Abstract
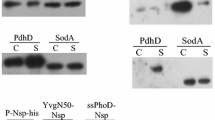
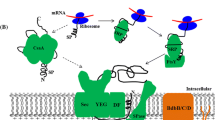
In this study, we examined the effects of modifying the C-terminal region of the SecA protein on the production of heterologous proteins in Bacillus subtilis. SecA was selected as a candidate among the components of the Sec system due to its ability to interact directly with both the precursors and membrane translocases. A phylogenetic comparison demonstrated that the C-terminal region is not well conserved among eubacterial SecA proteins. The deletion of the 61 amino acids at the C-terminal region led to an 83% increase in extracellular alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. thermostable alkaline cellulase (Egl-237) activity. Moreover, the productivity of human interferon α (hIFN-α2b) was increased by 2.2-fold compared to the wild-type SecA, by deletion of these 61 amino acids. We indicated that the deletion of the C-terminal domain (CTD) of SecA enhanced the secretion of two different heterologous protein, Egl-237 and hIFN-α2b. This study provides a useful method to enhance the extracellular production of heterologous proteins in B. subtilis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braun, P., Gerritse, G., van Dijl, J. M., & Quax, W. J. (1999). Improving protein secretion by engineering components of the bacterial translocation machinery. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 10, 376–381.
Tjalsma, H., Bolhuis, A., Jongbloed, J. D., Bron, S., & van Dijl, J. M. (2000). Signal peptide-dependent protein transport in Bacillus subtilis: A genome-based survey of the secretome. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 64, 515–547.
Westers, L., Westers, H., & Quax, W. J. (2004). Bacillus subtilis as cell factory for pharmaceutical proteins: A biotechnological approach to optimize the host organism. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1694, 299–310.
Tjalsma, H., Antelmann, H., Jongbloed, J. D., Braun, P. G., Darmon, E., Dorenbos, R., et al. (2004). Proteomics of protein secretion by Bacillus subtilis: Separating the “secrets” of the secretome. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 68, 207–233.
Yamane, K., Bunai, K., & Kakeshita, H. (2004). Protein traffic for secretion and related machinery of Bacillus subtilis. Bioscience Biotechnology Biochemistry, 68, 2007–2023.
van Wely, K. H., Swaving, J., Freudl, R., & Driessen, A. J. (2001). Translocation of proteins across the cell envelope of Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 25, 437–454.
Harwood, C. R., & Cranenburgh, R. (2008). Bacillus protein secretion: An unfolding story. Trends in Microbiology, 16, 73–79.
Hartl, F. U., Lecker, S., Schiebel, E., Hendrick, J. P., & Wickner, W. (1990). The binding cascade of SecB to SecA to SecY/E mediates preprotein targeting to the E. coli plasma membrane. Cell, 63, 269–279.
Fekkes, P., van der Does, C., & Driessen, A. J. (1997). The molecular chaperone SecB is released from the carboxy-terminus of SecA during initiation of precursor protein translocation. The EMBO Journal, 16, 6105–6113.
Kunst, F., Ogasawara, N., Moszer, I., Albertini, A. M., Alloni, G., Azevedo, V., et al. (1997). The complete genome sequence of the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Nature, 390, 249–256.
van Wely, K. H., Swaving, J., Klein, M., Freudl, R., & Driessen, A. J. (2000). The carboxyl terminus of the Bacillus subtilis SecA is dispensable for protein secretion and viability. Microbiology, 146, 2573–2581.
Henner, D. J. (1990). Inducible expression of regulatory genes in Bacillus subtilis. Methods in Enzymology, 185, 223–228.
Morimoto, T., Kadoya, R., Endo, K., Tohata, M., Sawada, K., Liu, S., et al. (2008). Enhanced recombinant protein productivity by genome reduction in Bacillus subtilis. DNA Research, 15, 73–81.
Hakamada, Y., Hatada, Y., Koike, K., Yoshimatsu, T., Kawai, S., Kobayashi, T., et al. (2000). Deduced amino acid sequence and possible catalytic residues of a thermostable, alkaline cellulase from an alkaliphilic bacillus strain. Bioscience Biotechnology Biochemistry, 64, 2281–2289.
Kakeshita, H., Oguro, A., Amikura, R., Nakamura, K., & Yamane, K. (2000). Expression of the ftsY gene, encoding a homologue of the α subunit of mammalian signal recognition particle receptor, is controlled by different promoters in vegetative and sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology, 146, 2595–2603.
Takamatsu, H., Fuma, S., Nakamura, K., Sadaie, Y., Shinkai, A., Matsuyama, S., et al. (1992). In vivo and in vitro characterization of the secA gene product of Bacillus subtilis. Journal of Bacteriology, 174, 4308–4316.
Matsuzaki, H., Yamane, K., Yamaguchi, K., Nagata, Y., & Maruo, B. (1974). Hybrid α-amylases produced by transformants of Bacillus subtilis. I. Purification and characterization of extracellular α-amylases produced by the parental strains and transformants. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta, 365, 235–247.
Herbort, M., Klein, M., Manting, E. H., Driessen, A. J., & Freudl, R. J. (1999). Temporal expression of the Bacillus subtilis secA gene, encoding a central component of the preprotein translocase. Journal of Bacteriology, 181, 493–500.
Ling, L., Xu, Z., Li, W., Shuai, J., Lu, P., & Hu, C. (2007). Protein secretion pathways in Bacillus subtilis: Implication for optimization of heterologous protein secretion. Biotechnology Advances, 25, 1–12.
Li, W., Zhou, X., & Lu, P. (2004). Bottlenecks in the expression and secretion of heterologous proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Research in Microbiology, 155, 605–610.
Kouwen, T. R., Dubois, J. Y., Freudl, R., Quax, W. J., & van Dijl, J. M. (2008). Modulation of thiol-disulfide oxidoreductases for increased production of disulfide-bond-containing proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 74, 7536–7545.
Kouwen, T. R., Nielsen, A. K., Denham, E. L., Dubois, J. Y., Dorenbos, R., Rasmussen, M. D., et al. (2010). Contributions of the pre- and pro-regions of a Staphylococcus hyicus lipase to secretion of a heterologous protein by Bacillus subtilis. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 76, 659–669.
Brockmeier, U., Caspers, M., Freudl, R., Jockwer, A., Noll, T., & Eggert, T. (2006). Systematic screening of all signal peptides from Bacillus subtilis: A powerful strategy in optimizing heterologous protein secretion in Gram-positive bacteria. Journal of Molecular Biology, 362, 393–402.
Bolhuis, A., Tjalsma, H., Smith, H. E., de Jong, A., Meima, R., Venema, G., et al. (1999). Evaluation of bottlenecks in the late stages of protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 65, 2934–2941.
Sarvas, M., Harwood, C. R., Bron, S., & van Dijl, J. M. (2004). Post-translocational folding of secretory proteins in Gram-positive bacteria. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1694, 311–327.
Hunt, J. F., Weinkauf, S., Henry, L., Fak, J. J., McNicholas, P., Oliver, D. B., et al. (2002). Nucleotide control of interdomain interactions in the conformational reaction cycle of SecA. Science, 297, 2018–2026.
Mostertz, J., Scharf, C., Hecker, M., & Homuth, G. (2004). Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression in response to superoxide and peroxide stress. Microbiology, 150, 497–512.
Takase, T., Mizuno, H., & Yamane, K. (1988). NH2-terminal processing of Bacillus subtilis α-amylase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 263, 11548–11553.
Acknowledgments
This study is the subproject, ‘Development of a Technology for Creation of a Host Cell’ included within the industrial technology project, ‘Development of a Generic Technology for Production Process Starting Productive Function’ of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), entrusted by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9313-2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kakeshtia, H., Kageyama, Y., Ara, K. et al. Enhanced Extracellular Production of Heterologous Proteins in Bacillus subtilis by Deleting the C-terminal Region of the SecA Secretory Machinery. Mol Biotechnol 46, 250–257 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9295-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9295-0