Abstract
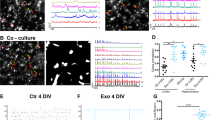
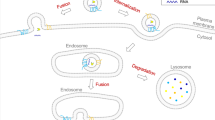
The effects of cocaine (150 nM, 300 nM, and 150 μM) on human glioblastoma cell cultures were studied on tunneling nanotube formation (1-h cocaine treatment) and extracellular vesicle release (1-, 3-, and 8-h cocaine treatment). Cocaine significantly increased the number of tunneling nanotubes only at the lowest concentration used. The release of extracellular vesicles (mainly exosomes) into the medium was stimulated by cocaine at each concentration used with a maximum effect at the highest concentration tested (150 μM). Moreover, cocaine (150 nM) significantly increased the number of vesicles with 61–80 nm diameter while at concentrations of 300 nM and 150 μM, and the smaller vesicles (30–40 nm diameter) were significantly increased with a reduction of the larger vesicles (41–60 nm diameter). A time dependence in the release of extracellular vesicles was observed. In view of the proposed role of these novel intercellular communication modes in the glial-neuronal plasticity, it seems possible that they can participate in the processes leading to cocaine addiction. The molecular target/s involved in these cocaine effects could be specific molecular components of plasma membrane lipid rafts and/or cocaine-induced modifications in cytoplasmic lipid composition.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnati LF, Fuxe K (2000) Volume transmission as a key feature of information handling in the central nervous system possible new interpretative value of the Turing’s B-type machine. Prog Brain Res 125:3–19
Agnati LF, Fuxe K, Baluska F, Guidolin D (2009) Implications of the ‘Energide’ concept for communication and information handling in the central nervous system. J Neural Transm 116:1037–1052
Agnati LF, Guidolin D, Guescini M, Genedani S, Fuxe K (2010) Understanding wiring and volume transmission. Brain Res Rev 64:137–159
Bailey DN (1998) Cocaine and cocaethylene binding to human milk. Am J Clin Pathol 110:491–494
Baluška F, Volkmann D, Barlow PW (2006) Cell–cell channels and their implications for cell theory. In: Baluška F, Volkmann D, Barlow PW (eds) Cell–cell channels. Landes Bioscience, Georgetown TX/Springer Science, New York, pp 1–18
Belting M, Wittrup A (2008) Nanotubes, exosomes, and nucleic acid-binding peptides provide novel mechanisms of intercellular communication in eukaryotic cells: implications in health and disease. J Cell Biol 183:1187–1191
Cai H, Reinisch K, Ferro-Novick S (2007) Coats, tethers, Rabs, and SNAREs work together to mediate the intracellular destination of a transport vesicle. Dev Cell 12:671–682
Cocucci E, Racchetti G, Meldolesi J (2009) Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol 19:43–51
de Gassart A, Geminard C, Fevrier B, Raposo G, Vidal M (2003) Lipid raft-associated protein sorting in exosomes. Blood 102:4336–4344
Di Chiara G, Imperato A (1988) Drugs abused by humans preferentially increase synaptic dopamine concentrations in the mesolimbic system of freely moving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85:5274–5278
Ferraro L, Frankowska M, Marcellino D et al (2012) A novel mechanism of cocaine to enhance dopamine d2-like receptor mediated neurochemical and behavioral effects. An in vivo and in vitro study. Neuropsychopharmacol 37:1856–1866
Fifadara NH, Beer F, Ono S, Ono SJ (2010) Interaction between activated chemokine receptor 1 and FcepsilonRI at membrane rafts promotes communication and F-actin-rich cytoneme extensions between mast cells. Int Immunol 22:113–128
Genedani S, Carone C, Guidolin D et al (2010) Differential sensitivity of A2A and especially D2 receptor trafficking to cocaine compared with lipid rafts in cotransfected CHO cell lines. Novel actions of cocaine independent of the DA transporter. J Mol Neurosci 41:347–357
Goncharova LB, Tarakanov AO (2008) Nanotubes at neural and immune synapses. Curr Med Chem 15:210–218
Gurke S, Barroso JF, Gerdes HH (2008) The art of cellular communication: tunnelling nanotubes bridge the divide. Histochem Cell Biol 129:539–550
Hase K, Kimura S, Takatsu H et al (2009) M-Sec promotes membrane nanotube formation by interacting with Ral and the exocyst complex. Nat Cell Biol 11:1427–1432
Hayashi T, Su TP (2005) The potential role of sigma-1 receptors in lipid transport and lipid raft reconstitution in the brain: implication for drug abuse. Life Sci 77:1612–1624
Hurley JH (2010) The ESCRT complexes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 45:463–487
Kabaso D, Lokar M, Kralj-Iglič V, Veranič P, Iglič A (2011) Temperature and cholera toxin B are factors that influence formation of membrane nanotubes in RT4 and T24 urothelial cancer cell lines. Int J Nanomedicine 6:495–509
Kabaso D, Bobrovska N, Góźdź W et al (2012) The transport along membrane nanotubes driven by the spontaneous curvature of membrane components. Bioelectrochemistry 87:204–210
Kalivas PW, Volkow ND (2005) The neural basis of addiction: a pathology of motivation and choice. Am J Psychiatry 162:1403–1413
Kimura S, Hase K, Ohno H (2012) Tunneling nanotubes: emerging view of their molecular components and formation mechanisms. Exp Cell Res 318:1699–1706
Koob GF, Bloom FE (1988) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of drug dependence. Science 242:715–723
Koyanagi M, Brandes RP, Haendeler J, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S (2005) Cell-to-cell connection of endothelial progenitor cells with cardiac myocytes by nanotubes: a novel mechanism for cell fate changes? Circ Res 96:1039–1041
Lakkaraju A, Rodriguez-Boulan E (2008) Itinerant exosomes: emerging roles in cell and tissue polarity. Trends Cell Biol 18:199–209
Laulagnier K, Motta C, Hamdi S et al (2004) Mast cell- and dendritic cell-derived exosomes display a specific lipid composition and an unusual membrane organization. Biochem J 380:161–171
Leskawa KC, Jackson GH, Moody CA, Spear LP (1994) Cocaine exposure during pregnancy affects rat neonate and maternal brain glycosphingolipids. Brain Res Bull 33:195–198
Llorente A, Skotland T, Sylvänne T et al (2013) Molecular lipidomics of exosomes released by PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1831:1302–1309
Lokar M, Kabaso D, Resnik N et al (2012) The role of cholesterol-sphingomyelin membrane nanodomains in the stability of intercellular membrane nanotubes. Int J Nanomedicine 7:1891–1902
Mallegol J, Van Niel G, Lebreton C et al (2007) T84-intestinal epithelial exosomes bear MHC class II/peptide complexes potentiating antigen presentation by dendritic cells. Gastroenterol 132:1866–1876
Möbius W, Ohno-Iwashita Y, van Donselaar EG et al (2002) Immunoelectron microscopic localization of cholesterol using biotinylated and non-cytolytic perfringolysin O. J Histochem Cytochem 50:43–55
Mortensen OV, Amara SG (2003) Dynamic regulation of the dopamine transporter. Eur J Pharmacol 479:159–170
Moskalenko S, Henry DO, Rosse C, Mirey G, Camonis JH, White MA (2002) The exocyst is a Ral effector complex. Nat Cell Biol 4:66–72
Nassogne MC, Lizarraga C, N’Kuli F et al (2004) Cocaine induces a mixed lysosomal lipidosis in cultured fibroblasts, by inactivation of acid sphingomyelinase and inhibition of phospholipase A1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 194:101–110
Onfelt B, Nedvetzki S, Benninger RK et al (2006) Structurally distinct membrane nanotubes between human macrophages support long-distance vesicular traffic or surfing of bacteria. J Immunol 177:8476–8483
Raiborg C, Stenmark H (2009) The ESCRT machinery in endosomal sorting of ubiquitylated membrane proteins. Nature 458:445–452
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W (2013) Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol 200:373–383
Ritz MC, Lamb RJ, Goldberg SR, Kuhar MJ (1987) Cocaine receptors on dopamine transporters are related to self-administration of cocaine. Science 237:1219–1223
Rustom A, Saffrich R, Markovic I, Walther P, Gerdes HH (2004) Nanotubular highways for intercellular organelle transport. Science 303:1007–1010
Schorey JS, Bhatnagar S (2008) Exosome function: from tumor immunology to pathogen biology. Traffic 9:871–881
Simons M, Raposo G (2009) Exosomes: vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:575–581
Soo JC, Zhang J, He Q et al (2010) Surface immobilized cholera toxin B subunit (CTB) facilitates vesicle docking, trafficking and exocytosis. Integr Biol (Camb) 2:250–257
Subra C, Grand D, Laulagnier K et al (2010) Exosomes account for vesicle-mediated transcellular transport of activatable phospholipases and prostaglandins. J Lipid Res 51:2105–2120
Sugihara K, Asano S, Tanaka K, Iwamatsu A, Okawa K, Ohta Y (2002) The exocyst complex binds the small GTPase RalA to mediate filopodia formation. Nat Cell Biol 4:73–78
Thery C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A (2006) Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol Chapter 3:Unit 3.22
Torres GE, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2003) Plasma membrane monoamine transporters: structure, regulation and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:13–25
Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S et al (2008) Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 319:1244–1247
Woodward JJ, Compton DM, Balster RL, Martin BR (1995) In vitro and in vivo effects of cocaine and selected local anesthetics on the dopamine transporter. Eur J Pharmacol 277:7–13
Wubbolts R, Leckie RS, Veenhuizen PT et al (2003) Proteomic and biochemical analyses of human B cell-derived exosomes. Potential implications for their function and multivesicular body formation. J Biol Chem 278:10963–10972
Zink CF, Pagnoni G, Martin ME, Dhamala M, Berns GS (2003) Human striatal response to salient nonrewarding stimuli. J Neurosci 23:8092–8097
Acknowledgments
We thank the Centro Interdipartimentale Grandi Strumenti of the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, and in particular Dr. M. Tonelli, for his support in the use of AFM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carone, C., Genedani, S., Leo, G. et al. In Vitro Effects of Cocaine on Tunneling Nanotube Formation and Extracellular Vesicle Release in Glioblastoma Cell Cultures. J Mol Neurosci 55, 42–50 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0365-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0365-9