Abstract
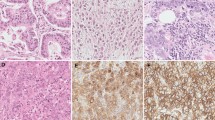
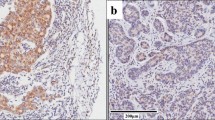
This study investigated the expression of the phospholipase C epsilon 1 (PLCE1) and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB)-related proteins in Kazakh patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Tissue microarrays of 90 ethnic Kazakh patients with ESCC and exhibiting clinical characteristics were analyzed for protein expression of PLCE1, IKKβ, IKBα, p50, and p65 by immunohistochemistry. Correlations between histoscores of PLCE1 and NF-κB-related proteins were determined using Spearman’s rank correlation tests. Expression of PLCE1 and NF-κB-related proteins significantly increased in tumor tissues compared with normal esophageal tissues (P = 9.48 × 10−7, 1.24 × 10−5, 0.004, 0.003, and 2.83 × 10−5, respectively). Upregulation of PLCE1 was significantly correlated with advanced tumor-node-metastasis stages (P = 0.018) and lymph node metastasis (P = 0.003). Overexpression of IKKβ and IKBα was associated with ESCC stages I/II (P = 3.36 × 10−4 and 0.022, respectively). Increased expression of p50 was significantly higher in patients with lymph node metastasis than without lymph node metastasis (P = 0.048). Elevated expression of p65 protein was significantly correlated with poor and moderately differentiated ESCC and depth of tumor invasion (P = 0.026 and 0.010, respectively). Significant positive correlations were observed between the expression of PLCE1 and NF-κB-related proteins, especially IKKβ (r = 0.246 and P = 0.025) and p50 (r = 0.244 and P = 0.024). These results suggest, for the first time, that upregulation of PLCE1 is correlated with increased expression of NF-κB-related proteins in Kazakh patients with ESCC, suggesting that interaction between PLCE1 with the NF-κB signal pathway may be responsible for the carcinogenesis of ESCC, such as ESCC-related inflammation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tytgat GN, Bartelink H, Bernards R, Giaccone G, van Lanschot JJ, Offerhaus GJ, et al. Cancer of the esophagus and gastric cardia: recent advances. Dis Esophagus. 2004;17:10–26.
Zhang YM. The distribution of esophageal cancer in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Yixueyuan Xuebao. 1988;11:139–44.
Lu XM, Monnier-Benoit S, Mo LZ, Xu SY, Pretet JL, Liu Z, et al. Human papillomavirus in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma of the high-risk Kazakh ethnic group in Xinjiang, China. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008;34:765–70.
Abnet CC, Freedman ND, Hu N, Wang Z, Yu K, Shu XO, et al. A shared susceptibility locus in PLCE1 at 10q23 for gastric adenocarcinoma and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2010;42:764–7.
Wang LD, Zhou FY, Li XM, Sun LD, Song X, Jin Y, et al. Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54. Nat Genet. 2010;42:759–63.
Wu C, Hu Z, He Z, Jia W, Wang F, Zhou Y, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies three new susceptibility loci for esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma in Chinese populations. Nat Genet. 2011;43:679–84.
Cui XB, Chen YZ, Pang XL, Liu W, JM Hu, Li SG, et al. Multiple polymorphisms within the PLCE1 are associated with esophageal cancer via promoting the gene expression in a Chinese Kazakh population. Gene. 2013;530:315–22.
Peng Z, Zhang F, Zhou C, Ling Y, Bai S, Liu W, et al. Genome-wide search for loss of heterozygosity in Chinese patients with sporadic colorectal cancer. Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 2003;34:39–48.
Wang X, Zbou C, Qiu G, Fan J, Tang H, Peng Z. Screening of new tumor suppressor genes in sporadic colorectal cancer patients. Hepatogastroenterology. 2008;55:2039–44.
Wang X, Zhou C, Qiu G, Yang Y, Yan D, Xing T, et al. Phospholipase C epsilon plays a suppressive role in incidence of colorectal cancer. Med Oncol. 2012;29:1051–8.
Ling Y, Chunli L, Xiaohou W, Qiaoling Z. Involvement of the PLC epsilon/PKCalpha pathway in human BIU-87 bladder cancer cell proliferation. Cell Biol Int. 2011;35:1031–6.
Ou L, Guo Y, Luo C, Wu X, Zhao Y, Cai X. RNA interference suppressing PLCE1 gene expression decreases invasive power of human bladder cancer T24 cell line. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2010;200:110–9.
Bourguignon LY, Gilad E, Brightman A, Diedrich F, Singleton P. Hyaluronan–CD44 interaction with leukemia-associated RhoGEF and epidermal growth factor receptor promotes Rho/Ras co-activation, phospholipase C epsilon-Ca2+ signaling, and cytoskeleton modification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:14026–40.
Ma H, Wang LE, Liu Z, Sturgis EM, Wei Q. Association between novel PLCE1 variants identified in published esophageal cancer genome-wide association studies and risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:258.
Bai Y, Edamatsu H, Maeda S, Saito H, Suzuki N, Satoh T, et al. Crucial role of phospholipase C epsilon in chemical carcinogen-induced skin tumor development. Cancer Res. 2004;64:8808–10.
Oka M, Edamatsu H, Kunisada M, Hu L, Takenaka N, Dien S, et al. Enhancement of ultraviolet B-induced skin tumor development in phospholipase C epsilon-knockout mice is associated with decreased cell death. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31:1897–902.
Li M, Edamatsu H, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Kataoka T. Phospholipase C epsilon promotes intestinal tumorigenesis of Apc (Min/+) mice through augmentation of inflammation and angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1424–32.
Oka M, Edamatsu H, Kunisada M, Hu L, Takenaka N, Sakaguchi M, et al. Phospholipase C varepsilon has a crucial role in ultraviolet B-induced neutrophil-associated skin inflammation by regulating the expression of CXCL1/KC. Lab Invest. 2011;91:711–8.
Ikuta S, Edamatsu H, Li M, Hu L, Kataoka T. Crucial role of phospholipase C epsilon in skin inflammation induced by tumor-promoting phorbol ester. Cancer Res. 2008;68:64–72.
Mercurio F, Zhu H, Murray BW, Shevchenko A, Bennett BL, Li J, et al. IKK-1 and IKK-2: cytokine-activated IkappaB kinases essential for NF-kappaB activation. Science. 1997;278:860–6.
Jacobs MD, Harrison SC. Structure of an IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB complex. Cell. 1998;95:749–58.
Li B, Li YY, Tsao SW, Cheung AL. Targeting NF-kappaB signaling pathway suppresses tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis of human esophageal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:2635–44.
Kang MR, Kim MS, Kim SS, Ahn CH, Yoo NJ, Lee SH. NF-kappaB signalling proteins p50/p105, p52/p100, RelA, and IKKepsilon are over-expressed in oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Pathology. 2009;41:622–5.
Oestreich EA, Malik S, Goonasekera SA, Blaxall BC, Kelley GG, Dirksen RT, et al. Epac and phospholipase C epsilon regulate Ca2+ release in the heart by activation of protein kinase C epsilon and calcium–calmodulin kinase II. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:1514–22.
Rhee SG. Regulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:281–312.
Kelm MK, Weinberg RJ, Criswell HE, Breese GR. The PLC/IP 3 R/PKC pathway is required for ethanol-enhanced GABA release. Neuropharmacology. 2010;58:1179–86.
Karin M. Signal transduction from cell surface to nucleus in development and disease. FASEB J. 1992;6:2581–90.
Park KA, Byun HS, Won M, Yang KJ, Shin S, Piao L, et al. Sustained activation of protein kinase C downregulates nuclear factor-kappaB signaling by dissociation of IKK-gamma and Hsp90 complex in human colonic epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28:71–80.
Hongo M, Nagasaki Y, Shoji T. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: orient to occident. Effects of chronology, geography and ethnicity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:729–35.
Cheung WY, Liu G. Genetic variations in esophageal cancer risk and prognosis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2009;38:75–91.
Chen YZ, Cui XB, Hu JM, Zhang WJ, Li SG, Yang L, et al. Overexpression of PLCE1 in Kazakh esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: implications in cancer metastasis and aggressiveness. APMIS. 2013;121:908–18.
Hu H, Yang J, Sun Y, Yang Y, Qian J, Jin L, et al. Putatively functional PLCE1 variants and susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC): a case–control study in eastern Chinese populations. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:2403–10.
Su C, Chen Z, Luo H, Su Y, Liu W, Cai L, et al. Different patterns of NF-kappaB and Notch1 signaling contribute to tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011;30:85.
Tian F, Zang WD, Hou WH, Liu HT, Xue LX. Nuclear factor-kB signaling pathway constitutively activated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines and inhibition of growth of cells by small interfering RNA. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2006;38:318–26.
Han Y, Guo XH, Zheng QF, Zhu YL, Fan YY, Zhang XY. Down-regulation of platelet-derived growth factor-D expression blockades NF-kappaB pathway to inhibit cell proliferation and invasion as well as induce apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;40:2473–83.
Wang F, He W, Wang PF, Fan Q. NF-kappaBP65 promotes invasion and metastasis of oesophageal squamous cell cancer by regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Biol Int. 2013;37:780–8.
Tian F, Zhang C, Tian W, Jiang Y, Zhang X. Comparison of the effect of p65 siRNA and curcumin in promoting apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and in nude mice. Oncol Rep. 2012;28:232–40.
Xia J, Wang F, Wang L, Fan Q. Elevated serine protease HtrA1 inhibits cell proliferation, reduces invasion, and induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by blocking the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:317–28.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–44.
Wang LD, Yang HH, Fan ZM, Lu XD, Wang JK, Liu XL, et al. Cytological screening and 15 years’ follow-up (1986–2001) for early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and precancerous lesions in a high-risk population in Anyang County, Henan Province, Northern China. Cancer Detect Prev. 2005;29:317–22.
Wen DG, Wang SJ, Zhang LW, Zhou W, Yu WF, Wang XL. Natural history of esophageal and gastric cardia precursor by repetitive endoscope screening with 425 adults in a high-risk area in China. Cancer Epidemiol. 2009;33:108–12.
Zhang GH, Su M, Tian DP, Huang HH, Wu XY, Zheng RM, et al. Analysis of basement membrane structure and inflammation during the development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in the Chinese Chaoshan high risk region. Cancer Invest. 2008;26:296–305.
Pikarsky E, Porat RM, Stein I, Abramovitch R, Amit S, Kasem S, et al. NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature. 2004;431:461–6.
Hopewell EL, Zhao W, Fulp WJ, Bronk CC, Lopez AS, Massengill M, et al. Lung tumor NF-kappaB signaling promotes T cell-mediated immune surveillance. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:2509–22.
Jang BC, Kim DH, Park JW, Kwon TK, Kim SP, Song DK, et al. Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in macrophages by catalase: role of NF-kappaB and PI3 K signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;316:398–406.
Balkwill F, Charles KA, Mantovani A. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:211–7.
Harada YEH, Kataoka T. PLCε cooperates with the NF-κB pathway to augment TNFα-stimulated CCL2/MCP1 expression in human keratinocyte. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;414:106–11.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81160301, 81360358, 81260301), Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2010DFB34100 and 2012AA02A503) and Maxin Pathology Fund of China (m1108).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiao-bin Cui and Xue-lian Pang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Xb., Pang, Xl., Li, S. et al. Elevated expression patterns and tight correlation of the PLCE1 and NF-κB signaling in Kazakh patients with esophageal carcinoma. Med Oncol 31, 791 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0791-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0791-5