Abstract
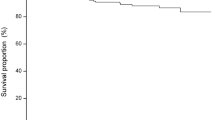
It has been suggested that type 2 diabetes mellitus may affect breast cancer prognosis, possibly due to increased diabetes-related comorbidity, or direct effects of insulin resistance and/or hyperinsulinemia. The aim of this study was to determine the impact of diabetes on disease-free survival (DFS) following mastectomy for breast cancer patients. The cases included in this retrospective study were selected from breast cancer women who had undergone mastectomy and completed adjuvant chemotherapy from 1998 to 2010. Patients were classified into two groups: diabetic and non-diabetic. Patients’ age, sex, menopausal status, body mass index (BMI), histopathological features, tumor size, lymph node involvement, hormone receptor and HER2-neu status, and treatment types were recorded. There were 483 breast cancer patients included in the study. Postmenopausal patients’ rate (53.7% vs. 36.8%, P = 0.016) and mean BMI levels were statistically higher (32.2 vs. 27.9, P = 0.007) in diabetic patients. There was no statistical difference for histological subgroup, grade, ER and PR positivity, HER2-neu overexpression rate, and tumor size between the diabetic and non-diabetic group. Lymph node involvements were statistically higher in diabetic patients compared with non-diabetic patients (P = 0.013). Median disease-free survival is 81 months (95% CI, 61.6–100.4) in non-diabetic patients and 36 months (95% CI, 13.6–58.4) in diabetic patients (P < 0.001). The odds ratio of recurrence was significantly increased in those with HER2-neu overexpression and lymph node involvement and decreased with PR-positive tumors. Our results suggest that diabetes is an independent prognostic factor for breast cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–53.
The DECODE Study Group. Age- and sex-specific prevalences of diabetes and impaired glucose regulation in 13 European cohorts. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:61–9.
Papa V, Costantino A, Belfiore A. Insulin receptor what role in breast cancer? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1997;8(8):306–12.
Van der Burg B, Rutteman GR, Blankenstein MA, de Laat SW, van Zoelen EJ. Mitogenic stimulation of human breast cancer cells in a growth factor-defined medium: synergistic action of insulin and estrogen. J Cell Physiol. 1988;134:101–8.
Belfiore A, Frittitta L, Costantino A, Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L, et al. Insulin receptors in breast cancer. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1996;784:173–88.
Mathieu MC, Clark GM, Allred DC, Goldfine ID, Vigneri R. Insulin receptor expression and clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1997;109:565–71.
Papa V, Belfiore A. Insulin receptors in breast cancer: biological and clinical role. J Endocrinol Invest. 1996;19:324–33.
Barone BB, Yeh HC, Snyder CF, Peairs KS, Stein KB, Derr RL. Long-term all-cause mortality in cancer patients with preexisting diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2008;300:2754–64.
Larsson SC, Mantzoros CS, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:856–62.
Peairs KS, Barone BB, Snyder CF, Yeh HC, Stein KB, Rl Derr, et al. Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(1):40–6.
Srokowski TP, Fang S, Hortobagyi GN, Giordano SH. Impact of diabetes mellitus on complications and outcomes of adjuvant chemotherapy in older patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2170–6.
Fleming ST, Rastogi A, Dmitrienko A, Jhonson KD. A comprehensive prognostic index to predict survival based on multiple comorbidities: a focus on breast cancer. Med Care. 1999;37:601–14.
Yancik R, Wesley MN, Ries LA, Havlik RJ, Edwards BK, Yates JW. Effect of age and comorbidity in postmenopausal breast cancer patients aged 55 years and older. JAMA. 2001;285:885–92.
Van de Poll-Franse LV, Houterman S, Janssen-Heijnen ML, Dercksen MW, Coebergh JW, Haak HR. Less aggressive treatment and worse overall survival in cancer patients with diabetes: a large population based analysis. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:1986–92.
Fleming ST, Pursley HG, Newman B, Pavlov D, Chen K. Comorbidity as a predictor of stage of illness for patients with breast cancer. Med Care. 2005;43:132–40.
Unterburger P, Sinop A, Noder W, Berger MR, Fink M, Edler L, et al. Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer. A retrospective follow-up study. Onkologie. 1990;13(1):17–20.
Li CI, Daling JR, Tang MT, Malone KE. Relationship between diabetes and risk of second primary contralateral breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;125(2):545–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaplan, M.A., Pekkolay, Z., Kucukoner, M. et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and prognosis in early stage breast cancer women. Med Oncol 29, 1576–1580 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-0109-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-0109-4