Abstract
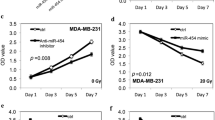
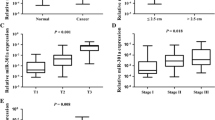
The triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), with a particularly poor prognosis, is increasingly recognized as heterogeneous in molecular signatures. MicroRNA expression profiles have been used for the classification and prognostication of breast cancer, numerous significantly upregulated microRNAs, i.e. miR-21, have been verified oncogenic in non-TNBCs. In present study, we determined the miR-21 levels in TNBC specimens, and TNBC cell levels in vitro, and then identified the role of miR-21 on tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, and then identified PTEN as the possible target of the microRNA. It was shown that miR-21 expression is upregulated generally, and heterogeneous in TNBC specimens, posing a correlation with poor prognosis for TNBC patients. Further results demonstrated that the upregulated miR-21 promoted the tumor proliferation and inhibited cell apoptosis in vitro. And pro-apoptotic PTEN had been shown being targeted and downregulated. Therefore, our finding emphasized the oncogenic role of miR-21 in TNBC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Putti TC, El-Rehim DM, Rakha EA, Paish CE, Lee AH, Pinder SE, Ellis IO. Estrogen receptor-negative breast carcinomas: a review of morphology and immunophenotypical analysis. Mod Pathol Off J U S Can Acad Pathol. 2005;18:26–35.
Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M, Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler L, Akslen LA, Ragaz J, Gown AM, Gilks CB, van de Rijn M, Perou CM. Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2004;10:5367–74.
Kreike B, van Kouwenhove M, Horlings H, Weigelt B, Peterse H, Bartelink H, van de Vijver MJ. Gene expression profiling and histopathological characterization of triple-negative/basal-like breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9:R65.
Prat A, Perou CM. Deconstructing the molecular portraits of breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2011;5:5–23.
Gelmon K, Dent R, Mackey JR, Laing K, McLeod D, Verma S. Targeting triple-negative breast cancer: optimising therapeutic outcomes. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. 2012;23:2223–34.
Thomssen C, Pierga JY, Pritchard KI, Biganzoli L, Cortes-Funes H, Petrakova K, Kaufman B, Duenne A, Smith I. First-line bevacizumab-containing therapy for triple-negative breast cancer: analysis of 585 patients treated in the ATHENA study. Oncology. 2012;82:218–27.
Rouzier R, Perou CM, Symmans WF, Ibrahim N, Cristofanilli M, Anderson K, Hess KR, Stec J, Ayers M, Wagner P, Morandi P, Fan C, Rabiul I, Ross JS, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L. Breast cancer molecular subtypes respond differently to preoperative chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2005;11:5678–85.
Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L, Moore DT, Collichio F, Ollila DW, Sartor CI, Graham ML, Perou CM. The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2007;13:2329–34.
Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, Kearney T, Higgins SA, Weidhaas J, Harris L, Hait W, Toppmeyer D. Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5652–7.
Kassam F, Enright K, Dent R, Dranitsaris G, Myers J, Flynn C, Fralick M, Kumar R, Clemons M. Survival outcomes for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: implications for clinical practice and trial design. Clin Breast Cancer. 2009;9:29–33.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136:215–33.
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM. Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in drosophila. Cell. 2003;113:25–36.
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2000;403:901–6.
Jay C, Nemunaitis J, Chen P, Fulgham P, Tong AW. Mirna profiling for diagnosis and prognosis of human cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 2007;26:293–300.
Yu SL, Chen HY, Yang PC, Chen JJ. Unique microRNA signature and clinical outcome of cancers. DNA Cell Biol. 2007;26:283–92.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Menard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin GA, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce CM. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7065–70.
Blenkiron C, Goldstein LD, Thorne NP, Spiteri I, Chin SF, Dunning MJ, Barbosa-Morais NL, Teschendorff AE, Green AR, Ellis IO, Tavare S, Caldas C, Miska EA. MicroRNA expression profiling of human breast cancer identifies new markers of tumor subtype. Genome Biol. 2007;8:R214.
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M, Croce CM. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:2999–3004.
Sempere LF, Christensen M, Silahtaroglu A, Bak M, Heath CV, Schwartz G, Wells W, Kauppinen S, Cole CN. Altered microRNA expression confined to specific epithelial cell subpopulations in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:11612–20.
Zheng SR, Guo GL, Zhang W, Huang GL, Hu XQ, Zhu J, Huang QD, You J, Zhang XH. Clinical significance of miR-155 expression in breast cancer and effects of miR-155 ASO on cell viability and apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 2012;27:1149–55.
Mulrane L, Madden SF, Brennan DJ, Gremel G, McGee SF, McNally S, Martin F, Crown JP, Jirstrom K, Higgins DG, Gallagher WM, O’Connor DP. MiR-187 is an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer and confers increased invasive potential in vitro. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2012;18:6702–13.
Rivas MA, Venturutti L, Huang YW, Schillaci R, Huang TH, Elizalde PV. Downregulation of the tumor-suppressor miR-16 via progestin-mediated oncogenic signaling contributes to breast cancer development. Breast Cancer Res. 2012;14:R77.
Zhang Y, Yan LX, Wu QN, Du ZM, Chen J, Liao DZ, Huang MY, Hou JH, Wu QL, Zeng MS, Huang WL, Zeng YX, Shao JY. miR-125b is methylated and functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating the ETS1 proto-oncogene in human invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3552–62.
Lowery AJ, Miller N, McNeill RE, Kerin MJ. MicroRNAs as prognostic indicators and therapeutic targets: potential effect on breast cancer management. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2008;14:360–5.
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, Sensinger K, Wong L, Scott GK, Fedele V, Ginzinger D, Getts R, Haqq C. Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer biopsies. Mol Cancer. 2006;5:24.
Volinia S, Galasso M, Sana ME, Wise TF, Palatini J, Huebner K, Croce CM. Breast cancer signatures for invasiveness and prognosis defined by deep sequencing of microRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:3024–9.
Pinho FG, Frampton AE, Nunes J, Krell J, Alshaker H, Jacob J, Pellegrino L, Roca-Alonso L, de Giorgio A, Harding V, Waxman J, Stebbing J, Pchejetski D, Castellano L. Downregulation of microRNA-515-5p by the estrogen receptor modulates sphingosine kinase 1 and breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2013;73:5936–48.
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng L, Wu QL, Zeng YX, Shao JY. MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA. 2008;14:2348–60.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Kim SW, Li Z, Moore PS, Monaghan AP, Chang Y, Nichols M, John B. A sensitive non-radioactive northern blot method to detect small RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e98.
Zhu Y, Hoell P, Ahlemeyer B, Krieglstein J. PTEN: a crucial mediator of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Apoptosis Int J Program Cell Death. 2006;11:197–207.
Zhao H, Dupont J, Yakar S, Karas M, LeRoith D. PTEN inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by downregulating cell surface IGF-IR expression in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:786–94.
Huang TH, Wu F, Loeb GB, Hsu R, Heidersbach A, Brincat A, Horiuchi D, Lebbink RJ, Mo YY, Goga A, McManus MT. Up-regulation of miR-21 by HER2/neu signaling promotes cell invasion. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:18515–24.
Terao M, Fratelli M, Kurosaki M, Zanetti A, Guarnaccia V, Paroni G, Tsykin A, Lupi M, Gianni M, Goodall GJ, Garattini E. Induction of miR-21 by retinoic acid in estrogen receptor-positive breast carcinoma cells: biological correlates and molecular targets. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:4027–42.
Corcoran C, Friel AM, Duffy MJ, Crown J, O’Driscoll L. Intracellular and extracellular microRNAs in breast cancer. Clin Chem. 2011;57:18–32.
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo YY. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 2007;26:2799–803.
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:1026–33.
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, Klinge CM, Ramos KS, Colburn NH, Li Y. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene. 2008;27:4373–9.
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem. 2007;282:14328–36.
Song B, Wang C, Liu J, Wang X, Lv L, Wei L, Xie L, Zheng Y, Song X. MicroRNA-21 regulates breast cancer invasion partly by targeting tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010;29:29.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:647–58.
Weng L, Brown J, Eng C. PTEN induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through phosphoinositol-3-kinase/akt-dependent and -independent pathways. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:237–42.
Zheng T, Meng X, Wang J, Chen X, Yin D, Liang Y, Song X, Pan S, Jiang H, Liu L. PTEN- and p53-mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by FTY720 in gastric cancer cells and nude mice. J Cell Biochem. 2010;111:218–28.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grant Weihai Sci and teach development Grant (No. 2010-3-93).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare on conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, G., Liang, X., Wang, D. et al. High expression of miR-21 in triple-negative breast cancers was correlated with a poor prognosis and promoted tumor cell in vitro proliferation. Med Oncol 31, 57 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0057-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0057-x