Abstract
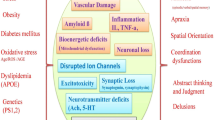
Aging is associated with an enhanced susceptibility to brain dysfunction, loss of memory, and cognitive decline and significantly influences the quality of life for the affected individual. Recent molecular–genetic approaches have provided powerful insights into common age-related diseases that are both progressive and multifactorial, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and in vitro in AD models. These investigations have uncovered consistent deficits in brain gene signaling mechanisms and neurotrophic substances known to contribute to normal brain function. Inflammatory signaling pathways involving up-regulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 and the arachidonic acid cycle, the depletion of the brain-essential fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and DHA-derived neuroprotectin D1, and changes in the expression of key proapoptotic and antiapoptotic members of the Bcl-2 gene family are thought to be major contributors to pathogenic processes in degenerating brain tissue. This review will focus on the roles of stress genes, apoptosis-related genes, and inflammation in the molecular genetics of AD with emphasis on the interactive nature of inflammatory, neurotrophic, and apoptotic signaling and will highlight areas of rapid progress in the characterization of action of DHA and neuroprotectin D1 and address important research challenges. We also attempt to integrate these molecular, genetic, and neurochemical changes with cellular pathways involved in brain aging to formulate an integrated understanding of multifactorial age-related neurologic disease and pharmacotherapeutic strategies that may be useful in the restoration of homeostatic brain function.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ42:
-
amyloid beta 42-amino-acid peptide
- AA:
-
arachidonic acid
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- ApoE4:
-
apolipoprotein E4 allele
- βAPP:
-
beta-amyloid precursor protein
- COX-2:
-
inducible cyclooxygenase-2
- cPLA2 :
-
cytosolic phosphoilpase A2
- DHA:
-
docosahexaenoic acid
- HNE:
-
hydroxynonenal
- LOX:
-
lipoxygenase
- LPX:
-
lipoxins
- LTR:
-
leukotrienes
- NFT:
-
neurofibrillary tangles
- NPD1:
-
neuroprotectin D1
- PG:
-
prostaglandin
- PLA2 :
-
phosphoilpase A2
- PUFA:
-
polyunsaturated fatty acid
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SP:
-
senile plaque
- sAPPα:
-
soluble amyloid precursor protein alpha fragment
- sPLA2 :
-
secreted phosphoilpase A2
- TNFAIP2:
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha inducible protein-2 (B94)
References
Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG (2008) Docosahexaenoic acid and the aging brain. J Nutr 138:2510–2514
Mann DM (1996) Pyramidal nerve cell loss in Alzheimer's disease. Neurodegeneration 5:423–427
Thangavel R, Sahu SK, Van Hoesen GW, Zaheer A (2009) Loss of nonphosphorylated neurofilament immunoreactivity in temporal cortical areas in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience 160:427–433
Colangelo V, Schurr J, Ball MJ, Pelaez RP, Bazan NG, Lukiw WJ (2002) Gene expression profiling of 12633 genes in Alzheimer hippocampal CA1: transcription and neurotrophic factor down-regulation and up-regulation of apoptotic and pro-inflammatory signaling. J Neurosci Res 70:462–473
Cui JG, Hill JM, Zhao Y, Lukiw WJ (2007) Expression of inflammatory genes in the primary visual cortex of late-stage Alzheimer's disease. NeuroReport 18:115–119
Webster JA, Gibbs JR, Clarke J, Ray M, Zhang W, Holmans P, Rohrer K, Zhao A, Marlowe L, Kaleem M, McCorquodale DS 3rd, Cuello C, Leung D, Bryden L, Nath P, Zismann VL, Joshipura K, Huentelman MJ, Hu-Lince D, Coon KD, Craig DW, Pearson JV, NACC-Neuropathology Group, Heward CB, Reiman EM, Stephan D, Hardy J, Myers AJ (2009) Genetic control of human brain transcript expression in Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet 84:445–458
Liang WS, Dunckley T, Beach TG, Grover A, Mastroeni D, Walker DG, Caselli RJ, Kukull WA, McKeel D, Morris JC, Hulette C, Schmechel D, Alexander GE, Reiman EM, Rogers J, Stephan DA (2006) Gene expression profiles in anatomically and functionally distinct regions of the normal aged human brain. Physiol Genomics 28:311–322
Lukiw WJ (2004) Gene expression profiling in fetal, aged, and Alzheimer hippocampus: a continuum of stress-related signaling. Neurochem Res 29:1287–1297
Boetkjaer A, Boedker M, Cui JG, Zhao Y, Lukiw WJ (2007) Synergism in the repression of COX-2- and TNFalpha-induction in platelet activating factor-stressed human neural cells. Neurosci Lett 426:59–63
Lukiw WJ, Rogaev EI, Bazan NG (1996) Synaptic and cytoskeletal RNA message levels in sporadic Alzheimer neocortex. Alzheimer’s Research 2:221–227
Lukiw WJ, Carver LA, LeBlanc HJ, Bazan NG (2000) Analysis of 1184 gene transcript levels in AD CA1 hippocampus: synaptic signaling and transcription factor deficits and upregulation of pro-inflammatory pathways. Alzheimer’s Rep 3:161–167
Loring JF, Wen X, Lee JM, Seilhamer J, Somogyi R (2001) Gene expression profile of Alzheimer's disease. DNA Cell Biol 20:683–695
Tsuji T, Shiozaki A, Kohno R, Yoshizato K, Shimohama S (2002) Proteomic profiling and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Res 27:1245–1253
Alzheimer A, Stelzmann RA, Schnitzlein HN, Murtagh FR (1995) An English translation of Alzheimer's 1907 paper, “Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde”. Clin Anat 8:429–431
Butterfield DA, Drake J, Pocernich C, Castegna A (2001) Evidence of oxidative damage in Alzheimer's disease brain: central role for amyloid beta-peptide. Trends Mol Med 7:548–554
Sleegers K, Van Duijn CM (2001) Alzheimer's disease: genes, pathogenesis and risk prediction. Community Genet 4:197–203
Gamblin TC, Chen F, Zambrano A, Abraha A, Lagalwar S, Guillozet AL, Lu M, Fu Y, Garcia-Sierra F, LaPointe N, Miller R, Berry RW, Binder LI, Cryns VL (2003) Caspase cleavage of tau: linking amyloid and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:10032–10037
Cotman CW, Poon WW, Rissman RA, Blurton-Jones M (2005) The role of caspase cleavage of tau in Alzheimer disease neuropathology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:104–112
Rohn TT, Head E (2008) Caspase activation in Alzheimer's disease: early to rise and late to bed. Rev Neurosci 19:383–393
Rohn TT (2009) Cytoplasmic inclusions of TDP-43 in neurodegenerative diseases: a potential role for caspases. Histol Histopathol 24:1081–1086
Whelan J (2008) n-6_and (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids and the aging brain: food for thought. J Nutr 138:2521–2522
Fukaya T, Fukaya T, Gondaira T, Kashiyae Y, Kotani S, Ishikura Y, Fujikawa S, Kiso Y, Sakakibara M (2007) Arachidonic acid preserves hippocampal neuron membrane fluidity in senescent rats. Neurobiol Aging 28:1179–1186
Montecucco C, Gutiérrez JM, Lomonte B (2008) Cellular pathology induced by snake venom phospholipase A2 myotoxins and neurotoxins: common aspects of their mechanisms of action. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:2897–2912
Sun GY, Shelat PB, Jensen MB, He Y, Sun AY, Simonyi A (2009) Phospholipases A2 and inflammatory responses in the central nervous system. Neuromolecular Med. doi:10.1007/s12017-009-8092-z Oct 24
Franceschi C, Valensin S, Lescai F, Olivieri F, Licastro F, Grimaldi LM, Monti D, De Benedictis G, Bonafe M (2001) Neuroinflammation and the genetics of Alzheimer's disease: the search for a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Aging 13:163–170
Sayre LM, Smith MA, Perry G (2001) Chemistry and biochemistry of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disease. Curr Med Chem 8:721–738
Rogers J (1995) Inflammation as a pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer's disease. Arzneimittelforschung 45:439–442
Tol J, Roks G, Slooter AJ, van Duijn CM (1999) Genetic and environmental factors in Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurol 155:10–16
Rogan S, Lippa CF (2002) Alzheimer's disease and other dementias: a review. Amer J Alzheimer's Dis Other Dement 17:11–17
Bazan NG, Colangelo V, Lukiw WJ (2002) Prostaglandins and other lipid mediators in Alzheimer's disease. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 68–69:197–210
Marcheselli VL, Hong S, Lukiw WJ, Tian XH, Gronert K, Musto A, Hardy M, Gimenez JM, Chiang N, Serhan CN, Bazan NG (2003) Novel docosanoids inhibit brain ischemia-reperfusion-mediated leukocyte infiltration and pro-inflammatory gene expression. J Biol Chem 278:43807–43817
Farkas E, de Wilde MC, Kiliaan AJ, Meijer J, Keijser JN, Luiten PG (2002) Dietary long chain PUFAs differentially affect hippocampal muscarinic 1 and serotonergic 1A receptors in experimental cerebral hypoperfusion. Brain Res 954:32–41
Heinemann KM, Bauer JE (2006) Docosahexaenoic acid and neurologic development in animals. J Am Vet Med Assoc 228:700–705
Lim GP, Calon F, Morihara T, Yang F, Teter B, Ubeda O, Salem N Jr, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2005) A diet enriched with the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid reduces amyloid burden in an aged Alzheimer mouse model. J Neurosci 25:3032–3040
Lukiw WJ, Percy ME, Kruck TP (2005) Nanomolar metal sulfates induce pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic gene expression in human brain cells in primary culture. J Inorg Biochem 99:1895–1898
Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG (2006) Survival signaling in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Soc Trans 34:1277–1282
Niemoller TD, Stark DT, Bazan NG (2009) Omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid is the precursor of neuroprotectin D1 in the nervous system. World Rev Nutr Diet 99:46–54
Bazan NG (2009) Neuroprotectin D1-mediated anti-inflammatory and survival signaling in stroke, retinal degenerations, and Alzheimer's disease. J Lipid Res 50:400–405
Minihane AM, Khan S, Leigh-Firbank EC, Talmud P, Wright JW, Murphy MC, Griffin BA, Williams CM (2005) ApoE polymorphism and fish oil supplementation in subjects with an atherogenic lipoprotein phenotype. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1990–1997
Huang TL, Zandi PP, Tucker KL, Fitzpatrick AL, Kuller LH, Fried LP, Burke GL, Carlson MC (2005) Benefits of fatty fish on dementia risk are stronger for those without APOE epsilon4. Neurology 65:1409–1414
Cole GM, Frautschy SA (2010) DHA may prevent age-related dementia. J Nutr. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 20181786
Repici M, Mariani J, Borsello T (2007) Neuronal death and neuroprotection: a review. Meth Mol Biol 399:1–14
Gorman AM (2008) Neuronal cell death in neurodegenerative diseases: recurring themes around protein handling. J Cell Mol Med 12:2263–2280
Lorz C, Mehmet H (2009) The role of death receptors in neural injury. Front Biosci 14:583–595
DeLegge MH, Smoke A (2008) Neurodegeneration and inflammation. Nutr Clin Pract 23:35–41
Du H, Yan SS (2009) Mitochondrial permeability transition pore in Alzheimer's disease: yclophilin D and amyloid beta. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802:198–204
Kalinichenko SG, Matveeva NY (2008) Morphological characteristics of apoptosis and its significance in neurogenesis. Neurosci Behav Physiol 38:333–342
Lukiw WJ (2008) Emerging amyloid beta (Aβ) peptide modulators for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 13:255–271
Lukiw WJ, Cui JG, Marcheselli VL, Bodker M, Botkjaer A, Gotlinger K, Serhan CN, Bazan NG (2005) A role for docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 in neural cell survival and Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest 115:2774–2783
Lukiw WJ (2009) Docosahexaenoic acid and amyloid-beta peptide signaling in Alzheimer's disease. World Rev Nutr Diet 99:55–70
Bazan NG (2009) Cellular and molecular events mediated by docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 signaling in photoreceptor cell survival and brain protection. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 81:205–211
Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG (2008) Docosahexaenoic acid and the aging brain. J Nutr 138:2510–2514
Zhao Y, Cui JG, Lukiw WJ (2006) Natural secretory products of human neural and microvessel endothelial cells: implications in pathogenic “spreading” and Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol 34:181–192
McGeer PL, Rogers J, McGeer EG (2006) Inflammation, anti-inflammatory agents and Alzheimer disease: the last 12 years. J Alzheimers Dis 9:271–276
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lukiw, W.J., Bazan, N.G. Inflammatory, Apoptotic, and Survival Gene Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 42, 10–16 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-010-8126-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-010-8126-4