Abstract
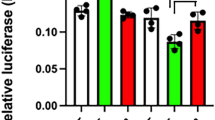
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) is predominantly localized in the nervous system, but the underlying mechanism in its neuron-specific expression remains unclear. In addition to two neural-restrictive silencer-like element (NRSLE1 and 2), as reported previously, we have identified the third element in −1,601 to −1,581 bp from the translational initiation site of mouse PACAP gene and termed it as NRSLE3, of which, the sequence and location were highly conserved among mouse, rat, and human PACAP genes. In luciferase reporter assay, the deletion or site-directed mutagenesis of NRSLE3 in the reporter gene construct, driven by heterologous SV40 promoter, cancelled the repression of luciferase activity in non-neuronal Swiss-3T3 cells. Furthermore, its promoter activity was significantly repressed in Swiss-3T3 cells, but not in neuronal-differentiated PC12 cells. The electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) with nuclear extracts of Swiss-3T3 cells demonstrated a specific complex with NRSLE3 probe that exhibited the same migration with the neural-restrictive silencer element (NRSE) probe of rat type II sodium channel gene. During neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells, the increment of PACAP mRNA exhibited the correlation with that of REST4 mRNA, which is a neuron-specific variant form of neural-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF). In undifferentiated PC12 cells, trichostatin A (TSA), a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, which indirectly inhibits NRSF-mediated gene silencing, increased PACAP mRNA level and attenuated the repression of promoter activity of 5′ flanking region of mouse PACAP gene containing NRSLEs. These suggest that the NRSE–NRSF system implicates in the regulatory mechanism of neuron-specific expression of PACAP gene.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrés ME, Burger C, Peral-Rubio MJ, Battaglioli E, Anderson ME, Grimes J, Dallman J, Ballas N, Mandel G (1999) CoREST: a functional corepressor required for regulation of neural-specific gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(17):9873–9878
Andrews NC, Faller DV (1991) A rapid micropreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from limiting numbers of mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 19:2499
Arimura A (1998) Perspectives on pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) in the neuroendocrine, endocrine, and nervous systems. Jpn J Physiol 48:301–331
Arimura A, Somogyvari VA, Miyata A, Mizuno K, Coy DH, Kitada C (1991) Tissue distribution of PACAP as determined by RIA: highly abundant in the rat brain and testes. Endocrinology 129:2787–2789
Ballas N, Mandel G (2005) The many faces of REST oversee epigenetic programming of neural genes. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15(5):500–506
Ballas N, Battaglioli E, Atouf F et al (2001) Regulation of neuronal traits by a novel transcriptional complex. Neuron 31(3):353–365
Chen ZF, Paquette AJ, Anderson DJ (1998) NRSF/REST is required in vivo for repression of multiple neuronal target genes during embryogenesis. Nat Genet 20(2):136–142
Chong JA, Tapia-Ramirez J, Kim S et al (1995) RSET: a mammalian silencer protein that restricts sodium channel gene expression to neurons. Cell 80:949–957
Coulson JM (2005) Transcriptional regulation: cancer, neurons and the REST. Curr Biol 15(17):R665–R668
Cummings KJ, Gray SL, Simmons CJ, Kozak CA, Sherwood NM (2002) Mouse pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP): gene, expression and novel splicing. Mol Cell Endocrinol 192:133–145
Hosoya M, Kimura C, Ogi K et al (1992) Structure of the human pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) gene. Biochem Biophys Acta 1129:199–206
Hung Y, Myers SJ, Dingledine R (1999) Transcriptional repression by REST: recruitment of Sin3A and histone deacetylase to neuronal genes. Nat Neurosci 2(10):867–872
Kallunki P, Jenkinson S, Edelman GM, Jones FS (1995) Silencer elements modulate the expression of the gene for the neuron-glia cell adhesion molecule, Ng-CAM. J Biol Chem 270(36):21291–21298
Kim SM, Yang JW, Park MJ, Lee JK, Kim SU, Lee YS, Lee MA (2006) Regulation of human tyrosin hydroxylase gene by neuron-restrictive silencer factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346(2):426–435
Kraner SD, Chong JA, Tsay HJ, Mandel G (1992) Silencing the type II sodium channel gene: a model for neural-specific gene regulation. Neuron 9:37–44
Li L, Suzuki T, Mori N, Greengard P (1993) Identification of a functional silencer element involved in neuron-specific expression of the synapsin I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:1460–1464
Majumder S (2006) REST in good times and bad: roles in tumor suppressor and oncogenic activities. Cell Cycle 5(17):1929–1935
Miyata A, Arimura A, Dahl RR et al (1989) Isolation of a novel 38 residue-hypothalamic polypeptide which stimulates adenylate cyclase in pituitary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 164:567–574
Miyata A, Sano H, Li M et al (2000) Genomic organization and chromosomal localization of the mouse pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) gene. Ann N Y Acad Sci 921:344–348
Mori N, Schoenherr C, Vandenbergh DJ, Anderson DJ (1992) A common silencer element in the SCG10 and type II Na + channel genes binds a factor present in nonneuronal cells but not in neuronal cells. Neuron 9:45–54
Naruse Y, Aoki T, Kojima T, Mori N (1999) Neural restrictive silencer factor recruits mSin3 and histone deacetylase complex to repress neuron-specific target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(24):13691–13696
Palm K, Belluardo N, Metsis M, Timmusk T (1998) Neuronal expression of zinc finger transcription factor REST/NRSF/XBR gene. J Neurosci 18(4):1280–1296
Palm K, Metsis M, Timmusk T (1999) Neuron-specific splicing of zinc finger transcription factor REST/NRSF/XBR is frequent in neuroblastomas and conserved in human, mouse and rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 72:30–39
Roopra A, Qazi R, Schoenike B, Daley TJ, Morrison JF (2004) Localized domains of G9a-mediated histone methylation are required for silencing of neuronal genes. Mol Cell 14(6):727–738
Schoenherr CJ, Anderson DJ (1995a) The neuron-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF): a coordinate repressor of multiple neuron-specific genes. Science 267:1360–1363
Schoenherr CJ, Anderson DJ (1995b) Silencing is golden: negative regulation in the control of neuronal gene transcription. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5(5):566–571
Schoenherr CJ, Paquette AJ, Anderson DJ (1996) Identification of potential target genes for the neuron-restrictive silencer factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:9881–9886
Shimojo M, Paquette AJ, Anderson DJ, Hersh LB (1999) Protein kinase A regulates cholinergic gene expression in PC12 cells: REST4 silences the silencing activity of neuron-restrictive silencer factor/REST. Mol Cell Biol 19:6788–6795
Sugawara H, Inoue K, Iwata S et al (2004) Neural-restrictive silencer in the regulatory mechanism of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide gene expression. Regul Pept 123:9–14
Vaudry D, Gonzalez BJ, Basille M, Yon L, Fournier A, Vaudry H (2000) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and its receptors: from structure to functions. Pharmacol Rev 52:269–324
White SL, May V, Braas KM (2000) Organization of the rat PACAP gene. Ann N Y Acad Sci 921:370–372
Yamamoto K, Hashimoto H, Hagihara N et al (1998) Cloning and characterization of the mouse pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) gene. Gene 211:63–69
Zuccato C, Belyaev N, Conforti P, Ooi L, Tartari M, Papadimou E, MacDonald M, Fossale E, Zeitlin S, Buckley N, Cattaneo E (2007) Widespread disruption of repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor/neuron-restrictive silencer factor occupancy at its target genes in Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci 27(26):6972–6983
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research #21591182 (to A.M.) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. We thank Dr. Yuki Kambe and Takashi Kurihara for their helpful discussion. We also acknowledge Drs. Kenji Kangawa and Akira Arimura for their support throughout the course of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugawara, H., Tominaga, A., Inoue, K. et al. Functional Characterization of Neural-Restrictive Silencer Element in Mouse Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide (PACAP) Gene Expression. J Mol Neurosci 54, 526–534 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0348-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0348-x