Abstract
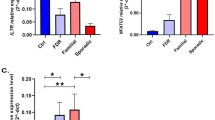
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder with several genetic and environmental factors being implicated in its pathogenesis. Protein prenylation as one of the important posttranslational modifications of proteins has crucial role in immune system regulation. In the current case–control study, we compared expression of five genes coding for the different subunits of proteins implicated in protein prenylation in 50 Iranian MS patients with those of healthy subjects. No significant difference has been found in FNTA and PGGT1B expressions between cases and controls. Spearman correlation analysis between FNTA relative expression and disease duration showed significant correlation in male patients (r = − 0.671, P = 0.024) but not female patients (r = 0.253, P = 0.12). FNTB expression was significantly higher in MS patients compared with healthy subjects. Spearman correlation analysis between FNTB relative expression and disease duration showed significant correlation in male patients (r = −0.876, P = 0.004) but not female patients (r = 0.296, P = 0.06). RABGGTA was significantly upregulated in total MS patients, total male patients, female patients aged between 30 and 40 and male patients aged >40 compared with corresponding control groups. RABGGTB was significantly downregulated in total MS patients, total female patients, and female patients aged > 40 compared with corresponding control groups. Totally, we demonstrated dysregulation of protein prenylation pathway in MS patients compared with healthy subjects. Future studies are needed to find the clinical implication of this pathway in MS patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Rashed F, Kochumon S, Usmani S, Sindhu S, Ahmad R (2017) Pam3CSK4 induces MMP-9 expression in human monocytic THP-1 cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 41:1993–2003
Cole SL, Vassar R (2006) Isoprenoids and Alzheimer’s disease: a complex relationship. Neurobiol Dis 22:209–222
Dunn SE, Youssef S, Goldstein MJ, Prod'Homme T, Weber MS, Zamvil SS, Steinman L (2006) Isoprenoids determine Th1/Th2 fate in pathogenic T cells, providing a mechanism of modulation of autoimmunity by atorvastatin. J Exp Med 203:401–412
Greenwood J, Steinman L, Zamvil SS (2006) Statin therapy in autoimmunity: from protein prenylation to immunomodulation. Nat RevImmuno l6
Harbo HF, Gold R, Tintore M (2013) Sex and gender issues in multiple sclerosis. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 6:237–248
Lacher SM, Bruttger J, Kalt B, Berthelet J, Rajalingam K, Wortge S, Waisman A (2017) HMG-CoA reductase promotes protein prenylation and therefore is indispensible for T-cell survival. Cell Death Dis 8:e2824
Magyari M (2016) Gender differences in multiple sclerosis epidemiology and treatment response. Dan Med J 63
Maurer-Stroh S, Washietl S, Eisenhaber F (2003) Protein prenyltransferases. Genome Biol 4:212
Mazdeh M, Taheri M, Sayad A, Bahram S, Omrani MD, Movafagh A, Inoko H, Akbari MT, Noroozi R, Hajilooi M, Solgi G (2016) HLA genes as modifiers of response to IFN-beta-1a therapy in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Pharmacogenomics 17:489–498
Mazdeh M, Noroozi R, Gharesouran J, Sayad A, Komaki A, Eftekharian MM, Habibi M, Toghi M, Taheri M (2017) The importance of VEGF-KDR signaling pathway genes should not be ignored when the risk of developing multiple sclerosis is taken into consideration. J Mol Neurosci 62:73–78
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, Fujihara K, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Montalban X, O'Connor P, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Thompson AJ, Waubant E, Weinshenker B, Wolinsky JS (2011) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 69:292–302
Sayad A, Ghafouri-FARD S, Omrani MD, Noroozi R, Taheri M (2017) Myxovirus resistance protein A (MxA) polymorphism is associated with IFNbeta response in Iranian multiple sclerosis patients. Neurol Sci 38:1093–1099
Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S, Solgi G, Sayad A, Mazdeh M, Omrani MD (2017) Determination of cytokine levels in multiple sclerosis patients and their relevance with patients’ response to Cinnovex. Cytokine 96:138–143
Trentini A, Manfrinato MC, Castellazzi M, Tamborino C, Roversi G, Volta CA, Baldi E, Tola MR, Granieri E, Dallocchio F, Bellini T, Fainardi E (2015) TIMP-1 resistant matrix metalloproteinase-9 is the predominant serum active isoform associated with MRI activity in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 21:1121–1130
Wong B, Lumma WC, Smith AM, Sisko JT, Wright SD, Cai TQ (2001) Statins suppress THP-1 cell migration and secretion of matrix metalloproteinase 9 by inhibiting geranylgeranylation. J Leukoc Biol 69:959–962
Funding
The current study was supported by a grant number 10250 from the Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was compliance with ethical committe of Shahid Beheshti University of MedicalSciences (IR.SBMU. MSP.REC.1396.44).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taheri, M., Ghafouri-Fard, S., Sayad, A. et al. Assessment of Protein Prenylation Pathway in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. J Mol Neurosci 64, 581–590 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1052-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1052-z