Abstract
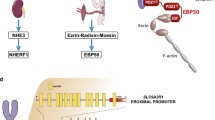
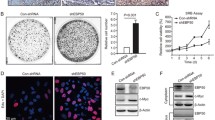
The scaffold protein ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein 50 (EBP50, also known as NHERF1 or NHERF) inhibits epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced breast cancer cell proliferation after 3 days by blocking EGF receptor (EGFR) phosphorylation. The loss of EBP50 stimulates EGFR activity and induces the appearance of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotypic features in biliary cancer cells. However, the involvement of EBP50 in breast cancer migration and invasion remains unknown. We report that EBP50 inhibits the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by inhibiting the phosphorylation of LIN-11, Isl1, and MEC-3 protein domain kinase, as well as cofilin. This phosphorylation is a critical step in cofilin recycling and actin polymerization mediating cytoskeletal rearrangement. Additionally, EGF-induced phosphorylation of Akt and mTOR was suppressed by upregulation of EBP50. Our results indicate that EBP50 is significantly involved in breast cancer invasion/metastasis via LIMK/cofilin and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/MMP signaling pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malakoff D. Intellectual property. Patent reform shuffles who is first in line. Science. 2011;333(6049):1559–60. doi:10.1126/science.333.6049.1559.
Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 2011;331(6024):1559–64. doi:10.1126/science.1203543.
Liang X. EMT: new signals from the invasive front. Oral Oncol. 2011;47(8):686–7. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2011.04.016.
Christofori G. New signals from the invasive front. Nature. 2006;441(7092):444–50.
Claperon A, Therrien M. KSR and CNK: two scaffolds regulating RAS-mediated RAF activation. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3143–58. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210408.
Zheng JF, Sun LC, Liu H, Huang Y, Li Y, He J. EBP50 exerts tumor suppressor activity by promoting cell apoptosis and retarding extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity. Amino Acids. 2010;38(4):1261–8. doi:10.1007/s00726-009-0437-2.
Hayashi Y, Molina JR, Hamilton SR, Georgescu MM. NHERF1/EBP50 is a new marker in colorectal cancer. Neoplasia. 2010;12(12):1013–22.
Bartholow TL, Becich MJ, Chandran UR, Parwani AV. Immunohistochemical analysis of ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein 50 in prostatic adenocarcinoma. BMC Urol. 2011;11:12. doi:10.1186/1471-2490-11-12.
Song J, Bai J, Yang W, Gabrielson EW, Chan DW, Zhang Z. Expression and clinicopathological significance of oestrogen-responsive ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein 50 in breast cancer. Histopathology. 2007;51(1):40–53. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02730.x.
Pan Y, Wang L, Dai JL. Suppression of breast cancer cell growth by Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 1 (NHERF1). Breast Cancer Res. 2006;8(6):R63. doi:10.1186/bcr1616.
Yao W, Feng D, Bian W, Yang L, Li Y, Yang Z, Xiong Y, Zheng J, Zhai R, He J. EBP50 inhibits EGF-induced breast cancer cell proliferation by blocking EGFR phosphorylation. Amino Acids. 2012;43(5):2027–35. doi:10.1007/s00726-012-1277-z.
Fouassier L, Rosenberg P, Mergey M, Saubamea B, Claperon A, Kinnman N, Chignard N, Jacobsson-Ekman G, Strandvik B, Rey C, Barbu V, Hultcrantz R, Housset C. Ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein (EBP50), an estrogen-inducible scaffold protein, contributes to biliary epithelial cell proliferation. Am J Pathol. 2009;174(3):869–80. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.080079.
Shibata T, Chuma M, Kokubu A, Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S. EBP50, a beta-catenin-associating protein, enhances Wnt signaling and is over-expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2003;38(1):178–86. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50270.
Claperon A, Guedj N, Mergey M, Vignjevic D, Desbois-Mouthon C, Boissan M, Saubamea B, Paradis V, Housset C, Fouassier L. Loss of EBP50 stimulates EGFR activity to induce EMT phenotypic features in biliary cancer cells. Oncogene. 2012;31(11):1376–88. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.334.
Shi L, Sun X, Zhang J, Zhao C, Li H, Liu Z, Fang C, Wang X, Zhang X, Zhou F, Lu S, Luo R, Zhang B. Gab2 expression in glioma and its implications for tumor invasion. Acta Oncol. 2012;. doi:10.3109/0284186X.2012.750032.
Guo H, Gu F, Li W, Zhang B, Niu R, Fu L, Zhang N, Ma Y. Reduction of protein kinase C zeta inhibits migration and invasion of human glioblastoma cells. J Neurochem. 2009;109(1):203–13.
Sun R, Gao P, Chen L, Ma D, Wang J, Oppenheim JJ, Zhang N. Protein kinase C zeta is required for epidermal growth factor-induced chemotaxis of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65(4):1433–41.
Li H, Yin C, Zhang B, Sun Y, Shi L, Liu N, Liang S, Lu S, Liu Y, Zhang J, Li F, Li W, Liu F, Sun L, Qi Y. PTTG1 promotes migration and invasion of human non-small cell lung cancer cells and is modulated by miR-186. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(9):2145–55. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt158.
Yamazaki D, Kurisu S, Takenawa T. Regulation of cancer cell motility through actin reorganization. Cancer Sci. 2005;96(7):379–86. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00062.x.
Bernard O. Lim kinases, regulators of actin dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(6):1071–6. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2006.11.011.
DesMarais V, Ghosh M, Eddy R, Condeelis J. Cofilin takes the lead. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 1):19–26. doi:10.1242/jcs.01631.
Wang XF, Du J, Zhang TL, Zhou QM, Lu YY, Zhang H, Su SB. Inhibitory effects of PC-SPESII herbal extract on human breast cancer metastasis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:894386. doi:10.1155/2013/894386.
Yin C, Li H, Zhang B, Liu Y, Lu G, Lu S, Sun L, Qi Y, Li X, Chen W. RAGE-binding S100A8/A9 promotes the migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells through actin polymerization and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;142(2):297–309. doi:10.1007/s10549-013-2737-1.
Grunt TW, Mariani GL. Novel approaches for molecular targeted therapy of breast cancer: interfering with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013;13(2):188–204.
Jiang H, Shang X, Wu H, Gautam SC, Al-Holou S, Li C, Kuo J, Zhang L, Chopp M. Resveratrol downregulates PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in human U251 glioma cells. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2009;8(1):25–33.
Yan B, Kong M, Chen S, Chen YH. VEGF stimulation enhances Livin protein synthesis through mTOR signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2010;111(5):1114–24. doi:10.1002/jcb.22797.
Lu S, Niu N, Guo H, Tang J, Guo W, Liu Z, Shi L, Sun T, Zhou F, Li H, Zhang J, Zhang B. ARK5 promotes glioma cell invasion, and its elevated expression is correlated with poor clinical outcome. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(3):752–63. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2012.09.018.
Cao B, Yang Y, Pan Y, Jia Y, Brock MV, Herman JG, Guo M. Epigenetic silencing of CXCL14 induced colorectal cancer migration and invasion. Discov Med. 2013;16(88):137–47.
Liu D, Guo H, Li Y, Xu X, Yang K, Bai Y. Association between polymorphisms in the promoter regions of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and risk of cancer metastasis: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(2):e31251. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031251.
Chien CS, Shen KH, Huang JS, Ko SC, Shih YW. Antimetastatic potential of fisetin involves inactivation of the PI3K/Akt and JNK signaling pathways with downregulation of MMP-2/9 expressions in prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;333(1–2):169–80. doi:10.1007/s11010-009-0217-z.
Chetty C, Lakka SS, Bhoopathi P, Rao JS. MMP-2 alters VEGF expression via alphaVbeta3 integrin-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling in A549 lung cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(5):1081–95. doi:10.1002/ijc.25134.
McAuliffe PF, Meric-Bernstam F, Mills GB, Gonzalez-Angulo AM. Deciphering the role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in breast cancer biology and pathogenesis. Clin Breast Cancer. 2010;10(Suppl 3):S59–65. doi:10.3816/CBC.2010.s.013.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Foundation of Shandong Province (BS2011YY060), Foundation of Shandong Educational Committee (J12LK03 and J13LK03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hongli Li and Baogang Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Zhang, B., Liu, Y. et al. EBP50 inhibits the migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells via LIMK/cofilin and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/MMP signaling pathway. Med Oncol 31, 162 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0162-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0162-x