Abstract
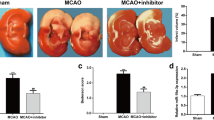
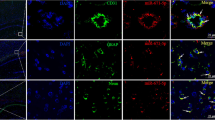
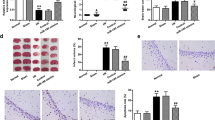
The mechanism contributing to blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption, involved in poststroke edema and hemorrhagic transformation, is important but elusive. We investigated microRNA-21 (miR-21)-mediated mechanism in the disruption of BBB following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. Rats with cerebral I/R injury were prepared after middle cerebral artery occlusion and subsequent reperfusion. The underlying regulatory mechanisms of miR-382 were investigated with treatment of miR-382 mimics, miR-382 inhibitors, or SB203580 (an inhibitor of the MAPK signaling pathway) prior to I/R modeling. Compared with sham-operated rats, rats following I/R showed increased Longa’s scores, ischemic hemisphere volume, cerebral infarct volume, EB content in brain tissues, enhanced levels of p38, iNOS, and MMP-9. The ectopic expression of miR-21 by mimics and MAPK signaling inhibition by SB203580 reduced Longa’s scores, ischemic hemisphere volume, cerebral infarct volume, EB content in brain tissues, decreased levels of p38, MAP2K3, iNOS, and MMP-9. The luciferase activity determination showed miR-21 bound to MAP2K3 in its 3′UTR. miR-21 downregulation mediated by inhibitors appeared to yield an opposed trend. We also found that MAPK signaling inhibition by SB203580 could rescue rats with treatment of miR-382 inhibitors. The study highlights the neuroprotective role of MiR-21 during cerebral I/R injury and its preventive effect against BBB disruption by blocking the MAPK signaling pathway via targeted inhibition of MAP2K3, potentially opening a novel therapeutic avenue for the treatment of cerebral ischemia.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen CL, Bayraktutan U (2009) Oxidative stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int J Stroke : Official J Int Stroke Soc 4(6):461–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-4949.2009.00387.x
Ansar S, Eftekhari S, Waldsee R, Nilsson E, Nilsson O, Saveland H, Edvinsson L (2013) MAPK signaling pathway regulates cerebrovascular receptor expression in human cerebral arteries. BMC Neurosci 14:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-14-12
Belayev L, Busto R, Zhao W, Ginsberg MD (1996) Quantitative evaluation of blood-brain barrier permeability following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res 739(1–2):88–96
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Germano SM, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski HM (1986) Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke 17(6):1304–1308
Buatti JM, Friedman WA, Theele DP, Bova FJ, Mendenhall WM (1996) The lazaroid U74389G protects normal brain from stereotactic radiosurgery-induced radiation injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 34(3):591–597
Buller B, Liu X, Wang X, Zhang RL, Zhang L, Hozeska-Solgot A, Chopp M, Zhang ZG (2010) MicroRNA-21 protects neurons from ischemic death. FEBS J 277(20):4299–4307. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07818.x
Bushi D, Stein ES, Golderman V, Feingold E, Gera O, Chapman J, Tanne D (2017) A linear temporal increase in thrombin activity and loss of its receptor in mouse brain following ischemic stroke. Front Neurol 8:138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00138
Che N, Ma Y, Xin Y (2017) Protective role of Fucoidan in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of MAPK signaling pathway. Biomol Ther 25(3):272–278. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2016.098
Chen J, Graham SH, Zhu RL, Simon RP (1996) Stress proteins and tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia. J Cerebral Blood Flow Metabolism : Official J Int Soc Cerebral Blood Flow Metabolism 16(4):566–577. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004647-199607000-00006
Cho HJ, Liu G, Jin SM, Parisiadou L, Xie C, Yu J, Sun L, Ma B, Ding J, Vancraenenbroeck R, Lobbestael E, Baekelandt V, Taymans JM, He P, Troncoso JC, Shen Y, Cai H (2013) MicroRNA-205 regulates the expression of Parkinson's disease-related leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 protein. Hum Mol Genet 22(3):608–620. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/dds470
Chumboatong W, Thummayot S, Govitrapong P, Tocharus C, Jittiwat J, Tocharus J (2017) Neuroprotection of agomelatine against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through an antiapoptotic pathway in rat. Neurochem Int 102:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2016.12.011
Deng X, Zhong Y, Gu L, Shen W, Guo J (2013) MiR-21 involve in ERK-mediated upregulation of MMP9 in the rat hippocampus following cerebral ischemia. Brain Res Bull 94:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.02.007
Di Y, Lei Y, Yu F, Changfeng F, Song W, Xuming M (2014) MicroRNAs expression and function in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. J Molecular Neuroscience: MN 53(2):242–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0293-8
Ge X, Han Z, Chen F, Wang H, Zhang B, Jiang R, Lei P, Zhang J (2015) MiR-21 alleviates secondary blood-brain barrier damage after traumatic brain injury in rats. Brain Res 1603:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.01.009
Guo YB, Ji TF, Zhou HW, Yu JL (2017) Effects of microRNA-21 on nerve cell regeneration and neural function recovery in diabetes mellitus combined with cerebral infarction rats by targeting PDCD4. Mol Neurobiol 55:2494–2505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0484-8
Hao JL, Li YF, Li RS (2013) A novel mechanism of NALP3 inducing ischemia reperfusion injury by activating MAPK pathway in acute renal failure. Med Hypotheses 80(4):463–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2012.12.041
Heeba GH, El-Hanafy AA (2012) Nebivolol regulates eNOS and iNOS expressions and alleviates oxidative stress in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Life Sci 90(11–12):388–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2011.12.001
Hu H, Jiang W, Xi X, Zou C, Ye Z (2014) MicroRNA-21 attenuates renal ischemia reperfusion injury via targeting caspase signaling in mice. Am J Nephrol 40(3):215–223. https://doi.org/10.1159/000368202
Hughes JN, Im MH (2016) Teacher-student relationship and peer disliking and liking across grades 1-4. Child Dev 87(2):593–611. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12477
Jiao G, Pan B, Zhou Z, Zhou L, Li Z, Zhang Z (2015) MicroRNA-21 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in H(2)O(2)-stimulated rat spinal cord neurons. Mol Med Rep 12(5):7011–7016. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4265
Kadera BE, Li L, Toste PA, Wu N, Adams C, Dawson DW, Donahue TR (2013) MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumor-associated fibroblasts promotes metastasis. PLoS One 8(8):e71978. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071978
Kim SW, Yu YM, Piao CS, Kim JB, Lee JK (2004) Inhibition of delayed induction of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase attenuates kainic acid-induced neuronal loss in the hippocampus. Brain Res 1007(1–2):188–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2004.02.009
Kovalska M, Kovalska L, Pavlikova M, Janickova M, Mikuskova K, Adamkov M, Kaplan P, Tatarkova Z, Lehotsky J (2012) Intracellular signaling MAPK pathway after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurochem Res 37(7):1568–1577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0752-y
Kwak HJ, Kim YJ, Chun KR, Woo YM, Park SJ, Jeong JA, Jo SH, Kim TH, Min HS, Chae JS, Choi EJ, Kim G, Shin SH, Gwak HS, Kim SK, Hong EK, Lee GK, Choi KH, Kim JH, Yoo H, Park JB, Lee SH (2011) Downregulation of Spry2 by miR-21 triggers malignancy in human gliomas. Oncogene 30(21):2433–2442. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.620
Lim AK, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Ma FY, Ozols E, Thomas MC, Flavell RA, Davis RJ, Tesch GH (2009) Role of MKK3-p38 MAPK signalling in the development of type 2 diabetes and renal injury in obese db/db mice. Diabetologia 52(2):347–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-008-1215-5
Liu F, Zheng S, Liu T, Liu Q, Liang M, Li X, Sheyhidin I, Lu X, Liu W (2013) MicroRNA-21 promotes the proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in Eca109 via activating ERK1/2/MAPK pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 381(1–2):115–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1693-8
Liu X, Li Z, Song Y, Wang R, Han L, Wang Q, Jiang K, Kang C, Zhang Q (2016) AURKA induces EMT by regulating histone modification through Wnt/beta-catenin and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 7(22):33152–33164. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8888
Min XL, Wang TY, Cao Y, Liu J, Li JT, Wang TH (2015) MicroRNAs: a novel promising therapeutic target for cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury? Neural Regen Res 10(11):1799–1808. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.170302
Ma N, Bai J, Zhang W, Luo H, Zhang X, Liu D, Qiao C (2016) Trimetazidine protects against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury via effects on cardiac miRNA21 expression, Akt and the Bcl2/Bax pathway. Mol Med Rep 14(5):4216–4222. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5773
Ma J, Shui S, Han X, Guo D, Li T, Yan L (2017) microRNA-200a silencing protects neural stem cells against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One 12(2):e0172178. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0172178
Mei Y, Bian C, Li J, Du Z, Zhou H, Yang Z, Zhao RC (2013) miR-21 modulates the ERK-MAPK signaling pathway by regulating SPRY2 expression during human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. J Cell Biochem 114(6):1374–1384. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24479
Qin Y, Yu Y, Dong H, Bian X, Guo X, Dong S (2012) MicroRNA 21 inhibits left ventricular remodeling in the early phase of rat model with ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing cell apoptosis. Int J Med Sci 9(6):413–423. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.4514
Qiao S, Olson JM, Paterson M, Yan Y, Zaja I, Liu Y, Riess ML, Kersten JR, Liang M, Warltier DC, Bosnjak ZJ, Ge ZD (2015) MicroRNA-21 mediates Isoflurane-induced Cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury via Akt/nitric oxide synthase/mitochondrial permeability transition pore pathway. Anesthesiology 123(4):786–798. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000000807
Roy Choudhury G, Ryou MG, Poteet E, Wen Y, He R, Sun F, Yuan F, Jin K, Yang SH (2014) Involvement of p38 MAPK in reactive astrogliosis induced by ischemic stroke. Brain Res 1551:45–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.01.013
Su D, Ma J, Zhang Z, Tian Y, Shen B (2016) Protective effects of UCF-101 on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (CIR) is depended on the MAPK/p38/ERK signaling pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 36(6):907–914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0275-6
Sun J, Nan G (2016) The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway as a discovery target in stroke. J Molecular Neuroscience: MN 59(1):90–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0717-8
Sun Y, Gui H, Li Q, Luo ZM, Zheng MJ, Duan JL, Liu X (2013) MicroRNA-124 protects neurons against apoptosis in cerebral ischemic stroke. CNS Neuroscience Therapeutics 19(10):813–819. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12142
Tang XJ, Yang MH, Cao G, Lu JT, Luo J, Dai LJ, Huang KM, Zhang LI (2016) Protective effect of microRNA-138 against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Experimental Therapeutic Medicine 11(3):1045–1050. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2016.3021
Tao Z, Zhao H, Wang R, Liu P, Yan F, Zhang C, Ji X, Luo Y (2015) Neuroprotective effect of microRNA-99a against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. J Neurol Sci 355(1–2):113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2015.05.036
Tuo YL, Li XM, Luo J (2015) Long noncoding RNA UCA1 modulates breast cancer cell growth and apoptosis through decreasing tumor suppressive miR-143. European Rev Medical Pharmacological Sci 19(18):3403–3411
Verma P, Pandey RK, Prajapati P, Prajapati VK (2016) Circulating MicroRNAs: potential and emerging biomarkers for diagnosis of human infectious diseases. Front Microbiol 7:1274. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01274
Wu G, Zhu L, Yuan X, Chen H, Xiong R, Zhang S, Cheng H, Shen Y, An H, Li T, Li H, Zhang W (2017) Britanin ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inducing the Nrf2 protective pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal 27:754–768. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2016.6885
Xie X, Song J, Li G (2016) MiR-21a-5p suppresses bisphenol A-induced pre-adipocyte differentiation by targeting map2k3 through MKK3/p38/MAPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 473(1):140–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.03.066
Yang Q, Yang K, Li A (2014) microRNA-21 protects against ischemia-reperfusion and hypoxia-reperfusion-induced cardiocyte apoptosis via the phosphatase and tensin homolog/Akt-dependent mechanism. Mol Med Rep 9(6):2213–2220. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2068
Yang W, Shao J, Bai X, Zhang G (2015) Expression of plasma microRNA-1/21/ 208a/499 in myocardial ischemic reperfusion injury. Cardiology 130(4):237–241. https://doi.org/10.1159/000371792
Yu H, Wu M, Zhao P, Huang Y, Wang W, Yin W (2015) Neuroprotective effects of viral overexpression of microRNA-22 in rat and cell models of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Cell Biochem 116(2):233–241. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24960
Zhang L, Dong LY, Li YJ, Hong Z, Wei WS (2012) miR-21 represses FasL in microglia and protects against microglia-mediated neuronal cell death following hypoxia/ischemia. Glia 60(12):1888–1895. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22404
Zhang JF, Shi LL, Zhang L, Zhao ZH, Liang F, Xu X, Zhao LY, Yang PB, Zhang JS, Tian YF (2016) MicroRNA-25 negatively regulates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced cell apoptosis through Fas/FasL pathway. J Molecular Neuroscience : MN 58(4):507–516. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0712-0
Zhou J, Zhang J (2014) Identification of miRNA-21 and miRNA-24 in plasma as potential early stage markers of acute cerebral infarction. Mol Med Rep 10(2):971–976. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2245
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the reviewers for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experimental protocols of the present study were approved by the Animal Care Committee at Xianyang hospital, Yan’an University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, X., Wang, Y. & Zhang, D. microRNA-21 Confers Neuroprotection Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Alleviates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in Rats via the MAPK Signaling Pathway. J Mol Neurosci 65, 43–53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1067-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1067-5