Abstract
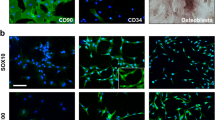
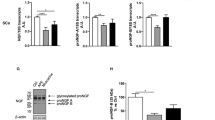
The Schwann-like cells can be considered as promising in stem cell therapies, at least in experimental models. Human adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) are induced into Schwann-like cells (SC-like cells) and are cultured on either a plastic surface or laminin-coated plates. The findings here reveal that laminin is a critical component in extracellular matrix (ECM) of SC-like cells at in vitro. The survival rate of SC-like cells on a laminin matrix are measured through MTT assay and it is found that this rate is significantly higher than that of the cells grown on a plastic surface (P < 0.05). Schwann cell markers and the myelinogenic ability of SC-like cells at the presence versus absence of laminin are assessed through immunocytochemistry. The analysis of GFAP/S100β and S100β/MBP markers indicate that laminin can increase the differentiated rate and myelinogenic potential of SC-like cells. The expression levels of SCs markers, myelin basic proteins (MBP), and neurotrophic factors in two conditions are analyzed by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The findings here demonstrated that gene expression of SCs markers, MBP, and brain-derived neurotrophic factors (BDNF) increase significantly on laminin compared to plastic surface (P < 0.01). In contrast, the nerve growth factor (NGF) expression is downregulated significantly on laminin-coated plates (P < 0.05). The obtained data suggest that production of neurotrophic factors in SC-like cell in presence of laminin can induce appropriate microenvironment for nerve repair in neurodegenerative diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armati PJ, Mathey EK (2014) Clinical implications of Schwann cell biology. J Peripher Nerv Syst 19:14–23
Blesch A, Tuszynski MH (2003) Cellular GDNF delivery promotes growth of motor and dorsal column sensory axons after partial and complete spinal cord transections and induces remyelination. J Comp Neurol 467:403–417
Chao MV (2003) Neurotrophins and their receptors: a convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:299–309
Chen Q et al. (2015) A fibrin matrix promotes the differentiation of EMSCs isolated from nasal respiratory mucosa to myelinating phenotypical Schwann-like cells. Molecules and cells 38:221
Chen X, Wang XD, Chen G, Lin WW, Yao J, Gu XS (2006) Study of in vivo differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells into Schwann cell-like cells. Microsurgery 26:111–115
Chen Z-L, Strickland S (2003) Laminin γ1 is critical for Schwann cell differentiation, axon myelination, and regeneration in the peripheral nerve. J Cell Biol 163:889–899
Chen Z-L, Yu W-M, Strickland S (2007) Peripheral regeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci 30:209–233
Chernousov MA, Yu WM, Chen ZL, Carey DJ, Strickland S (2008) Regulation of Schwann cell function by the extracellular matrix. Glia 56:1498–1507
Crigler L, Robey RC, Asawachaicharn A, Gaupp D, Phinney DG (2006) Human mesenchymal stem cell subpopulations express a variety of neuro-regulatory molecules and promote neuronal cell survival and neuritogenesis. Exp Neurol 198:54–64
Dezawa M, Takahashi I, Esaki M, Takano M, Sawada H (2001) Sciatic nerve regeneration in rats induced by transplantation of in vitro differentiated bone-marrow stromal cells. Eur J Neurosci 14:1771–1776
Dhar S, Yoon ES, Kachgal S, Evans GR (2007) Long-term maintenance of neuronally differentiated human adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Tissue Eng 13:2625–2632
di Summa PG, Kalbermatten DF, Raffoul W, Terenghi G, Kingham PJ (2012) Extracellular matrix molecules enhance the neurotrophic effect of Schwann cell-like differentiated adipose-derived stem cells and increase cell survival under stress conditions. Tissue Eng A 19:368–379
Faroni A, Calabrese F, Riva MA, Terenghi G, Magnaghi V (2013) Baclofen modulates the expression and release of neurotrophins in schwann-like adipose stem cells. J Mol Neurosci 49:233–243. doi:10.1007/s12031-012-9813-6
Faroni A, Mantovani C, Shawcross SG, Motta M, Terenghi G, Magnaghi V (2011) Schwann-like adult stem cells derived from bone marrow and adipose tissue express γ-aminobutyric acid type B receptors. J Neurosci Res 89:1351–1362
Faroni A, Smith RJ, Lu L, Reid AJ (2015) Human Schwann-like cells derived from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells rapidly de-differentiate in the absence of stimulating medium European Journal of Neuroscience
Firouzi M, Moshayedi P, Saberi H, Mobasheri H, Abolhassani F, Jahanzad I, Raza M (2006) Transplantation of Schwann cells to subarachnoid space induces repair in contused rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 402:66–70
Fortino V, Torricelli C, Gardi C, Valacchi G, Paccani SR, Maioli E (2002) ERKs are the point of divergence of PKA and PKC activation by PTHrP in human skin fibroblasts. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences CMLS 59:2165–2171
Fu SY, Gordon T (1997) The cellular and molecular basis of peripheral nerve regeneration. Molecular neurobiology 14:67–116
Garratt AN, Voiculescu O, Topilko P, Charnay P, Birchmeier C (2000) A dual role of erbB2 in myelination and in expansion of the schwann cell precursor pool. J Cell Biol 148:1035–1046
Gordon T (2009) The role of neurotrophic factors in nerve regeneration. Neurosurg Focus 26:E3
Guo Z-y, Sun X, Xu X-l, Zhao Q, Peng J, Wang Y (2015) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote peripheral nerve repair via paracrine mechanisms. Neural regeneration research 10:651
Heuckeroth RO, Lampe PA, Johnson EM, Milbrandt J (1998) Neurturin and GDNF promote proliferation and survival of enteric neuron and glial progenitorsin vitro. Dev Biol 200:116–129
Jessen K, Mirsky R (2005) Symposium S01: molecules and mechanisms in Schwann cell development. J Neurochem 94:2–3
Keilhoff G, Stang F, Goihl A, Wolf G, Fansa H (2006) Transdifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells as alternative therapy in supporting nerve regeneration and myelination. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:1233–1250
Kingham PJ, Kalbermatten DF, Mahay D, Armstrong SJ, Wiberg M, Terenghi G (2007) Adipose-derived stem cells differentiate into a Schwann cell phenotype and promote neurite outgrowth in vitro. Exp Neurol 207:267–274
Kingham PJ, Kolar MK, Novikova LN, Novikov LN, Wiberg M (2013) Stimulating the neurotrophic and angiogenic properties of human adipose-derived stem cells enhances nerve repair. Stem Cells Dev 23:741–754
Madduri S, Gander B (2010) Schwann cell delivery of neurotrophic factors for peripheral nerve regeneration. J Peripher Nerv Syst 15:93–103
Mantovani C, Mahay D, Kingham PJ, Terenghi G, Shawcross SG, Wiberg M (2010) Bone marrow-and adipose-derived stem cells show expression of myelin mRNAs and proteins. Regen Med 5:403–410
Matsuoka I, Meyer M, Thoenen H (1991) Cell-type-specific regulation of nerve growth factor (NGF) synthesis in non-neuronal cells: comparison of Schwann cells with other cell types. J Neurosci 11:3165–3177
McCall J, Weidner N, Blesch A (2012) Neurotrophic factors in combinatorial approaches for spinal cord regeneration. Cell Tissue Res 349:27–37
Meyer M, Matsuoka I, Wetmore C, Olson L, Thoenen H (1992) Enhanced synthesis of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the lesioned peripheral nerve: different mechanisms are responsible for the regulation of BDNF and NGF mRNA. J Cell Biol 119:45–54
Nave K-A (2010) Myelination and support of axonal integrity by glia. Nature 468:244–252
Nodari A et al. (2007) β1 integrin activates Rac1 in Schwann cells to generate radial lamellae during axonal sorting and myelination. J Cell Biol 177:1063–1075
Platt C, Krekoski C, Ward R, Edwards D, Gavrilovic J (2003) Extracellular matrix and matrix metalloproteinases in sciatic nerve. J Neurosci Res 74:417–429
Razavi S, Ahmadi N, Kazemi M, Mardani M, Esfandiari E (2012) Efficient transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into Schwann-like cells: a promise for treatment of demyelinating diseases. Advanced biomedical research 1:12
Razavi S, Mardani M, Kazemi M, Esfandiari E, Narimani M, Esmaeili A, Ahmadi N (2013a) Effect of leukemia inhibitory factor on the myelinogenic ability of Schwann-like cells induced from human adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:283–289
Razavi S, Razavi MR, Kheirollahi-Kouhestani M, Mardani M, Mostafavi FS (2013b) Co-culture with neurotrophic factor secreting cells induced from adipose-derived stem cells: promotes neurogenic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 440: 381–7
Razavi S, Zarkesh-Esfahani H, Morshed M, Vaezifar S, Karbasi S, Golozar MA (2015) Nanobiocomposite of poly (lactide-co-glycolide)/chitosan electrospun scaffold can promote proliferation and transdifferentiation of Schwann-like cells from human adipose-derived stem cells. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 103:2628–2634
Soto I, Rosenthal JJ, Blagburn JM, Blanco RE (2006) Fibroblast growth factor 2 applied to the optic nerve after axotomy up-regulates BDNF and TrkB in ganglion cells by activating the ERK and PKA signaling pathways. J Neurochem 96:82–96
Tate CC, Shear DA, Tate MC, Archer DR, Stein DG, LaPlaca MC (2009) Laminin and fibronectin scaffolds enhance neural stem cell transplantation into the injured brain. Journal of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine 3:208–217
Terenghi G (1999) Peripheral nerve regeneration and neurotrophic factors. J Anat 194:1–14
Tomita K, Madura T, Mantovani C, Terenghi G (2012) Differentiated adipose-derived stem cells promote myelination and enhance functional recovery in a rat model of chronic denervation. J Neurosci Res 90:1392–1402
Tomita K, Madura T, Sakai Y, Yano K, Terenghi G, Hosokawa K (2013) Glial differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells: implications for cell-based transplantation therapy. Neuroscience 236:55–65
Woodhoo A et al. (2007) Schwann cell precursors: a favourable cell for myelin repair in the central nervous system. Brain 130:2175–2185
Worth DC, Parsons M (2008) Adhesion dynamics: mechanisms and measurements. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:2397–2409
Xu Y et al. (2008) Myelin-forming ability of Schwann cell-like cells induced from rat adipose-derived stem cells in vitro. Brain Res 1239:49–55
Yamamoto M, Sobue G, Li M, Arakawa Y, Mitsuma T, Kimata K (1993) Nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor (LNGFR) mRNA levels in cultured rat Schwann cells; differential time-and dose-dependent regulation by cAMP. Neurosci Lett 152:37–40
Yu W-M, Chen Z-L, North AJ, Strickland S (2009) Laminin is required for Schwann cell morphogenesis. J Cell Sci 122:929–936
Zafra F, Castren E, Thoenen H, Lindholm D (1991) Interplay between glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid transmitter systems in the physiological regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci 88:10037–10041
Zhu T, Tang Q, Gao H, Shen Y, Chen L, Zhu J (2014) Current status of cell-mediated regenerative therapies for human spinal cord injury. Neurosci Bull 30:671–682
Zuk PA et al. (2002) Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell 13:4279–4295
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Iranian Council of Stem Cell Technology, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences for financial support (Grant No. 193070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures of this study are applied in accordance with the Ethics Committee of the Medical Faculty in Isfahan University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarinfard, G., Tadjalli, M., Razavi, S. et al. Effect of Laminin on Neurotrophic Factors Expression in Schwann-Like Cells Induced from Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells In Vitro. J Mol Neurosci 60, 465–473 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0808-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0808-6