Abstract
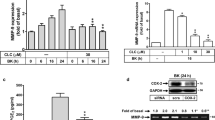
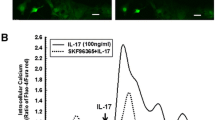
The expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) has been shown to be elevated in some pathophysiological conditions and is involved in the degradation of extracellular matrix in astrocytes. In current study, the function of MMP-13 was further investigated. The conditioned medium (CM) collected from activated microglia increased interleukin (IL)-18 production and enhanced MMP-13 expression in astrocytes. Furthermore, treatment with recombinant IL-18 increased MMP-13 protein and mRNA levels in astrocytes. Recombinant IL-18 stimulation also increased the enzymatic activity of MMP-13 and the migratory activity of astrocytes, while administration of MMP-13 or pan-MMP inhibitors antagonized IL-18-induced migratory activity of astrocytes. In addition, administration of recombinant IL-18 to astrocytes led to the phosphorylation of JNK, Akt, or PKCδ, and treatment of astrocytes with JNK, PI3 kinase/Akt, or PKCδ inhibitors significantly decreased the IL-18-induced migratory activity. Taken together, the results suggest that IL-18-induced MMP-13 expression in astrocytes is regulated by JNK, PI3 kinase/Akt, and PKCδ signaling pathways. These findings also indicate that IL-18 is an important regulator leading to MMP-13 expression and cell migration in astrocytes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sofroniew MV, Vinters HV (2010) Astrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 119(1):7–35. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0619-8
Burda JE, Bernstein AM, Sofroniew MV (2015) Astrocyte roles in traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.03.020
Finsterwald C, Magistretti PJ, Lengacher S (2015) Astrocytes: new targets for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Pham Des 21(25):3570–3581
Sofroniew MV (2014) Multiple roles for astrocytes as effectors of cytokines and inflammatory mediators. Neuroscientist 20(2):160–172. doi:10.1177/1073858413504466
Loihl AK, Murphy S (1998) Expression of nitric oxide synthase-2 in glia associated with CNS pathology. Prog Brain Res 118:253–267
Alboni S, Cervia D, Sugama S, Conti B (2010) Interleukin 18 in the CNS. J Neuroinflammation 7:9. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-7-9
Ryu HJ, Kim JE, Kim MJ, Kwon HJ, Suh SW, Song HK, Kang TC (2010) The protective effects of interleukin-18 and interferon-gamma on neuronal damages in the rat hippocampus following status epilepticus. Neuroscience 170(3):711–721. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.07.048
Yatsiv I, Morganti-Kossmann MC, Perez D, Dinarello CA, Novick D, Rubinstein M, Otto VI, Rancan M et al (2002) Elevated intracranial IL-18 in humans and mice after traumatic brain injury and evidence of neuroprotective effects of IL-18-binding protein after experimental closed head injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22(8):971–978. doi:10.1097/00004647-200208000-00008
Jander S, Schroeter M, Stoll G (2002) Interleukin-18 expression after focal ischemia of the rat brain: association with the late-stage inflammatory response. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22(1):62–70. doi:10.1097/00004647-200201000-00008
Kast RE (2015) The role of interleukin-18 in glioblastoma pathology implies therapeutic potential of two old drugs-disulfiram and ritonavir. Chin J Cancer 34(4):161–165. doi:10.1186/s40880-015-0010-1
Ishida Y, Migita K, Izumi Y, Nakao K, Ida H, Kawakami A, Abiru S, Ishibashi H et al (2004) The role of IL-18 in the modulation of matrix metalloproteinases and migration of human natural killer (NK) cells. FEBS Lett 569(1–3):156–160. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.05.039
Chandrasekar B, Mummidi S, Mahimainathan L, Patel DN, Bailey SR, Imam SZ, Greene WC, Valente AJ (2006) Interleukin-18-induced human coronary artery smooth muscle cell migration is dependent on NF-kappaB- and AP-1-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and is inhibited by atorvastatin. J Biol Chem 281(22):15099–15109. doi:10.1074/jbc.M600200200
Ala-aho R, Kahari VM (2005) Collagenases in cancer. Biochimie 87(3–4):273–286. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2004.12.009
Yong VW, Power C, Forsyth P, Edwards DR (2001) Metalloproteinases in biology and pathology of the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(7):502–511. doi:10.1038/35081571
Sendon-Lago J, Seoane S, Eiro N, Bermudez MA, Macia M, Garcia-Caballero T, Vizoso FJ, Perez-Fernandez R (2014) Cancer progression by breast tumors with Pit-1-overexpression is blocked by inhibition of metalloproteinase (MMP)-13. Breast Cancer Res 16(6):505. doi:10.1186/s13058-014-0505-8
Hsieh WT, Yeh WL, Cheng RY, Lin C, Tsai CF, Huang BR, Wu CY, Lin HY et al (2014) Exogenous endothelin-1 induces cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase expression in U251 human glioblastoma multiforme. J Neuro-Oncol 118(2):257–269. doi:10.1007/s11060-014-1442-1
Tsai CF, Yeh WL, Chen JH, Lin C, Huang SS, Lu DY (2014) Osthole suppresses the migratory ability of human glioblastoma multiforme cells via inhibition of focal adhesion kinase-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression. Int J Mol Sci 15(3):3889–3903. doi:10.3390/ijms15033889
Lu DY, Leung YM, Cheung CW, Chen YR, Wong KL (2010) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor induces cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in glioma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 80(8):1201–1209. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.046
Yeh WL, Lu DY, Lee MJ, Fu WM (2009) Leptin induces migration and invasion of glioma cells through MMP-13 production. Glia 57(4):454–464. doi:10.1002/glia.20773
Chuang JY, Tsai CF, Chang SW, Chiang IP, Huang SM, Lin HY, Yeh WL, Lu DY (2013) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor induces cell migration in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 49(12):1103–1112. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.08.009
Lu DY, Yu WH, Yeh WL, Tang CH, Leung YM, Wong KL, Chen YF, Lai CH et al (2009) Hypoxia-induced matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in astrocytes enhances permeability of brain endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 220(1):163–173. doi:10.1002/jcp.21746
Griner EM, Kazanietz MG (2007) Protein kinase C and other diacylglycerol effectors in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7(4):281–294. doi:10.1038/nrc2110
Liu JF, Crepin M, Liu JM, Barritault D, Ledoux D (2002) FGF-2 and TPA induce matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion in MCF-7 cells through PKC activation of the Ras/ERK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293(4):1174–1182. doi:10.1016/s0006-291x(02)00350-9
Urtreger AJ, Grossoni VC, Falbo KB, Kazanietz MG, de Kier Joffe ED B (2005) Atypical protein kinase C-zeta modulates clonogenicity, motility, and secretion of proteolytic enzymes in murine mammary cells. Mol Carcinog 42(1):29–39. doi:10.1002/mc.20066
Sokolova O, Vieth M, Naumann M (2013) Protein kinase C isozymes regulate matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression and cell invasion in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 62(3):358–367. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302103
Wu LH, Lin C, Lin HY, Liu YS, Wu CY, Tsai CF, Chang PC, Yeh WL et al (2015) Naringenin suppresses neuroinflammatory responses through inducing suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 expression. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-9042-9
Moriya C, Jinnin M, Yamane K, Maruo K, Muchemwa FC, Igata T, Makino T, Fukushima S et al (2011) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 is controlled by IL-13 via PI3K/Akt3 and PKC-delta in normal human dermal fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol 131(3):655–661. doi:10.1038/jid.2010.361
Amin MA, Mansfield PJ, Pakozdi A, Campbell PL, Ahmed S, Martinez RJ, Koch AE (2007) Interleukin-18 induces angiogenic factors in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue fibroblasts via distinct signaling pathways. Arthritis Rheum 56(6):1787–1797. doi:10.1002/art.22705
Hamby ME, Uliasz TF, Hewett SJ, Hewett JA (2006) Characterization of an improved procedure for the removal of microglia from confluent monolayers of primary astrocytes. J Neurosci Methods 150(1):128–137
Chen PS, Peng GS, Li G, Yang S, Wu X, Wang CC, Wilson B, Lu RB et al (2006) Valproate protects dopaminergic neurons in midbrain neuron/glia cultures by stimulating the release of neurotrophic factors from astrocytes. Mol Psychiatry 11(12):1116–1125
Hsu HH, Liu CJ, Shen CY, Chen YJ, Chen LM, Kuo WH, Lin YM, Chen RJ et al (2012) p38alpha MAPK mediates 17beta-estradiol inhibition of MMP-2 and -9 expression and cell migration in human lovo colon cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 227(11):3648–3660. doi:10.1002/jcp.24072
Lin HY, Tang CH, Chen JH, Chuang JY, Huang SM, Tan TW, Lai CH, Lu DY (2011) Peptidoglycan induces interleukin-6 expression through the TLR2 receptor, JNK, c-Jun, and AP-1 pathways in microglia. J Cell Physiol 226(6):1573–1582. doi:10.1002/jcp.22489
Zhou J, Ping FF, Lv WT, Feng JY, Shang J (2014) Interleukin-18 directly protects cortical neurons by activating PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB/CREB pathways. Cytokine 69(1):29–38. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2014.05.003
Amin MA, Rabquer BJ, Mansfield PJ, Ruth JH, Marotte H, Haas CS, Reamer EN, Koch AE (2010) Interleukin 18 induces angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo via Src and Jnk kinases. Ann Rheum Dis 69(12):2204–2212. doi:10.1136/ard.2009.127241
Xia S, Forman LW, Faller DV (2007) Protein kinase C delta is required for survival of cells expressing activated p21RAS. J Biol Chem 282(18):13199–13210. doi:10.1074/jbc.M610225200
Mitsutake N, Namba H, Shklyaev SS, Tsukazaki T, Ohtsuru A, Ohba M, Kuroki T, Ayabe H et al (2001) PKC delta mediates ionizing radiation-induced activation of c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase through MKK7 in human thyroid cells. Oncogene 20(8):989–996. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204179
Das S, Mishra MK, Ghosh J, Basu A (2008) Japanese encephalitis virus infection induces IL-18 and IL-1beta in microglia and astrocytes: correlation with in vitro cytokine responsiveness of glial cells and subsequent neuronal death. J Neuroimmunol 195(1–2):60–72. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.01.009
Yeh WL, Lu DY, Liou HC, Fu WM (2012) A forward loop between glioma and microglia: glioma-derived extracellular matrix-activated microglia secrete IL-18 to enhance the migration of glioma cells. J Cell Physiol 227(2):558–568. doi:10.1002/jcp.22746
Dai SM, Shan ZZ, Nishioka K, Yudoh K (2005) Implication of interleukin 18 in production of matrix metalloproteinases in articular chondrocytes in arthritis: direct effect on chondrocytes may not be pivotal. Ann Rheum Dis 64(5):735–742. doi:10.1136/ard.2004.026088
Frank-Cannon TC, Alto LT, McAlpine FE, Tansey MG (2009) Does neuroinflammation fan the flame in neurodegenerative diseases? Mol Neurodegener 4:47. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-4-47
Walker AK, Kavelaars A, Heijnen CJ, Dantzer R (2014) Neuroinflammation and comorbidity of pain and depression. Pharmacol Rev 66(1):80–101. doi:10.1124/pr.113.008144
Ownby RL (2010) Neuroinflammation and cognitive aging. Curr Psychiatry Rep 12(1):39–45. doi:10.1007/s11920-009-0082-1
Hein AM, O’Banion MK (2009) Neuroinflammation and memory: the role of prostaglandins. Mol Neurobiol 40(1):15–32. doi:10.1007/s12035-009-8066-z
Biesmans S, Meert TF, Bouwknecht JA, Acton PD, Davoodi N, De Haes P, Kuijlaars J, Langlois X et al (2013) Systemic immune activation leads to neuroinflammation and sickness behavior in mice. Mediat Inflamm 2013:271359. doi:10.1155/2013/271359
Sparkman NL, Johnson RW (2008) Neuroinflammation associated with aging sensitizes the brain to the effects of infection or stress. Neuroimmunomodulation 15(4–6):323–330. doi:10.1159/000156474
Arend WP, Palmer G, Gabay C (2008) IL-1, IL-18, and IL-33 families of cytokines. Immunol Rev 223:20–38. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00624.x
Dinarello CA (2000) Interleukin-18, a proinflammatory cytokine. Eur Cytokine Netw 11(3):483–486
Meraz-Rios MA, Toral-Rios D, Franco-Bocanegra D, Villeda-Hernandez J, Campos-Pena V (2013) Inflammatory process in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Integr Neurosci 7:59. doi:10.3389/fnint.2013.00059
Felderhoff-Mueser U, Schmidt OI, Oberholzer A, Buhrer C, Stahel PF (2005) IL-18: a key player in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration? Trends Neurosci 28(9):487–493. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2005.06.008
Zhang Y, Liu L, Peng YL, Liu YZ, Wu TY, Shen XL, Zhou JR, Sun DY et al (2014) Involvement of inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced mice depressive-like behaviors. CNS Neurosci Ther 20(2):119–124. doi:10.1111/cns.12170
Spinale FG (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases: regulation and dysregulation in the failing heart. Circ Res 90(5):520–530
Brinckerhoff CE, Rutter JL, Benbow U (2000) Interstitial collagenases as markers of tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res 6(12):4823–4830
Stickens D, Behonick DJ, Ortega N, Heyer B, Hartenstein B, Yu Y, Fosang AJ, Schorpp-Kistner M et al (2004) Altered endochondral bone development in matrix metalloproteinase 13-deficient mice. Development 131(23):5883–5895
Tromp G, Gatalica Z, Skunca M, Berguer R, Siegel T, Kline RA, Kuivaniemi H (2004) Elevated expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Vasc Surg 18(4):414–420
Hamann GF, Okada Y, Fitridge R, del Zoppo GJ (1995) Microvascular basal lamina antigens disappear during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Stroke 26(11):2120–2126
Rosell A, Alvarez-Sabin J, Arenillas JF, Rovira A, Delgado P, Fernandez-Cadenas I, Penalba A, Molina CA et al (2005) A matrix metalloproteinase protein array reveals a strong relation between MMP-9 and MMP-13 with diffusion-weighted image lesion increase in human stroke. Stroke 36(7):1415–1420
Cserr HF, Bunggaard M (1986) The neuronal microenvironment: a comparative view. Ann N Y Acad Sci 481:1–6
Ueno M, Wu B, Nishiyama A, Huang CL, Hosomi N, Kusaka T, Nakagawa T, Onodera M et al (2009) The expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 is increased in vessels with blood–brain barrier impairment in a stroke-prone hypertensive model. Hypertens Res 32(5):332–338. doi:10.1038/hr.2009.26
Yang CM, Hsieh HL, Yao CC, Hsiao LD, Tseng CP, Wu CB (2009) Protein kinase C-delta transactivates platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha in mechanical strain-induced collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase-13) expression by osteoblast-like cells. J Biol Chem 284(38):26040–26050. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.040154
Huang CY, Lin HJ, Chen HS, Cheng SY, Hsu HC, Tang CH (2013) Thrombin promotes matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression through the PKCdelta c-Src/EGFR/PI3K/Akt/AP-1 signaling pathway in human chondrocytes. Mediat Inflamm 2013:326041. doi:10.1155/2013/326041
Im HJ, Muddasani P, Natarajan V, Schmid TM, Block JA, Davis F, van Wijnen AJ, Loeser RF (2007) Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates matrix metalloproteinase-13 via the molecular cross-talk between the mitogen-activated protein kinases and protein kinase Cdelta pathways in human adult articular chondrocytes. J Biol Chem 282(15):11110–11121. doi:10.1074/jbc.M609040200
Wheeler RD, Culhane AC, Hall MD, Pickering-Brown S, Rothwell NJ, Luheshi GN (2000) Detection of the interleukin 18 family in rat brain by RT-PCR. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 77(2):290–293
Conti B, Park LC, Calingasan NY, Kim Y, Kim H, Bae Y, Gibson GE, Joh TH (1999) Cultures of astrocytes and microglia express interleukin 18. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 67(1):46–52
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by grants from the National Science Council (NSC 102-2320-B-039-051-MY3, NSC 102-2320-B-039-026-MY3, NSC 103-2811-B-039-021, and NSC 104-2320-B-468 -002), China Medical University (CMU103-ASIA-02), and Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial and Research Center of Excellence (MOHW104-TDU-B-212-113002). The authors thank Ms Y.-R Chen and Ms S.-H. Ko for the technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors report that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Jia-Hong Chen and Chon-Haw Tsai contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JH., Tsai, CH., Lin, HY. et al. Interlukin-18 Is a Pivot Regulatory Factor on Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 Expression and Brain Astrocytic Migration. Mol Neurobiol 53, 6218–6227 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9529-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9529-z