective and promotes regeneration after ischemic brain injury. Cell Death Dis 5:e1481
Huang SS, Cheng H, Tang CM, Nien MW, Huang YS, Lee IH et al (2013) Anti-oxidative, anti-apoptotic, and pro-angiogenic effects mediate functional improvement by sonic hedgehog against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp Neurol Sep 247:680–8
Cheng W, Yu P, Wang L, Shen C, Song X, Chen J et al (2015) Sonic hedgehog signaling mediates resveratrol to increase proliferation of neural stem cells after oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation injury in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem 35(5):2019–32
Huang JG, Shen CB, Wu WB, Ren JW, Xu L, Liu S et al (2014) Primary cilia mediate sonic hedgehog signaling to regulate neuronal-like differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells for resveratrol induction in vitro. J Neurosci Res 92:587–596
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Redmond L, Kashani AH, Ghosh A (2002) Calcium regulation of dendritic growth via CaM kinase IV and CREB-mediated transcription. Neuron 34:999–1010
Chen T, Liu W, Chao X, Qu Y, Zhang L, Luo P et al (2011) Neuroprotective effect of osthole against oxygen and glucose deprivation in rat cortical neurons: involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Neurosci 183:203–11
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Daves RL (1986) Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17:472–476
Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, Zhang Z, Lu D, Lu M et al (2001) Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 32:1005–1011
Tatlisumak T, Carano RA, Takano K, Opgenorth TJ, Sotak CH, Fisher M (1998) A novel endothelin antagonist, A-127722, attenuates ischemic lesion size in rats with temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion: a diffusion and perfusion MRI study. Stroke 29:850–857
Perez-Pinzon MA, Young JI, Neumann JT, Thompson JW, Camarena V, Koronowski KB et al (2015) Resveratrol preconditioning induces a novel extended window of ischemic tolerance in the mouse brain. Stroke 46(8):2293–8
Narayanan SV, Dave KR, Saul I, Perez-Pinzon MA (2015) Resveratrol preconditioning protects against cerebral ischemic injury via nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2. Stroke Jun 46(6):1626–32
Della-Morte D, Dave KR, DeFazio RA, Bao YC, Raval AP, Perez-Pinzon MA (2009) Resveratrol pretreatment protects rat brain from cerebral ischemic damage via a sirtuin 1-uncoupling protein 2 pathway. Neuroscience 159:993–1002
Sakata Y, Zhuang H, Kwansa H, Koehler RC, Doré S (2010) Resveratrol protects against experimental stroke: putative neuroprotective role of heme oxygenase 1. Exp Neurol Jul 224(1):325–9
Dong W, Li N, Gao D, Zhen H, Zhang X, Li F (2008) Resveratrol attenuates ischemic brain damage in the delayed phase after stroke and induces messenger RNA and protein express for angiogenic factors. J Vasc Surg 48:709–714
Tsai SK, Hung LM, Fu YT, Cheng H, Nien MW, Liu HY et al (2007) Resveratrol neuroprotective effects during focal cerebral ischemia injury via nitric oxide mechanism in rats. J Vasc Surg 46(2):346–53
Shin JA, Lee H, Lim YK, Koh Y, Choi JH, Park EM (2010) Therapeutic effects of resveratrol during acute periods following experimental ischemic stroke. J Neuroimmunol 227(1–2):93–100
Hermann DM, Zechariah A, Kaltwasser B, Bosche B, Caglayan AB, Kilic E et al (2015) Sustained neurological recovery induced by resveratrol is associated with angioneurogenesis rather than neuroprotection after focal cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis Nov 83:16–25
Lin SL, Chang SJ, Ying SY (2006) Transcriptional control of Shh/Ptc1 signaling in embryonic development. Gene 367:56–65
Ji H, Miao J, Zhang X, Du Y, Liu H, Li S et al (2012) Inhibition of sonic hedgehog signaling aggravates brain damage associated with the down-regulation of Gli1, Ptch1 and SOD1 expression in acute ischemic stroke. Neurosci Lett 506:1–6
Amankulor NM, Hambardzumyan D, Pyonteck SM, Becher OJ, Joyce JA, Holland EC (2009) Sonic hedgehog pathway activation is induced by acute brain injury and regulated by injury-related inflammation. J Neurosci 29:10299–10308
Vazin T, Ball KA, Lu H, Park H, Ataeijannati Y, Head-Gordon T et al (2014) Efficient derivation of cortical glutamatergic neurons from human pluripotent stem cells: a model system to study neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis Feb 62:62–72
Wang Y, Imitola J, Rasmussen S, O’Connor KC, Khoury SJ (2008) Paradoxical dysregulation of the neural stem cell pathway sonic hedgehog-Gli1 in autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol Oct 64(4):417–27
Zhang Y, Dong W, Guo S, Zhao S, He S, Zhang L et al (2014) Lentivirus-mediated delivery of sonic hedgehog into the striatum stimulates neuroregeneration in a rat model of Parkinson disease. Neurol Sci Dec 35(12):1931–40
Gulino R, Gulisano M (2012) Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and sonic hedgehog in the spinal cord plasticity after neurotoxic partial removal of lumbar motoneurons. Neurosci Res Jul 73(3):238–47
Peterson R, Turnbull J (2012) Sonic hedgehog is cytoprotective against oxidative challenge in a cellular model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci May 47(1):31–41
Wang LM, Wang YJ, Cui M, Luo WJ, Wang XJ, Barber PA et al (2013) A dietary polyphenol resveratrol acts to provide neuroprotection in recurrent stroke models by regulating AMPK and SIRT1 signaling, thereby reducing energy requirements during ischemia. Eur J Neurosci 37:1669–81
Lin Y, Chen F, Zhang J, Wang T, Wei X, Wu J et al (2013) Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol on ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through TRPC6/CREB pathways. J Mol Neurosci 50(3):504–13
Huang T, Gao D, Jiang X, Hu S, Zhang L, Fei Z (2014) Resveratrol inhibits oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced MMP-3 expression and cell apoptosis in primary cortical cells via the NF-κB pathway. Mol Med Rep 10(2):1065–71
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81071119) and the National Key Clinical Specialties Construction Program of China for Neurology (The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University No. [2014]27).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Pingping Yu and Li Wang contributed equally to this work and they are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, P., Wang, L., Tang, F. et al. Resveratrol Pretreatment Decreases Ischemic Injury and Improves Neurological Function Via Sonic Hedgehog Signaling After Stroke in Rats. Mol Neurobiol 54, 212–226 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9639-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9639-7