Abstract
Purpose
Recent studies revealed that metabolic stress influences the outcomes of breast cancer treatment. We sought to evaluate the prognostic effect of type 2 diabetes and find the molecular mechanism of relapses in postoperative HER-2+ breast cancer patients treated with HER-2 targeted therapy.
Materials and methods
We evaluated 190 HER-2+ breast cancer patients (pT1-4N0-2M0) who were treated with surgical resection and trastuzumab (HER-2 targeted therapy) between 2006 and 2015. Survival outcomes and failure patterns were compared between such patients with (n = 12) and without (n = 178) type 2 diabetes.
Results
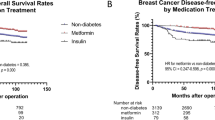
The median follow-up period was 42.4 months (range 12.0–124.7 months). Twenty-one patients (11.1%) showed relapse (including nine patients with locoregional failure), and three patients (1.6%) died as a result of cancer relapse. One-third of the patients with diabetes experienced relapse (4/12, 33.3%). The 3-year disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) rates were 90.7% and 98.6%, respectively. Diabetic patients showed shorter DFS compared with non-diabetic patients (p = 0.006, 74.1% vs. 91.9%). OS was also shorter in diabetic patients compared with non-diabetic patients (p = 0.017, 91.7% vs. 99.1%). Of our interest, the levels of HER-3 and its ligand neuregulin-1 were significantly increased in the tumor specimen in HER-2+ breast cancer patients suffering with type 2 diabetes than that in the euglycemic control group.
Conclusions
Type 2 diabetes was associated with detrimental effects on survival in postoperative HER-2+ breast cancer patients who were treated with trastuzumab. The poor prognostic effect of diabetes in HER-2+ breast cancer patients could be associated with the high levels of HER-3 and neuregulin 1, thus it should be considered and evaluated more.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohkuma T, Peters SAE, Woodward M. Sex differences in the association between diabetes and cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 121 cohorts including 20 million individuals and one million events. Diabetologia. 2018;61:2140–54.
Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA, et al. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:1674–85.
Coller HA. Is cancer a metabolic disease? Am J Pathol. 2014;184:4–17.
Seyfried TN, Flores RE, Poff AM, D’Agostino DP. Cancer as a metabolic disease: implications for novel therapeutics. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:515–27.
Gristina V, Cupri MG, Torchio M, Mezzogori C, Cacciabue L, Danova M. Diabetes and cancer: a critical appraisal of the pathogenetic and therapeutic links. Biomed Rep. 2015;3:131–6.
Chowdhury TA. Diabetes and cancer. Qjm. 2010;103:905–15.
Kasznicki J, Sliwinska A, Drzewoski J. Metformin in cancer prevention and therapy. Ann Transl Med. 2014;2:57.
Calip GS, Yu O, Hoskins KF, Boudreau DM. Associations between diabetes medication use and risk of second breast cancer events and mortality. Cancer Causes Control. 2015;26:1065–77.
Yang SX, Polley E, Lipkowitz S. New insights on PI3K/AKT pathway alterations and clinical outcomes in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016;45:87–96.
Redaniel MT, Jeffreys M, May MT, Ben-Shlomo Y, Martin RM. Associations of type 2 diabetes and diabetes treatment with breast cancer risk and mortality: a population-based cohort study among British women. Cancer Causes Control. 2012;23:1785–95.
Choi Y, Park SK, Ahn KJ, Cho H, Kim TH, Yoon HK, et al. Being overweight or obese increases the risk of progression in triple-negative breast cancer after surgical resection. J Korean Med Sci. 2016;31:886–91.
Hauner D, Hauner H. Metabolic syndrome and breast cancer: is there a link? Breast Care (Basel). 2014;9:277–81.
Mu L, Zhu N, Zhang J, Xing F, Li D, Wang X. Type 2 diabetes, insulin treatment and prognosis of breast cancer. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;33:e2823.
Jiralerspong S, Kim ES, Dong W, Feng L, Hortobagyi GN, Giordano SH. Obesity, diabetes, and survival outcomes in a large cohort of early-stage breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:2506–14.
Bonifazi M, Franchi M, Rossi M, Zambelli A, Moja L, Zambon A, et al. Long term survival of HER2-positive early breast cancer treated with trastuzumab-based adjuvant regimen: a large cohort study from clinical practice. Breast. 2014;23:573–8.
de Alava E, Ocana A, Abad M, Montero JC, Esparis-Ogando A, Rodriguez CA, et al. Neuregulin expression modulates clinical response to trastuzumab in patients with metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2656–63.
Yang L, Li Y, Shen E, Cao F, Li L, Li X, et al. NRG1-dependent activation of HER3 induces primary resistance to trastuzumab in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2017;51:1553–62.
Park J, Sarode VR, Euhus D, Kittler R, Scherer PE. Neuregulin 1-HER axis as a key mediator of hyperglycemic memory effects in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:21058–63.
Britsch S. The neuregulin-I/ErbB signaling system in development and disease. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2007;190:1–65.
Ocana A, Vera-Badillo F, Seruga B, Templeton A, Pandiella A, Amir E. HER3 overexpression and survival in solid tumors: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:266–73.
Chiu CG, Masoudi H, Leung S, Voduc DK, Gilks B, Huntsman DG, et al. HER-3 overexpression is prognostic of reduced breast cancer survival: a study of 4046 patients. Ann Surg. 2010;251:1107–16.
Lee Y, Ma J, Lyu H, Huang J, Kim A, Liu B. Role of erbB3 receptors in cancer therapeutic resistance. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014;46:190–8.
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ, et al. Strategies for subtypes-dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1736–47.
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH, et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3997–4013.
Garcia Vicente AM, Soriano Castrejon A, Leon Martin A, Chacon Lopez-Muniz I, Munoz Madero V, Munoz Sanchez Mdel M, et al. Molecular subtypes of breast cancer: metabolic correlation with (1)(8)F-FDG PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:1304–11.
Ferroni P, Riondino S, Buonomo O, Palmirotta R, Guadagni F, Roselli M. Type 2 diabetes and breast cancer: the interplay between impaired glucose metabolism and oxidant stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:183928.
Davis AA, Kaklamani VG. Metabolic syndrome and triple-negative breast cancer: a new paradigm. Int J Breast Cancer. 2012;2012:809291.
Park B, Yee C, Lee KM. The effect of radiation on the immune response to cancers. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:927–43.
Ma J, Lyu H, Huang J, Liu B. Targeting of erbB3 receptor to overcome resistance in cancer treatment. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:105.
Davis NM, Sokolosky M, Stadelman K, Abrams SL, Libra M, Candido S, et al. Deregulation of the EGFR/PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTORC1 pathway in breast cancer: possibilities for therapeutic intervention. Oncotarget. 2014;5:4603–50.
Leung WY, Roxanis I, Sheldon H, Buffa FM, Li JL, Harris AL, et al. Combining lapatinib and pertuzumab to overcome lapatinib resistance due to NRG1-mediated signalling in HER2-amplified breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:5678–94.
Guenancia C, Lefebvre A, Cardinale D, Yu AF, Ladoire S, Ghiringhelli F, et al. Obesity as a risk factor for anthracyclines and trastuzumab cardiotoxicity in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:3157–65.
Kim HJ, Kwon H, Lee JW, Kim HJ, Lee SB, Park HS, et al. Metformin increases survival in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-positive breast cancer patients with diabetes. Breast Cancer Res. 2015;17:64.
Acknowledgements
The biospecimens and data used in this study were provided by the Biobank of Inje University PAIK Hospital (InJeBiobank), a member of Korea Biobank Network.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI, HI14C1277), the Bio-Synergy Research Project (NRF-2017M3A9C4065956) of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and Basic Science Research Program (NRF-2018R1A2B6003878) through the National Research Foundation to J.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, A., Jo, S., Lee, C. et al. Diabetes as a prognostic factor in HER-2 positive breast cancer patients treated with targeted therapy. Breast Cancer 26, 672–680 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-019-00967-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-019-00967-2