Abstract
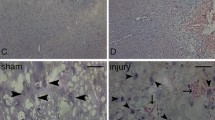
The cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB) family can regulate biological functions of various types of cells by forming homo- or heterodimers to bind the target DNA sequences; it plays an essential role in individual neuronal function and entire neuronal circuits. One attractive activity of the CREB family is regulating the transcription of apoptosis-suppressor gene bcl-2. Cyclic AMP response element modulator-1 (CREM-1) is one member of the family with limited acquaintance. To investigate whether CREM-1 is involved in central nervous system injury and repair, we performed an acute traumatic brain injury (TBI) model in adult rats. Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry showed a significant upregulation of CREM-1 in ipsilateral peritrauma cortex. Immunofluorescent labeling indicated that CREM-1 was localized mainly in the nuclei of neurons; co-localization of CREM-1 and active-caspase-3 in the ipsilateral cortex suggested that CREM-1 might participate in neuronal apoptosis. To further investigate the function of CREM-1, a neuronal cell line PC12 was employed to establish an apoptosis model. We analyzed the association of CREM-1 with p-CREB on PC12 cells by Western blot, immunofluorescent labeling, and co-immunoprecipitation. The result implied that the association of CREM-1 with p-CREB was enhanced in apoptotic cells. Additionally, knocking CREM-1 down with siRNA demonstrated the probable pro-apoptotic role played by CREM-1 in neuronal apoptosis. Together with our data, we hypothesized that CREM-1 might play an important role in regulating neuronal death after TBI by interacting with CREB.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allagnat F, Martin D, Condorelli DF, Waeber G, Haefliger JA (2005) Glucose represses connexin36 in insulin-secreting cells. J Cell Sci 118:5335
Andriessen TMJC, Horn J, Franschman G, van der Naalt J, Haitsma I, Jacobs B, Steyerberg EW, Vos PE (2011) Epidemiology, severity classification, and outcome of moderate and severe traumatic brain injury: a prospective multicenter study. J Neurotrauma 28:2019
Balasubramanian G, Hanumegowda U, Reddy CS (2000) Secalonic acid D alters the nature of and inhibits the binding of the transcription factors to the phorbol 12-O-tetradecanoate-13 acetate-response element in the developing murine secondary palate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 169:142
Barco A, Marie H (2011) Genetic approaches to investigate the role of CREB in neuronal plasticity and memory. Mol Neurobiol 44:330
Clark RS, Chen J, Watkins SC, Kochanek PM, Chen M, Stetler RA, Loeffert JE, Graham SH (1997) Apoptosis-suppressor gene bcl-2 expression after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurosci 17:9172
Clark RS, Kochanek PM, Watkins SC, Chen M, Dixon CE, Seidberg NA, Melick J, Loeffert JE, Nathaniel PD, Jin KL, Graham SH (2000) Caspase-3 mediated neuronal death after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurochem 74:740
Deveraux QL, Leo E, Stennicke HR, Welsh K, Salvesen GS, Reed JC (1999) Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for caspases. EMBO J 18:5242
Dey S, Mactutus CF, Booze RM, Snow DM (2007) Cocaine exposure in vitro induces apoptosis in fetal locus coeruleus neurons by altering the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and through caspase-3 apoptotic signaling. Neuroscience 144:509
Engel T, Plesnila N, Prehn JH, Henshall DC (2011) In vivo contributions of BH3-only proteins to neuronal death following seizures, ischemia, and traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1196
Finkbeiner S (2000) CREB couples neurotrophin signals to survival messages. Neuron 25:11
Guo Z, Du X, Iacovitti L (1998) Regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression during transdifferentiation of striatal neurons: changes in transcription factors binding the AP-1 site. J Neurosci 18:8163
Haddad JJ (2007) The role of Bax/Bcl-2 and pro-caspase peptides in hypoxia/reperfusion-dependent regulation of MAPK(ERK): discordant proteomic effect of MAPK(p38). Protein Pept Lett 14:361
Hartings JA, Bullock MR, Okonkwo DO, Murray LS, Murray GD, Fabricius M, Maas AI, Woitzik J, Sakowitz O, Mathern B, Roozenbeek B, Lingsma H, Dreier JP, Puccio AM, Shutter LA, Pahl C, Strong AJ, Co-Operative Study on Brain Injury, D (2011) Spreading depolarisations and outcome after traumatic brain injury: a prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol 10:1058
He Z, Jiang J, Kokkinaki M, Golestaneh N, Hofmann MC, Dym M (2008) Gdnf upregulates c-Fos transcription via the Ras/Erk1/2 pathway to promote mouse spermatogonial stem cell proliferation. Stem Cells 26:266
Herdegen T, Leah JD (1998) Inducible and constitutive transcription factors in the mammalian nervous system: control of gene expression by Jun, Fos and Krox, and CREB/ATF proteins. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 28:370
Herold S, Jagasia R, Merz K, Wassmer K, Lie DC (2011) CREB signalling regulates early survival, neuronal gene expression and morphological development in adult subventricular zone neurogenesis. Mol Cell Neurosci 46:79
Hoh NZ, Wagner AK, Alexander SA, Clark RB, Beers SR, Okonkwo DO, Ren D, Conley YP (2010) BCL2 genotypes: functional and neurobehavioral outcomes after severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 27:1413
Jaworski J, Mioduszewska B, Sanchez-Capelo A, Figiel I, Habas A, Gozdz A, Proszynski T, Hetman M, Mallet J, Kaczmarek L (2003) Inducible cAMP early repressor, an endogenous antagonist of cAMP responsive element-binding protein, evokes neuronal apoptosis in vitro. J Neurosci 23:4519
Jurgensmeier JM, Xie Z, Deveraux Q, Ellerby L, Bredesen D, Reed JC (1998) Bax directly induces release of cytochrome C from isolated mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:4997
Kernie SG, Erwin TM, Parada LF (2001) Brain remodeling due to neuronal and astrocytic proliferation after controlled cortical injury in mice. J Neurosci Res 66:317
Loane DJ, Faden AI (2010) Neuroprotection for traumatic brain injury: translational challenges and emerging therapeutic strategies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 31:596
Logan A, Frautschy SA, Gonzalez AM, Baird A (1992) A time course for the focal elevation of synthesis of basic fibroblast growth factor and one of its high-affinity receptors (flg) following a localized cortical brain injury. J Neurosci 12:3828
Lonze BE, Riccio A, Cohen S, Ginty DD (2002) Apoptosis, axonal growth defects, and degeneration of peripheral neurons in mice lacking CREB. Neuron 34:371
Maas AI, Stocchetti N, Bullock R (2008) Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet Neurol 7:728
Martinou JC, Youle RJ (2011) Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell 21:92
Mayr B, Montminy M (2001) Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:599
Ola MS, Nawaz M, Ahsan H (2011) Role of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 351:41
Raghupathi R, Strauss KI, Zhang C, Krajewski S, Reed JC, McIntosh TK (2003) Temporal alterations in cellular Bax:Bcl-2 ratio following traumatic brain injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma 20:421
Rink A, Fung KM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Neugebauer E, McIntosh TK (1995) Evidence of apoptotic cell death after experimental traumatic brain injury in the rat. Am J Pathol 147:1575
Saggioro D (2011) Anti-apoptotic effect of Tax: an NF-kappaB path or a CREB way? Viruses 3:1001
Sawka-Verhelle D, Escoubet-Lozach L, Fong AL, Hester KD, Herzig S, Lebrun P, Glass CK (2004) PE-1/METS, an antiproliferative Ets repressor factor, is induced by CREB-1/CREM-1 during macrophage differentiation. J Biol Chem 279:17772
Servillo G, Della Fazia MA, Sassone-Corsi P (2002) Coupling cAMP signaling to transcription in the liver: pivotal role of CREB and CREM. Exp Cell Res 275:143
Shankar E, Krishnamurthy S, Paranandi R, Basu A (2010) PKCepsilon induces Bcl-2 by activating CREB. Int J Oncol 36:883
Stoica BA, Faden AI (2010) Cell death mechanisms and modulation in traumatic brain injury. Neurotherapeutics 7:3
Wennersten A, Holmin S, Mathiesen T (2003) Characterization of Bax and Bcl-2 in apoptosis after experimental traumatic brain injury in the rat. Acta Neuropathol 105:281
Wilson BE, Mochon E, Boxer LM (1996) Induction of bcl-2 expression by phosphorylated CREB proteins during B-cell activation and rescue from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 16:5546
Wong J, Hoe NW, Zhiwei F, Ng I (2005) Apoptosis and traumatic brain injury. Neurocrit Care 3:177
Yakovlev AG, Faden AI (2001) Caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways in CNS injury. Mol Neurobiol 24:131
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81070992) and funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD). Nantong University graduate scientific and technological innovation projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xinmin Wu and Wei Jin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Jin, W., Liu, X. et al. Cyclic AMP Response Element Modulator-1 (CREM-1) Involves in Neuronal Apoptosis after Traumatic Brain Injury. J Mol Neurosci 47, 357–367 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9761-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9761-1