Abstract
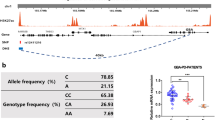
Alpha-synuclein gene (SNCA) polymorphisms have been associated with the common sporadic form of Parkinson’s disease (PD). We searched for DNA variants at the SNCA 3′ UTR through single strand conformation analysis and direct sequencing in a cohort of Spanish PD patients and controls. We have genotyped the rs356165 SNCA 3′ UTR polymorphism in a total of 1,135 PD patients and 772 healthy controls from two Spanish cohorts (Asturias and Navarre). We identified six SNCA 3′ UTR variants. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs356165 was significantly associated with PD risk in the Spanish cohort (p = 0.0001; odd ratio = 1.37, 95%CI = 1.19–1.58). This SNP was also significantly associated with early age at onset of PD. Our work highlights rs356165 as an important determinant of the risk of developing PD and early age at onset and encourages future research to identify a functional effect on SNCA expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borchert GM, Gilmore BL, Spengler RM, Xing Y, Lanier W, Bhattacharya D, Davidson BL (2009) Adenosine deamination in human transcripts generates novel microRNA binding sites. Hum Mol Genet 18:4801–4807
de Lau LM, Breteler MM (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5:525–535
Dickson DW, Braak H, Duda JE, Duyckaerts C, Gasser T, Halliday GM, Hardy J, Leverenz JB, Del Tredici K, Wszolek ZK, Litvan I (2009) Neuropathological assessment of Parkinson’s disease: refining the diagnostic criteria. Lancet Neurol 8:1150–1157
Doxakis E (2010) Post-transcriptional regulation of alpha-synuclein expression by mir-7 and mir-153. J Biol Chem 285:12726–12734
Edwards TL, Scott WK, Almonte C, Burt A, Powell EH, Beecham GW, Wang L, Zuchner S, Konidari I, Wang G, Singer C, Nahab F, Scott B, Stajich JM, Pericak-Vance M, Haines J, Vance JM, Martin ER (2010) Genome-wide association study confirms SNPs in SNCA and the MAPT region as common risk factors for Parkinson disease. Ann Hum Genet 74:97–109
Hebert SS, De Strooper B (2007) Molecular biology. miRNAs in neurodegeneration. Science 317:1179–1180
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184
Junn E, Lee KW, Jeong BS, Chan TW, Im JY, Mouradian MM (2009) Repression of alpha-synuclein expression and toxicity by microRNA-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13052–13057
Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 18:106–108
Mata IF, Ross OA, Kachergus J, Huerta C, Ribacoba R, Moris G et al (2006) LRRK2 mutations are a common cause of Parkinson’s disease in Spain. Eur J Neurol 13:391–394
Mata IF, Yearout D, Alvarez V, Coto E, de Mena L, Ribacoba R, Lorenzo-Betancor O, Samaranch L, Pastor P, Cervantes S, Infante J, Garcia-Gorostiaga I, Sierra M, Combarros O, Snapinn KW, Edwards KL, Zabetian CP (2011) Replication of MAPT and SNCA, but not PARK16–18, as susceptibility genes for parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 5:819–823
McCarthy JJ, Linnertz C, Saucier L, Burke JR, Hulette CM, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Chiba-Falek O (2011) The effect of SNCA 3′ region on the levels of SNCA-112 splicing variant. Neurogenetics 12:59–64
Mizuta I, Satake W, Nakabayashi Y, Ito C, Suzuki S, Momose Y, Nagai Y, Oka A, Inoko H, Fukae J, Saito Y, Sawabe M, Murayama S, Yamamoto M, Hattori N, Murata M, Toda T (2006) Multiple candidate gene analysis identifies alpha-synuclein as a susceptibility gene for sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 15:1151–1158
Mueller JC, Fuchs J, Hofer A, Zimprich A, Lichtner P, Illig T, Berg D, Wullner U, Meitinger T, Gasser T (2005) Multiple regions of alpha-synuclein are associated with Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 57:535–541
Myhre R, Toft M, Kachergus J, Hulihan MM, Aasly JO, Klungland H, Farrer MJ (2008) Multiple alpha-synuclein gene polymorphisms are associated with Parkinson’s disease in a Norwegian population. Acta Neurol Scand 118:320–327
Pals P, Lincoln S, Manning J, Heckman M, Skipper L, Hulihan M, Van den Broeck M, De Pooter T, Cras P, Crook J, Van Broeckhoven C, Farrer MJ (2004) Alpha-synuclein promoter confers susceptibility to Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 56:591–595
Pastor P, Munoz E, Ezquerra M, Obach V, Marti MJ, Valldeoriola F, Tolosa E, Oliva R (2001) Analysis of the coding and the 5′ flanking regions of the alpha-synuclein gene in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 16:1115–1119
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Satake W, Nakabayashi Y, Mizuta I, Hirota Y, Ito C, Kubo M, Kawaguchi T, Tsunoda T, Watanabe M, Takeda A, Tomiyama H, Nakashima K, Hasegawa K, Obata F, Yoshikawa T, Kawakami H, Sakoda S, Yamamoto M, Hattori N, Murata M, Nakamura Y, Toda T (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1303–1307
Simon-Sanchez J, Schulte C, Bras JM, Sharma M, Gibbs JR, Berg D, Paisan-Ruiz C, Lichtner P, Scholz SW, Hernandez DG, Kruger R, Federoff M, Klein C, Goate A, Perlmutter J, Bonin M, Nalls MA, Illig T, Gieger C, Houlden H, Steffens M, Okun MS, Racette BA, Cookson MR, Foote KD, Fernandez HH, Traynor BJ, Schreiber S, Arepalli S, Zonozi R, Gwinn K, van der Brug M, Lopez G, Chanock SJ, Schatzkin A, Park Y, Hollenbeck A, Gao J, Huang X, Wood NW, Lorenz D, Deuschl G, Chen H, Riess O, Hardy JA, Singleton AB, Gasser T (2009) Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1308–1312
Sotiriou S, Gibney G, Baxevanis AD, Nussbaum RL (2009) A single nucleotide polymorphism in the 3′UTR of the SNCA gene encoding alpha-synuclein is a new potential susceptibility locus for Parkinson disease. Neurosci Lett 461:196–201
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Wang G, van der Walt JM, Mayhew G, Li YJ, Zuchner S, Scott WK, Martin ER, Vance JM (2008) Variation in the miRNA-433 binding site of FGF20 confers risk for Parkinson disease by overexpression of alpha-synuclein. Am J Hum Genet 82:283–289
Warner TT, Schapira AH (2003) Genetic and environmental factors in the cause of Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53(Suppl 3):S16–S23, discussion S23–15
Yu L, Xu P, He X, Hu F, Lin Z, Zhu M, Liu Z, He L, Xu Y (2010) SNP rs7684318 of the α-synuclein gene is associated with Parkinson’s disease in the Han Chinese population. Brain Res 1346:262–265
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, Vidal L, Hoenicka J, Rodriguez O, Atares B, Llorens V, Gomez Tortosa E, del Ser T, Munoz DG, de Yebenes JG (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55:164–173
Acknowledgments
Authors thank the “Fundacion Parkinson Asturias” and “Obra Social Cajastur” for their support. This work was supported by grants from the Spanish “Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias-Fondos FEDER” European Union (FIS-05/008 and 08/0915). LFC and LDM are predoctoral fellowships of FICYT-Principado de Asturias. LS held a “Torres Quevedo” fellowship from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology, co-financed by the European Social Fund. This study was supported by a grant from the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science (SAF2006-10126, 2006–2009) by the project 061131 from the “Fundació La Marató de TV3” and by the UTE project FIMA, Spain to PP.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
Primers designed to amplify the four 3´UTR SNCA fragments. SNP rs356165 was genotyped through amplification with fragment 4 primers, followed by digestion with TaiI and electrophoresis on 4% agarose gel to visualize the two alleles: A 273 bp and G 199 + 74 bp (DOC 32 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 1
a PCR-RFLP genotypes for the rs356165 SNP. b SSCA patterns of heterozygotes (arrows) for the c.404 C>T and the c.*139 T>G (SNP rs10024743). c DNA sequences showing the c.404 C>T and the c.*575_579 deletion (DOC 79 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cardo, L.F., Coto, E., de Mena, L. et al. A Search for SNCA 3′ UTR Variants Identified SNP rs356165 as a Determinant of Disease Risk and Onset Age in Parkinson’s Disease. J Mol Neurosci 47, 425–430 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9669-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9669-1