Abstract
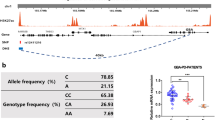
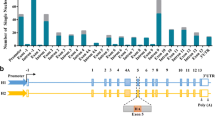
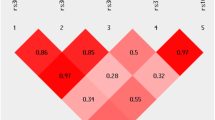
Genetic variability at the 3′ region of SNCA locus has been repeatedly associated with susceptibility to sporadic Parkinson’s disease (PD). Accumulated evidence emphasizes the importance of SNCA dosage and expression levels in PD pathogenesis. However, the mechanism through which the 3′ region of SNCA gene modulates the risk to develop sporadic PD remained elusive. We studied the effect of PD risk-associated variants at SNCA 3′ regions on SNCA112-mRNA (exon 5 in-frame skipping) levels in vivo in 117 neuropathologically normal, human brain frontal cortex samples. SNPs tagging the SNCA 3′ showed significant effects on the relative levels of SNCA112-mRNA from total SNCA transcripts levels. The “risk” alleles were correlated with increased expression ratio of SNCA112-mRNA from total. We provide evidence for functional consequences of PD-associated SNCA gene variants at the 3′ region, suggesting that genetic regulation of SNCA splicing plays an important role in the development of the disease. Further studies to determine the definite functional variant/s within SNCA 3′and to establish their association with PD pathology are necessary.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A et al (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S et al (2003) alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:841
Farrer M, Kachergus J, Forno L, Lincoln S, Wang DS et al (2004) Comparison of kindreds with parkinsonism and alpha-synuclein genomic multiplications. Ann Neurol 55:174–179
Miller DW, Hague SM, Clarimon J, Baptista M, Gwinn-Hardy K et al (2004) Alpha-synuclein in blood and brain from familial Parkinson disease with SNCA locus triplication. Neurology 62:1835–1838
Chartier-Harlin MC, Kachergus J, Roumier C, Mouroux V, Douay X et al (2004) Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 364:1167–1169
Ibanez P, Bonnet AM, Debarges B, Lohmann E, Tison F et al (2004) Causal relation between alpha-synuclein gene duplication and familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 364:1169–1171
Fuchs J, Nilsson C, Kachergus J, Munz M, Larsson EM et al (2007) Phenotypic variation in a large Swedish pedigree due to SNCA duplication and triplication. Neurology 68:916–922
Ross OA, Braithwaite AT, Skipper LM, Kachergus J, Hulihan MM et al (2008) Genomic investigation of alpha-synuclein multiplication and parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 63:743–750
Chiba-Falek O, Lopez GJ, Nussbaum RL (2006) Levels of alpha-synuclein mRNA in sporadic Parkinson disease patients. Mov Disord 21:1703–1708
Grundemann J, Schlaudraff F, Haeckel O, Liss B (2008) Elevated alpha-synuclein mRNA levels in individual UV-laser-microdissected dopaminergic substantia nigra neurons in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e38
Maraganore DM, de Andrade M, Elbaz A, Farrer MJ, Ioannidis JP et al (2006) Collaborative analysis of alpha-synuclein gene promoter variability and Parkinson disease. Jama 296:661–670
Pals P, Lincoln S, Manning J, Heckman M, Skipper L et al (2004) alpha-Synuclein promoter confers susceptibility to Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 56:591–595
Mueller JC, Fuchs J, Hofer A, Zimprich A, Lichtner P et al (2005) Multiple regions of alpha-synuclein are associated with Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 57:535–541
Mizuta I, Satake W, Nakabayashi Y, Ito C, Suzuki S et al (2006) Multiple candidate gene analysis identifies alpha-synuclein as a susceptibility gene for sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 15:1151–1158
Winkler S, Hagenah J, Lincoln S, Heckman M, Haugarvoll K et al (2007) alpha-Synuclein and Parkinson disease susceptibility. Neurology 69:1745–1750
Myhre R, Toft M, Kachergus J, Hulihan MM, Aasly JO et al (2008) Multiple alpha-synuclein gene polymorphisms are associated with Parkinson’s disease in a Norwegian population. Acta Neurol Scand 118:320–327
Satake W, Nakabayashi Y, Mizuta I, Hirota Y, Ito C et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1303–1307
Simon-Sanchez J, Schulte C, Bras JM, Sharma M, Gibbs JR et al (2009) Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1308–1312
Fuchs J, Tichopad A, Golub Y, Munz M, Schweitzer KJ et al (2008) Genetic variability in the SNCA gene influences alpha-synuclein levels in the blood and brain. FASEB J 22:1327–1334
Linnertz C, Saucier L, Ge D, Cronin KD, Burke JR et al (2009) Genetic regulation of alpha-synuclein mRNA expression in various human brain tissues. PLoS ONE 4:e7480
Beyer K, Domingo-Sabat M, Humbert J, Carrato C, Ferrer I et al (2008) Differential expression of alpha-synuclein, parkin, and synphilin-1 isoforms in Lewy body disease. Neurogenetics 9:163–172
Campion D, Martin C, Heilig R, Charbonnier F, Moreau V et al (1995) The NACP/synuclein gene: chromosomal assignment and screening for alterations in Alzheimer disease. Genomics 26:254–257
Ueda K, Saitoh T, Mori H (1994) Tissue-dependent alternative splicing of mRNA for NACP, the precursor of non-A beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 205:1366–1372
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R et al (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Beyer K (2006) Alpha-synuclein structure, posttranslational modification and alternative splicing as aggregation enhancers. Acta Neuropathol 112:237–251
Lee HJ, Choi C, Lee SJ (2002) Membrane-bound alpha-synuclein has a high aggregation propensity and the ability to seed the aggregation of the cytosolic form. J Biol Chem 277:671–678
Cronin KD, Ge D, Manninger P, Linnertz C, Rossoshek A et al (2009) Expansion of the Parkinson disease-associated SNCA-Rep1 allele upregulates human alpha-synuclein in transgenic mouse brain. Hum Mol Genet 18:3274–3285
Bengtsson M, Stahlberg A, Rorsman P, Kubista M (2005) Gene expression profiling in single cells from the pancreatic islets of Langerhans reveals lognormal distribution of mRNA levels. Genome Res 15:1388–1392
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21:263–265
Scholz SW, Houlden H, Schulte C, Sharma M, Li A et al (2009) SNCA variants are associated with increased risk for multiple system atrophy. Ann Neurol 65:610–614
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Ellison Medical Foundation New Scholar award AG-NS-0441-08 (O.C.) and the Institute for Genome Sciences and Policy at Duke University (O.C.). We thank the Kathleen Price Bryan Brain Bank (KPBBB) at Duke University funded by NIA AG028377, the National NeuroAIDS Tissue Consortium (NNTC), Layton Aging & Alzheimer’s Disease Center at Oregon Health and Science University funded by NIA AG008017, and the NICHD Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders at the University of Maryland, Baltimore (NICHD contract no. HHSN275200900011C, Ref. No. NO1-HD-9-0011), for providing us with the brain tissues. We would also like to thank Dr. Randy Woltjer, Dr. Kathleen Hayden, Dr. Lauren Warren, Mari Szymanski, and John Ervin for their assistance in obtaining the required brain samples for the study.
Ethical standards
The experiments comply with the current laws of the USA.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCarthy, J.J., Linnertz, C., Saucier, L. et al. The effect of SNCA 3′ region on the levels of SNCA-112 splicing variant. Neurogenetics 12, 59–64 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-010-0263-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-010-0263-4