Abstract
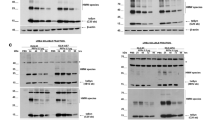
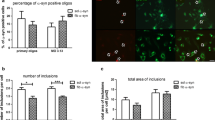
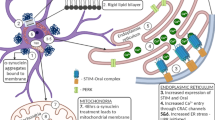
The accumulation and aggregation of α-synuclein (α-Syn) in glial cytoplasmic inclusions originating in oligodendrocytes is a characteristic hallmark of multiple system atrophy, a progressive adult onset neurodegenerative disorder. The origin of α-Syn deposition in oligodendrocytes in multiple system atrophy is still unclear, but the uptake of α-Syn from the environment after neuronal secretion has been discussed. The present study was undertaken to investigate the consequences of α-Syn uptake from the environment in cultured oligodendroglial cells and its localization and potential to form intracellular aggregates in the absence or presence of the microtubule-associated protein tau, which has been demonstrated to act synergistically with α-Syn. Primary rat brain oligodendrocytes and clonal oligodendroglial OLN-93 cells were incubated with human recombinant soluble and pre-aggregated α-Syn. The data show that oligodendrocytes are capable to take up and internalize soluble and pre-aggregated α-Syn from their growth medium. In a time-dependent manner, α-Syn oligomerizes and small intracellular aggregates are formed. These do not exert cytotoxic responses or mitochondrial impairment. Oxidative stress exerted by hydrogen peroxide further promotes α-Syn oligomer formation and leads to an enlargement of the aggregates. This process is not affected or modified by the presence of tau in OLN-93 cells. Furthermore, membrane lipid modification by docosahexaenoic acid promotes α-Syn uptake and oligomerization, indicating that changing the membrane lipid composition and structure contributes to the protein aggregation process and pathological events. Hence, although α-Syn taken up by oligodendrocytes from the environment is not toxic per se, under conditions of oxidative stress, which might occur during chronic disease progression and aging, aggregates are enlarged and eventually may contribute to cytotoxicity and cellular death.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angot E, Steiner JA, Hansen C, Li JY, Brundin P (2010) Are synucleinopathies prion-like disorders? Lancet Neurol 9:1128–1138
Angot E, Steiner JA, Lema Tome CM et al. (2012) Alpha-synuclein cell-to-cell transfer and seeding in grafted dopaminergic neurons in vivo. PLoS One 7:e39465
Assayag K, Yakunin E, Loeb V, Selkoe DJ, Sharon R (2007) Polyunsaturated fatty acids induce alpha-synuclein-related pathogenic changes in neuronal cells. Am J Pathol 171:2000–2011
Badiola N, de Oliveira RM, Herrera F et al (2011) Tau enhances alpha-synuclein aggregation and toxicity in cellular models of synucleinopathy. PLoS One 6:e26609
Ben-Gedalya T, Loeb V, Israeli E, Altschuler Y, Selkoe DJ, Sharon R (2009) Alpha-synuclein and polyunsaturated fatty acids promote clathrin-mediated endocytosis and synaptic vesicle recycling. Traffic 10:218–234
Borghi R, Marchese R, Negro A et al (2000) Full length alpha-synuclein is present in cerebrospinal fluid from Parkinson’s disease and normal subjects. Neurosci Lett 287:65–67
Brand A, Bauer NG, Hallott A et al (2010) Membrane lipid modification by polyunsaturated fatty acids sensitizes oligodendroglial OLN-93 cells against oxidative stress and promotes up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1 (HSP32). J Neurochem 113:465–476
Brand A, Gil S, Seger R, Yavin E (2001) Lipid constituents in oligodendroglial cells alter susceptibility to H2O2-induced apoptotic cell death via ERK activation. J Neurochem 76:910–918
Cairns NJ, Atkinson PF, Hanger DP, Anderton BH, Daniel SE, Lantos PL (1997) Tau protein in the glial cytoplasmic inclusions of multiple system atrophy can be distinguished from abnormal tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 230:49–52
Chin SS, Goldman JE (1996) Glial inclusions in CNS degenerative diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:499–508
Choubey V, Safiulina D, Vaarmann A et al (2011) Mutant A53T alpha-synuclein induces neuronal death by increasing mitochondrial autophagy. J Biol Chem 286:10814–10824
De Franceschi G, Frare E, Bubacco L, Mammi S, Fontana A, de Laureto PP (2009) Molecular insights into the interaction between alpha-synuclein and docosahexaenoic acid. J Mol Biol 394:94–107
Desplats P, Lee HJ, Bae EJ et al (2009) Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:13010–13015
Dohm CP, Kermer P, Bahr M (2008) Aggregopathy in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic implication. Neurodegener Dis 5:321–338
Dyall SC, Michael-Titus AT (2008) Neurological benefits of omega-3 fatty acids. Neuromol Med 10:219–235
El-Agnaf OM, Salem SA, Paleologou KE et al (2003) Alpha-synuclein implicated in Parkinson’s disease is present in extracellular biological fluids, including human plasma. FASEB J 17:1945–1947
Emmanouilidou E, Elenis D, Papasilekas T et al (2011) Assessment of alpha-synuclein secretion in mouse and human brain parenchyma. PLoS One 6:e22225
Fellner L, Jellinger KA, Wenning GK, Stefanova N (2011) Glial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of alpha-synucleinopathies: emerging concepts. Acta Neuropathol 121:675–693
Frost B, Diamond MI (2010) Prion-like mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:155–159
Galpern WR, Lang AE (2006) Interface between tauopathies and synucleinopathies: a tale of two proteins. Ann Neurol 59:449–458
Geddes JW (2005) alpha-Synuclein: a potent inducer of tau pathology. Exp Neurol 192:244–250
Giasson BI, Forman MS, Higuchi M et al (2003) Initiation and synergistic fibrillization of tau and alpha-synuclein. Science 300:636–640
Goedert M, Clavaguera F, Tolnay M (2010) The propagation of prion-like protein inclusions in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 33:317–325
Goldbaum O, Oppermann M, Handschuh M et al (2003) Proteasome inhibition stabilizes tau inclusions in oligodendroglial cells that occur after treatment with okadaic acid. J Neurosci 23
Goldbaum O, Richter-Landsberg C (2004) Proteolytic stress causes heat shock protein induction, tau ubiquitination, and the recruitment of ubiquitin to tau-positive aggregates in oligodendrocytes in culture. J Neurosci 24
Hansen C, Angot E, Bergstrom AL et al (2011) Alpha-synuclein propagates from mouse brain to grafted dopaminergic neurons and seeds aggregation in cultured human cells. J Clin Invest 121:715–725
Hsu LJ, Sagara Y, Arroyo A et al (2000) Alpha-synuclein promotes mitochondrial deficit and oxidative stress. Am J Pathol 157:401–410
Jang A, Lee H-J, Suk J-E, Jung J-W, Kim K-P, Lee S-J (2010) Non-classical exocytosis of alpha-synuclein is sensitive to folding states and promoted under stress conditions. J Neurochem 113
Jellinger KA, Lantos PL (2010) Papp-Lantos inclusions and the pathogenesis of multiple system atrophy: an update. Acta Neuropathol 119:657–667
Kanda S, Bishop JF, Eglitis MA, Yang Y, Mouradian MM (2000) Enhanced vulnerability to oxidative stress by alpha-synuclein mutations and C-terminal truncation. Neuroscience 97:279–284
Kisos H, Pukass K, Ben-Hur T, Richter-Landsberg C, Sharon R (2012) Increased neuronal alpha-synuclein pathology associates with its accumulation in oligodendrocytes in mice modeling alpha-synucleinopathies. PLoS One 7:e46817
Kragh CL, Lund LB, Febbraro F et al (2009) Alpha-Synuclein aggregation and Ser-129 phosphorylation-dependent cell death in oligodendroglial cells. J Biol Chem 284:10211–10222
Lee HJ, Choi C, Lee SJ (2002) Membrane-bound alpha-synuclein has a high aggregation propensity and the ability to seed the aggregation of the cytosolic form. J Biol Chem 277:671–678
Lee HJ, Khoshaghideh F, Patel S, Lee SJ (2004a) Clearance of alpha-synuclein oligomeric intermediates via the lysosomal degradation pathway. J Neurosci 24:1888–1896
Lee HJ, Patel S, Lee SJ (2005) Intravesicular localization and exocytosis of alpha-synuclein and its aggregates. J Neurosci 25:6016–6024
Lee HJ, Suk JE, Bae EJ, Lee JH, Paik SR, Lee SJ (2008) Assembly-dependent endocytosis and clearance of extracellular alpha-synuclein. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:1835–1849
Lee HJ, Suk JE, Patrick C et al (2010) Direct transfer of alpha-synuclein from neuron to astroglia causes inflammatory responses in synucleinopathies. J Biol Chem 285:9262–9272
Lee VM, Giasson BI, Trojanowski JQ (2004b) More than just two peas in a pod: common amyloidogenic properties of tau and alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 27:129–134
Luk KC, Kehm VM, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012) Intracerebral inoculation of pathological alpha-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative alpha-synucleinopathy in mice. J Exp Med 209:975–986
Luk KC, Song C, O’Brien P et al (2009) Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils seed the formation of Lewy body-like intracellular inclusions in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:20051–20056
Miller DW, Johnson JM, Solano SM, Hollingsworth ZR, Standaert DG, Young AB (2005) Absence of alpha-synuclein mRNA expression in normal and multiple system atrophy oligodendroglia. J Neural Transm 112:1613–1624
Mori F, Tanji K, Yoshimoto M, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K (2002) Demonstration of alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in neuronal and glial cytoplasm in normal human brain tissue using proteinase K and formic acid pretreatment. Exp Neurol 176:98–104
Nakamura K, Nemani VM, Azarbal F et al (2011) Direct membrane association drives mitochondrial fission by the Parkinson disease-associated protein alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 286:20710–20726
Neuhoff V., Philipp K, Zimmer HG, Mesecke S (1979) simple, versatile, sensitive and volume-independent method for quantitative protein determination which is independent of other external influences. Hoppe-Seylers Zeitschrift Fur Physiologische Chemie 360
Norris EH, Giasson BI, Ischiropoulos H, Lee VM (2003) Effects of oxidative and nitrative challenges on alpha-synuclein fibrillogenesis involve distinct mechanisms of protein modifications. J Biol Chem 278:27230–27240
Ostrerova-Golts N, Petrucelli L, Hardy J, Lee JM, Farer M, Wolozin B (2000) The A53T alpha-synuclein mutation increases iron-dependent aggregation and toxicity. J Neurosci 20:6048–6054
Perrin RJ, Woods WS, Clayton DF, George JM (2001) Exposure to long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids triggers rapid multimerization of synucleins. J Biol Chem 276:41958–41962
Richter-Landsberg C, Gorath M, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2000) alpha-synuclein is developmentally expressed in cultured rat brain oligodendrocytes. J Neurosci Res 62:9–14
Richter-Landsberg C, Heinrich M (1996) OLN-93: a new permanent oligodendroglia cell line derived from primary rat brain glial cultures. J Neurosci Res 45:161–173
Riedel M, Goldbaum O, Richter-Landsberg C (2009) Alpha-synuclein promotes the recruitment of tau to protein inclusions in oligodendroglial cells: effects of oxidative and proteolytic stress. J Mol Neurosci 39:226–234
Riedel M, Goldbaum O, Schwarz L, Schmitt S, Richter-Landsberg C (2010) 17-AAG induces cytoplasmic alpha-synuclein aggregate clearance by induction of autophagy. PLoS One 5:e8753
Riedel M, Goldbaum O, Wille M, Richter-Landsberg C (2011) Membrane lipid modification by docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) promotes the formation of alpha-synuclein inclusion bodies immunopositive for SUMO-1 in oligodendroglial cells after oxidative stress. J Mol Neurosci 43:290–302
Ross CA, Poirier MA (2005) Opinion: what is the role of protein aggregation in neurodegeneration? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:891–898
Sharon R, Bar-Joseph I, Frosch MP, Walsh DM, Hamilton JA, Selkoe DJ (2003a) The formation of highly soluble oligomers of alpha-synuclein is regulated by fatty acids and enhanced in Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 37:583–595
Sharon R, Bar-Joseph I, Mirick GE, Serhan CN, Selkoe DJ (2003b) Altered fatty acid composition of dopaminergic neurons expressing alpha-synuclein and human brains with alpha-synucleinopathies. J Biol Chem 278:49874–49881
Skovronsky DM, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2006) Neurodegenerative diseases: new concepts of pathogenesis and their therapeutic implications. Annu Rev Pathol 1:151–170
Stahnke T, Stadelmann C, Netzler A, Bruck W, Richter-Landsberg C (2007) Differential upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 (HSP32) in glial cells after oxidative stress and in demyelinating disorders. J Mol Neurosci 32:25–37
Stefanova N, Klimaschewski L, Poewe W, Wenning GK, Reindl M (2001) Glial cell death induced by overexpression of alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci Res 65:432–438
Stefanova N, Reindl M, Neumann M et al (2005) Oxidative stress in transgenic mice with oligodendroglial alpha-synuclein overexpression replicates the characteristic neuropathology of multiple system atrophy. Am J Pathol 166:869–876
Takeda A, Arai N, Komori T, Iseki E, Kato S, Oda M (1997) Tau immunoreactivity in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy. Neurosci Lett 234:63–66
Tanaka Y, Engelender S, Igarashi S et al (2001) Inducible expression of mutant alpha-synuclein decreases proteasome activity and increases sensitivity to mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Hum Mol Genet 10:919–926
Tsuboi K, Grzesiak JJ, Bouvet M, Hashimoto M, Masliah E, Shults CW (2005) Alpha-synuclein overexpression in oligodendrocytic cells results in impaired adhesion to fibronectin and cell death. Mol Cell Neurosci 29:259–268
Tu PH, Galvin JE, Baba M et al (1998) Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in white matter oligodendrocytes of multiple system atrophy brains contain insoluble alpha-synuclein. Ann Neurol 44:415–422
Vogiatzi T, Xilouri M, Vekrellis K, Stefanis L (2008) Wild type alpha-synuclein is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy and macroautophagy in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 283:23542–23556
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2006) Cellular pathology in multiple system atrophy. Neuropathology 26:338–345
Waxman EA, Giasson BI (2011) Induction of intracellular tau aggregation is promoted by alpha-synuclein seeds and provides novel insights into the hyperphosphorylation of tau. J Neurosci 31:7604–7618
Webb JL, Ravikumar B, Atkins J, Skepper JN, Rubinsztein DC (2003) Alpha-synuclein is degraded by both autophagy and the proteasome. J Biol Chem 278:25009–25013
Wenning GK, Stefanova N, Jellinger KA, Poewe W, Schlossmacher MG (2008) Multiple system atrophy: a primary oligodendrogliopathy. Ann Neurol 64:239–246
Yakunin E, Loeb V, Kisos H et al (2012) Alpha-synuclein neuropathology is controlled by nuclear hormone receptors and enhanced by docosahexaenoic acid in a mouse model for Parkinson’s disease. Brain Pathol 22:280–294
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Poul Henning Jensen, Aarhus University, Denmark, for the generous gift of human recombinant α-Syn. We thank Angelika Spanjer and Irina Fomins for expert technical help and Dr. Olaf Goldbaum for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pukaß, K., Richter-Landsberg, C. Oxidative Stress Promotes Uptake, Accumulation, and Oligomerization of Extracellular α-Synuclein in Oligodendrocytes. J Mol Neurosci 52, 339–352 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0154-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0154-x