Abstract
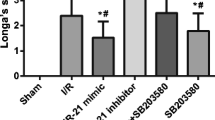
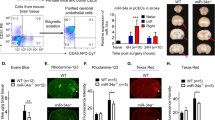
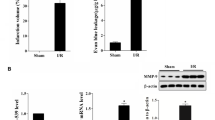
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption can induce further hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke (IS). miR-671-5p, a micro-RNA, is abundant in the cortex of mammalian brains. Herein, we investigated the roles and potential mechanisms for the effects of miR-671-5p on BBB permeability in IS. Results showed that miR-671-5p levels were significantly downregulated in the cerebral cortex of middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) C57/BL6 mice in vivo. miR-671-5p agomir administration via right intracerebroventricular injection significantly reduced infarct volume, improved neurological deficits, the axon of neurons and nerve fiber, attenuated cell injury and apoptosis, as well as reduced BBB permeability in MCAO/R mice. Treatment with miR-671-5p agomir alleviated tight junction proteins degradation, including claudin, occludin, and ZO-1 in MCAO/R mice, and these effects were reversed following NF-κB overexpression. Bend.3 brain endothelial cells were subjected to oxygen and glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) treatment in vivo, and then miR-671-5p agomir was transfected into the cells. This resulted in reduction of cytotoxicity, improved cell viability, trans-endothelial electrical resistance, reduced fluorescein sodium permeability, and inhibited tight junction degradation in Bend.3 OGD/R cells. However, these effects were reversed following NF-κB overexpression. These results demonstrated that upregulation of miR-671-5p in IS models in vivo and in vitro alleviated BBB permeability by targeting NF-κB/MMP-9. In summary, miR-671-5p is a potential therapeutic target for protecting BBB permeability in IS to minimize cerebral hemorrhage transformation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author's email.
References
Mendelson SJ, Prabhakaran S (2021) Diagnosis and Management of Transient Ischemic Attack and Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Review. JAMA 325(11):1088–1098. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.26867
Campbell BCV, Khatri P (2020) Stroke. Lancet 396(10244):129–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31179-X
Phipps MS, Cronin CA (2020) Management of acute ischemic stroke. BMJ 368:l6983. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l6983
Feske SK (2021) Ischemic Stroke. Am J Med 134(12):1457–1464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2021.07.027
Ronaldson PT, Davis TP (2020) Regulation of blood-brain barrier integrity by microglia in health and disease. A therapeutic opportunity J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 40(1_suppl):6–24. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X20951995
Abdullahi W, Tripathi D, Ronaldson PT (2018) Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 315(3):C343–C356. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00095.2018
Saleem S, Wang D, Zhao T, Sullivan RD, Reed GL (2021) Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Expression is Enhanced by Ischemia and Tissue Plasminogen Activator and Induces Hemorrhage, Disability and Mortality in Experimental Stroke. Neuroscience 460:120–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.01.003
Eyileten C, Wicik Z, De Rosa S, Mirowska-Guzel D, Soplinska A, Indolfi C, Jastrzebska-Kurkowska I, Czlonkowska A et al (2018) MicroRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Ischemic Stroke-A Comprehensive Review and Bioinformatic Analysis. Cells 7(12):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120249
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(3):203–222. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.246
Qian Y, Chopp M, Chen J (2020) Emerging role of microRNAs in ischemic stroke with comorbidities. Exp Neurol 331:113382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113382
Eyileten C, Sharif L, Wicik Z, Jakubik D, Jarosz-Popek J, Soplinska A, Postula M, Czlonkowska A et al (2021) The Relation of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor with MicroRNAs in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Ischemic Stroke. Mol Neurobiol 58(1):329–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02101-2
Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Yin K-J (2019) Noncoding RNAs and Stroke. Neuroscientist 25(1):22–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858418769556
Piwecka M, Glažar P, Hernandez-Miranda LR, Memczak S, Wolf SA, Rybak-Wolf A, Filipchyk A, Klironomos F et al (2017) Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science 357(6357):eaam8526. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aam8526
Kleaveland B, Shi CY, Stefano J, Bartel DP (2018) A Network of Noncoding Regulatory RNAs Acts in the Mammalian Brain. Cell 174(2):350-362.e17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.05.022
Ma C, Nie Z-K, Guo H-M, Kong Y (2020) MiR-671–5p plays a promising role in restraining osteosarcoma cell characteristics through targeting TUFT1. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 34(7):e22490. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22490
Lin J-C, Kuo C-Y, Tsai J-T, Liu W-H (2021) miR-671–5p Inhibition by MSI1 Promotes Glioblastoma Tumorigenesis via Radioresistance, Tumor Motility and Cancer Stem-like Cell Properties. Biomedicines 10(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010021
Yang C, Hawkins KE, Doré S, Candelario-Jalil E (2019) Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 316(2):C135–C153. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00136.2018
Zhang S, An Q, Wang T, Gao S, Zhou G (2018) Autophagy- and MMP-2/9-mediated Reduction and Redistribution of ZO-1 Contribute to Hyperglycemia-increased Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability During Early Reperfusion in Stroke. Neuroscience 377:126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.02.035
Mohamed HA, Said RS (2021) Coenzyme Q10 attenuates inflammation and fibrosis implicated in radiation enteropathy through suppression of NF-kB/TGF-β/MMP-9 pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 92:107347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107347
Ha S-H, Kwon K-M, Park J-Y, Abekura F, Lee Y-C, Chung T-W, Ha K-T, Chang HW et al (2019) Esculentoside H inhibits colon cancer cell migration and growth through suppression of MMP-9 gene expression via NF-kB signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem 120(6):9810–9819. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28261
Deng L, Guo Y, Liu J, Wang X, Chen S, Wang Q, Rao J, Wang Y et al (2021) miR-671-5p Attenuates Neuroinflammation via Suppressing NF-κB Expression in an Acute Ischemic Stroke Model. Neurochem Res 46(7):1801–1813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03321-1
Liu H, Zhao M-J, Wang Z-Y, Han Q-Q, Wu H-Y, Mao X-F, Wang Y-X (2019) Involvement of d-amino acid oxidase in cerebral ischaemia induced by transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in mice. Br J Pharmacol 176(17):3336–3349. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14764
Li F, Xu D, Hou K, Gou X, Lv N, Fang W, Li Y (2021) Pretreatment of Indobufen and Aspirin and their Combinations with Clopidogrel or Ticagrelor Alleviates Inflammasome Mediated Pyroptosis Via Inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway in Ischemic Stroke. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 16(4):835–853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-020-09978-9
Hayashi K, Hasegawa Y, Takemoto Y, Cao C, Takeya H, Komohara Y, Mukasa A, Kim-Mitsuyama S (2019) Continuous intracerebroventricular injection of Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide induces systemic organ dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Gerontol 120:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2019.02.007
Ji Y, Teng L, Zhang R, Sun J, Guo Y (2017) NRG-1β exerts neuroprotective effects against ischemia reperfusion-induced injury in rats through the JNK signaling pathway. Neuroscience 362:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.08.032
Wang C, Jiang Q, Zhao P (2022) Sevoflurane exposure during the second trimester induces neurotoxicity in offspring rats by hyperactivation of PARP-1. Psychopharmacology 239(9):3031–3045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-022-06188-4
Ding Y-X, Eerduna G-W, Duan S-J, Li T, Liu R-X, Zhang L-M, Wang T, Fu F-H (2021) Escin ameliorates the impairments of neurological function and blood brain barrier by inhibiting systemic inflammation in intracerebral hemorrhagic mice. Exp Neurol 337:113554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113554
Xu S-Y, Bian H-J, Shu S, Xia S-N, Gu Y, Zhang M-J, Xu Y, Cao X (2021) AIM2 deletion enhances blood-brain barrier integrity in experimental ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther 27(10):1224–1237. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13699
Qi Z, Liang J, Pan R, Dong W, Shen J, Yang Y, Zhao Y, Shi W et al (2016) Zinc contributes to acute cerebral ischemia-induced blood-brain barrier disruption. Neurobiol Dis 95:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2016.07.003
Ng FC, Churilov L, Yassi N, Kleinig TJ, Thijs V, Wu TY, Shah DG, Dewey HM et al (2021) Microvascular Dysfunction in Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Hypoperfusion Within the Infarct Posttreatment Are Associated With Cerebral Edema. Stroke 53(5):1579-1605.https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.036104
D’Souza A, Dave KM, Stetler RA, Manickam DS (2021) Targeting the blood-brain barrier for the delivery of stroke therapies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 171:332–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.01.015
Arumugam TV, Baik S-H, Balaganapathy P, Sobey CG, Mattson MP, Jo D-G (2018) Notch signaling and neuronal death in stroke. Prog Neurobiol 165–167:103–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2018.03.002
Walter L, Canup B, Pujada A, Bui TA, Arbasi B, Laroui H, Merlin D, Garg P (2020) Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) limits reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and DNA damage in colitis-associated cancer. Cell Death Dis 11(9):767. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02959-z
Zeng C, Wang D, Chen C, Chen L, Chen B, Li L, Chen M, Xing H (2020) Zafirlukast protects blood-brain barrier integrity from ischemic brain injury. Chem Biol Interact 316:108915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108915
Liao B, Geng L, Zhang F, Shu L, Wei L, Yeung PKK, Lam KSL, Chung SK et al (2020) Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein exacerbates cerebral ischaemia injury by disrupting the blood-brain barrier. Eur Heart J 41(33):3169–3180. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa207
Bauer AT, Bürgers HF, Rabie T, Marti HH (2010) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates hypoxia-induced vascular leakage in the brain via tight junction rearrangement. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(4):837–848. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2009.248
Jiang X, Andjelkovic AV, Zhu L, Yang T, Bennett MVL, Chen J, Keep RF, Shi Y (2018) Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and recovery after ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 163–164:144–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.10.001
Liu W, Hendren J, Qin X-J, Shen J, Liu KJ (2009) Normobaric hyperoxia attenuates early blood-brain barrier disruption by inhibiting MMP-9-mediated occludin degradation in focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 108(3):811–820. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05821.x
Pan Y, Zhang Y, Yuan J, Ma X, Zhao Y, Li Y, Li F, Gong X et al (2020) Tetrahydrocurcumin mitigates acute hypobaric hypoxia-induced cerebral oedema and inflammation through the NF-κB/VEGF/MMP-9 pathway. Phytother Res 34(11):2963–2977. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6724
Zhang L, Graf I, Kuang Y, Zheng X, Haupt M, Majid A, Kilic E, Hermann DM et al (2021) Neural Progenitor Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity by NF-κB (Nuclear Factor-κB)-Dependent Regulation of ABCB1 (ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter B1) in Stroke Mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 41(3):1127–1145. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315031
Bell RD, Winkler EA, Singh I, Sagare AP, Deane R, Wu Z, Holtzman DM, Betsholtz C et al (2012) Apolipoprotein E controls cerebrovascular integrity via cyclophilin A. Nature 485(7399):512–516. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11087
Mondal S, Adhikari N, Banerjee S, Amin SA, Jha T (2020) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and its inhibitors in cancer: A minireview. Eur J Med Chem 194:112260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112260
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by funds from the Science and Technology Bureau of Yuzhong in Chongqing, Chongqing Science and Technology Bureau, and Chongqing Health Commission.
Funding
This study was partially supported by the General Topics of Basic Research and Frontier Exploration of Yuzhong district, Chongqing (20210121); Medical Research Project of Chongqing Science and Technology Bureau and Chongqing Health Commission (2022QNXM068); Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTB2022NSCQ-BHX0.684).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ling Deng participated in the conceptualization, design of methodology, writing, and editing the manuscript. Jiyu Zhang and Sha Chen contributed to the conceptualization, writing, reviewing, & editing the manuscript. Yu Wu, Xiaomei Fan, Tianrui Zuo, Qingwen Hu, Lu Jiang, and Shaolan Yang designed the methodology and performed experiments. Zhi Dong provided funding acquisition and administrated the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. All animal procedures were approved by the Ethical Committee of Chongqing Medical University. The authors have no ethical conflicts to disclose.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, L., Zhang, J., Chen, S. et al. miR-671-5p Upregulation Attenuates Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption in the Ischemia Stroke Model Via the NF-кB/MMP-9 Signaling Pathway. Mol Neurobiol 60, 3824–3838 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03318-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03318-7