Abstract
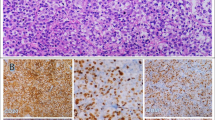
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common form of lymphoma. According to the clinical risk factors and biological heterogeneity, clinical outcome of DLBCL is extremely various, with 5-year survival rates between 30 and 80 %. Although the International Prognostic Index (IPI) remains the primary clinical tool used to predict outcome for patients with DLBCL, notable variability in outcome is still observed within the same IPI score. The cell division cycle 7 (CDC7) is a serine–threonine kinase, which is required to initiate DNA replication. Study showed that high expression of CDC7 was correlated with poor prognosis in patients with DLBCL. Whether CDC7 is an independent prognostic factor for DLBCL remains debatable. We studied the expression of CDC7 protein in 60 Chinese DLBCL patients with immunohistochemical analysis, 34 patients (56.7 %) categorized as low CDC7 expression and 26 patients (43.3 %) as high CDC7 expression. The median survival time of patients with low CDC7 expression was not achieved and that of high expression was 9 months (P = 0.027). A multivariate analysis showed that IPI score and Ann Arbor stage were independent prognostic factors in relation to patients’ OS (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that CDC7 expression level was positively correlated with IPI score and Ann Arbor stage (P < 0.001). The results suggest that CDC7 expression level in combination with IPI score and Ann Arbor stage can be specific prognostic factors for DLBCL patients. CDC7 could also be a potential therapeutic target in DLBCL, especially for ABC-DLBCL.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW. Tumors of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue. Lyon: IARC Press; 2001.
Fisher RI, Shah P. Current trends in large cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2003;17(10):948–1960.
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(25):1937–47.
Montagnoli A, Moll J, Colotta F. Targeting cell division cycle 7 kinase: a new approach for cancer therapy. Review. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(18):4503–8. [Epub 2010 July 20].
Krawczyk J, Egan C, Mulvihill M, et al. Increased activity of the S phase kinase Cdc7 is associated with poor outcome in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) [abstract]. Blood (ASH Annu Meet Abstr). 2009;114:Abstract nr 1914.
A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The International Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:987–994.
Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood. 2007;109:1857–61.
Hermine O, Haioun C, Lepage E, et al. Prognostic significance of bcl-2 protein expression in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte (GELA). Blood. 1996;87:265–72.
Alas S, Bonavida B. Rituximab inactivates signal transducer and activation of transcription 3 (STAT3) activity in B-non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma through inhibition of the interleukin 10 autocrine/paracrine loop and results in down-regulation of Bcl-2 and sensitization to cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5137–44.
Mounier N, Briere J, Gisselbrecht C, et al. Rituximab plus CHOP (R-CHOP) overcomes bcl-2—associated resistance to chemotherapy in elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Blood. 2003;101:4279–84.
Wilson K, Sehn LH, Berry B, et al. CHOP-R therapy overcomes the adverse prognostic influence of BCL-2 expression in DLBCL [abstract]. Proc Annu Meet Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2004;23:562a.
Lossos IS, Jones CD, Warnke R, et al. Expression of a single gene, BCL-6, strongly predicts survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2001;98:945–51.
Winter JN, Weller EA, Horning SJ, et al. Prognostic significance of Bcl-6 protein expression in DLBCL treated with CHOP or R-CHOP: a prospective correlative study. Blood. 2006;107:4207–13.
Takeda DY, Dutta A. DNA replication and progression through S phase. Oncogene. 2005;24:2827–43.
Acknowledgments
We have financial relationship with Tianjin cancer hospital that sponsored the research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Y., Wang, HQ. & Ba, Y. High expression of cell division cycle 7 protein correlates with poor prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Med Oncol 29, 3498–3503 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0223-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0223-y