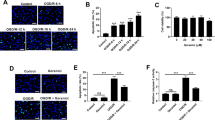
Abstract
Curcumin (Cur) is a major active component of the food flavor turmeric isolated from the powdered dry rhizome of Curcuma longa Linn., which has been used in traditional Chinese medicine to ameliorate intracerebral ischemic damage and reduce brain edema. However, the effects of Cur on the disruption of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) induced by brain ischemia are still unclear. The effects of Cur on the disruption of BBB and changes of tight junction (TJ) proteins induced by oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD) were studied in BBB in vitro. The transendothelial electrical resistance and the flux of horseradish peroxidase in BBB in vitro were measured. The expression and localization of the TJ proteins occludin and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) were evaluated by Western blots and immunofluorescence microscopy. The protein levels of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) were also analyzed via Western blots. Cur attenuated OGD-induced disruption of paracellular permeability and increased the expression of HO-1 protein in rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (RBMECs). After administration of OGD, the expression of occludin and ZO-1 proteins was restored by Cur, and this effect was blocked by a HO-1 inhibitor, zinc protoporphyrin (ZnPP). Cur protects RBMECs against OGD-induced disruption of TJ and barrier dysfunction via the HO-1 pathway. We propose that Cur is capable of improving the barrier function of BBB under ischemic conditions and this beneficial effect might be reversed by a HO-1 inhibitor, ZnPP.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Ahmad A, Gassmann M, Ogunshola OO (2012) Involvement of oxidative stress in hypoxia-induced blood–brain barrier breakdown. Microvasc Res 84:222–225
Araujo JA, Zhang M, Yin F (2012) Heme oxygenase-1, oxidation, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol 3:119
Balbuena P, Li W, Ehrich M (2011) Assessments of tight junction proteins occludin, claudin 5 and scaffold proteins ZO1 and ZO2 in endothelial cells of the rat blood–brain barrier: cellular responses to neurotoxicants malathion and lead acetate. Neurotoxicology 32:58–67
Bhaskaran N, Shukla S, Kanwal R, Srivastava JK, Gupta S (2012) Induction of heme oxygenase-1 by chamomile protects murine macrophages against oxidative stress. Life Sci 90:1027–1033
Chen YB, Li CG, Xu CS (2005) Curcumin for the protection and treatment of cerebral vascular disease. Chin J Integr Med Cardio-Cerebrovasc Dis 3:631–633
Coisne C, Engelhardt B (2011) Tight junctions in brain barriers during central nervous system inflammation. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:1285–1303
Das L, Vinayak M (2012) Anti-carcinogenic action of curcumin by activation of antioxidant defence system and inhibition of NF-κB signalling in lymphoma-bearing mice. Biosci Rep 32:161–170
Farkas AE, Capaldo CT, Nusrat A (2012) Regulation of epithelial proliferation by tight junction proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1258:115–124
Gandapu U, Chaitanya RK, Kishore G, Reddy RC, Kondapi AK (2011) Curcumin-loaded apotransferrin nanoparticles provide efficient cellular uptake and effectively inhibit HIV-1 replication in vitro. PLoS One 6:e23388
Gerjevic LN, Lu S, Chaky JP, Harrison-Findik DD (2011) Regulation of heme oxygenase expression by alcohol, hypoxia and oxidative stress. World J Biol Chem 2:252–260
González-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Nava P, Jaramillo BE (2003) Tight junction proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 81:1–44
Hao XE, Wang XG, Li N, Wang SP, Zhang XJ, Li GM (2002) The effect of the compound curcumin capsule on focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Shandong J Tradit Chin Med 7:427–429
Jiang J, Wang W, Sun YJ, Hu M, Li F, Zhu DY (2007) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on focal cerebral ischemic rats by preventing blood–brain barrier damage. Eur J Pharmacol 561:54–62
Kaur C, Ling EA (2008) Blood brain barrier in hypoxic-ischemic conditions. Curr Neurovasc Res 5:71–81
Kim SJ, Park JG, Lee SM (2012) Protective effect of heme oxygenase-1 induction against hepatic injury in alcoholic steatotic liver exposed to cold ischemia/reperfusion. Life Sci 90:169–176
Kunwar A, Sandur SK, Krishna M, Priyadarsini KI (2009) Curcumin mediates time and concentration dependent regulation of redox homeostasis leading to cytotoxicity in macrophage cells. Eur J Pharmacol 611:8–16
Lee JC, Kinniry PA, Arguiri E, Serota M, Kanterakis S, Chatterjee S, Solomides CC, Javvadi P, Koumenis C, Cengel KA, Christofidou-Solomidou M (2010) Dietary curcumin increases antioxidant defenses in lung, ameliorates radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis, and improves survival in mice. Radiat Res 173:590–601
Liu Y, Sun XJ, Liu J, Kang ZM, Deng XM (2011) Heme oxygenase-1 could mediate the protective effects of hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 38:675–682
Liu WY, Wang ZB, Zhang LC, Wei X, Li L (2012) Tight junction in blood–brain barrier: an overview of structure, regulation, and regulator substances. CNS Neurosci Ther doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00340.x
Luo F, Huang R, Yang YJ, Yu XH (2003) Protective effect and mechanism of pretreatment with curcumin on infectious brain edema in rats. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 41:940–944
McNally SJ, Harrison EM, Ross JA, Garden OJ, Wigmore SJ (2007) Curcumin induces heme oxygenase 1 through generation of reactive oxygen species, p38 activation and phosphatase inhibition. Int J Mol Med 19:165–172
Motterlini R, Foresti R, Bassi R, Green CJ (2000) Curcumin, an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, induces heme oxygenase-1 and protects endothelial cells against oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 28:1303–1312
Panchal HD, Vranizan K, Lee CY, Ho J, Ngai J, Timiras PS (2008) Early anti-oxidative and anti-proliferative curcumin effects on neuroglioma cells suggest therapeutic targets. Neurochem Res 33:1701–1710
Persidsky Y, Ramirez SH, Haorah J, Kanmogne GD (2006) Blood–brain barrier: structural components and function under physiologic and pathologic conditions. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 1:223–236
Preston E, Foster DO (1997) Evidence for pore-like opening of the blood–brain barrier following forebrain ischemia in rats. Brain Res 761:4–10
Pun PB, Lu J, Moochhala S (2003) Involvement of ROS in BBB dysfunction. Free Radic Res 43:348–364
Reed JR, Huber WJ 3rd, Backes WL (2010) Human heme oxygenase-1 efficiently catabolizes heme in the absence of biliverdin reductase. Drug Metab Dispos 38:2060–2066
Rosenberg GA (2012) Neurological diseases in relation to the blood–brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:1139–1151
Scott PA, Bicknell R (1993) The isolation and culture of microvascular endothelium. J Cell Sci 105(Pt 2):269–273
Wang N, Wang G, Hao J, Ma J, Wang Y, Jiang X, Jiang H (2012) Curcumin ameliorates hydrogen peroxide-induced epithelial barrier disruption by upregulating heme oxygenase-1 expression in human intestinal epithelial cells. Dig Dis Sci 57:1792–1801
Xie H, Xue YX, Liu LB, Liu YH, Wang P (2012) Role of RhoA/ROCK signaling in endothelial-monocyte-activating polypeptide II opening of the blood-tumor barrier: role of RhoA/ROCK signaling in EMAP II opening of the BTB. J Mol Neurosci 46(3):666–676
Yang Y, Rosenberg GA (2011) Blood–brain barrier breakdown in acute and chronic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 42:3323–3328
Yang G, Cao H, Zeng YM (2005) The protective effect of curcumin on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Foreign Medical Sciences. Anesthesiol Resuscitation 3:157–160
Yang C, Zhang X, Fan H, Liu Y (2009) Curcumin upregulates transcription factor Nrf2, HO-1 expression and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Brain Res 1282:133–141
Zhao J, Zhao Y, Zheng W, Lu Y, Feng G, Yu S (2008) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1229:224–232
Zhu H, Wang Z, Xing Y, Gao Y, Ma T, Lou L, Lou J, Gao Y, Wang S, Wang YJ (2012) Baicalin reduces the permeability of the blood–brain barrier during hypoxia in vitro by increasing the expression of tight junction proteins in brain microvascular endothelial cells. Ethnopharmacol 141:714–720
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation for China (no. 81100924).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yan-feng Wang and Yan-ting Gu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Yf., Gu, Yt., Qin, Gh. et al. Curcumin Ameliorates the Permeability of the Blood–Brain Barrier During Hypoxia by Upregulating Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. J Mol Neurosci 51, 344–351 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9989-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9989-4