Abstract
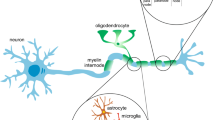
Oligodendrocytes have a complex cytoarchitecture and are characterized by an elaborate network of microtubules. They provide the tracks for organelle trafficking and the intracellular translocation of myelin-specific gene products. The integrity of the cytoskeleton is an essential determinant of the function and survival of oligodendrocytes. Microtubule growth and stability are regulated by microtubule-associated proteins. Oligodendrocytes contain a number of microtubule-associated proteins, including the tau proteins, which are developmentally regulated and especially prominent in the branching points of the cellular processes. Process outgrowth is regulated by the interaction of Fyn kinase with the cytoskeleton and by microtubule-severing proteins, such as stathmin. Alterations or disruption of the cytoskeleton and abundant abnormal aggregates of cytoskeletal proteins often accompany neurodegenerative diseases, and inclusion bodies, resembling protein aggregates found in neurons, are prominent in oligodendroglial lesions in white matter pathology. This review emphasizes the role of the cytoskeleton, particularly of microtubules and their associated proteins, in oligodendrocytes during developmental processes. Furthermore, recent data on protein aggregate formation in oligodendroglial cells, which might occur during aging and disease processes, are summarized.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers, D. S., & Augood, S. J. (2001). New insights into progressive supranuclear palsy. Trends in Neurosciences, 24, 347–353.
Andersen, S. S. (2000). Spindle assembly and the art of regulating microtubule dynamics by MAPs and Stathmin/Op18. Trends in Cell Biology, 10, 261–267.
Baas, P. W. (1999). Microtubules and neuronal polarity: lessons from mitosis. Neuron, 22, 23–31.
Barry, C., Pearson, C., & Barbarese, E. (1996). Morphological organization of oligodendrocyte processes during development in culture and in vivo. Developmental Neuroscience, 18, 233–242.
Bauer, N. G., & Richter-Landsberg, C. (2006). The dynamic instability of microtubules is required for aggresome formation in oligodendroglial cells after proteolytic stress. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 29, 153–168.
Buée, L., Bussiere, T., Buee-Scherrer, V., Delacourte, A., & Hof, P. R. (2000). Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain research. Brain research reviews, 33, 95–130.
Cairns, N. J., Atkinson, P. F., Hanger, D. P., Anderton, B. H., Daniel, S. E., & Lantos, P. L. (1997). Tau protein in the glial cytoplasmic inclusions of multiple system atrophy can be distinguished from abnormal tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience Letters, 230, 49–52.
Carson, J. H., Worboys, K., Ainger, K., & Barbarese, E. (1997). Translocation of myelin basic protein mRNA in oligodendrocytes requires microtubules and kinesin. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton, 38, 318–328.
Chin, S. S., & Goldman, J. E. (1996). Glial inclusions in CNS degenerative diseases. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 55, 499–508.
Ciechanover, A., & Brundin, P. (2003). The ubiquitin proteasome system in neurodegenerative diseases: sometimes the chicken, sometimes the egg. Neuron, 40, 427–446.
Dabir, D. V., Trojanowski, J. Q., Richter-Landsberg, C., Lee, V. M., & Forman, M. S. (2004). Expression of the small heat-shock protein alphaB-crystallin in tauopathies with glial pathology. American Journal of Pathology, 164, 155–166.
Dickson, D. W., Lin, W., Liu, W. K., & Yen, S. H. (1999). Multiple system atrophy: a sporadic synucleinopathy. Brain Pathology, 9, 721–732.
Dyer, C. A., & Benjamins, J. A. (1989). Organization of oligodendroglial membrane sheets. I: Association of myelin basic protein and 2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′-phosphohydrolase with cytoskeleton. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 24, 201–211.
Fass, E., Shvets, E., Degani, I., Hirschberg, K., & Elazar, Z. (2006). Microtubules support production of starvation-induced autophagosomes but not their targeting and fusion with lysosomes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 36303–36316.
Fischer, I., Konola, J., & Cochary, E. (1990). Microtubule associated protein (MAP1B) is present in cultured oligodendrocytes and co-localizes with tubulin. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 27, 112–124.
Forman, M. S., Trojanowski, J. Q., & Lee, V. M. (2004). Neurodegenerative diseases: a decade of discoveries paves the way for therapeutic breakthroughs. Natural Medicines, 10, 1055–1063.
Galiano, M. R., Andrieux, A., Deloulme, J. C., Bosc, C., Schweitzer, A., Job, D. et al. (2006). Myelin basic protein functions as a microtubule stabilizing protein in differentiated oligodendrocytes. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 84, 534–541.
Garcia-Mata, R., Bebok, Z., Sorscher, E. J., & Sztul, E. S. (1999). Characterization and dynamics of aggresome formation by a cytosolic GFP-chimera. Journal of Cell Biology, 146, 1239–1254.
Giasson, B. I., Lee, V. M. Y., & Trojanowski, J. Q. (2004). Animal models of neurodegenerative dementing disorders othe than Alzheimer`s disease. Clinical Neuroscience Research, 3, 427–436.
Goedert, M. (2001). The significance of tau and alpha-synuclein inclusions in neurodegenerative diseases. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 11, 343–351.
Goedert, M., Crowther, R. A., & Garner, C. C. (1991). Molecular characterization of microtubule-associated proteins tau and MAP2. Trends in Neurosciences, 14, 193–199.
Goedert, M., Spillantini, M. G., & Davies, S. W. (1998). Filamentous nerve cell inclusions in neurodegenerative diseases. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 8, 619–632.
Goldbaum, O., Oppermann, M., Handschuh, M., Dabir, D., Zhang, B., Forman, M. S. et al. (2003). Proteasome inhibition stabilizes tau inclusions in oligodendroglial cells that occur after treatment with okadaic acid. Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 8872–8880.
Goldbaum, O., & Richter-Landsberg, C. (2004). Proteolytic stress causes heat shock protein induction, tau ubiquitination, and the recruitment of ubiquitin to tau-positive aggregates in oligodendrocytes in culture. Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 5748–5757.
Gorath, M., Stahnke, T., Mronga, T., Goldbaum, O., & Richter-Landsberg, C. (2001). Developmental changes of tau protein and mRNA in cultured rat brain oligodendrocytes. Glia, 36, 89–101.
Götz, J., Tolnay, M., Barmettler, R., Chen, F., Probst, A., & Nitsch, R. M. (2001). Oligodendroglial tau filament formation in transgenic mice expressing G272V tau. European Journal of Neuroscience, 13, 2131–2140.
Grinspan, J. (2002). Cells and signaling in oligodendrocyte development. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 61, 297–306.
Higuchi, M., Ishihara, T., Zhang, B., Hong, M., Andreadis, A., Trojanowski, J. et al. (2002). Transgenic mouse model of tauopathies with glial pathology and nervous system degeneration. Neuron, 35, 433–446.
Higuchi, M., Zhang, B., Forman, M. S., Yoshiyama, Y., Trojanowski, J. Q., & Lee, V. M. (2005). Axonal degeneration induced by targeted expression of mutant human tau in oligodendrocytes of transgenic mice that model glial tauopathies. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 9434–9443.
Hirokawa, N., Noda, Y., & Okada, Y. (1998). Kinesin and dynein superfamily proteins in organelle transport and cell division. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 10, 60–73.
Irving, E. A., Nicoll, J., Graham, D. I., & Dewar, D. (1996). Increased tau immunoreactivity in oligodendrocytes following human stroke and head injury. Neuroscience Letters, 213, 189–192.
Johnston, J. A., Ward, C. L., & Kopito, R. R. (1998). Aggresomes: a cellular response to misfolded proteins. Journal of Cell Biology, 143, 1883–1898.
Keller, J. N., Gee, J., & Ding, Q. (2002). The proteasome in brain aging. Ageing Research Reviews, 1, 279–293.
Klein, C., Kramer, E. M., Cardine, A. M., Schraven, B., Brandt, R., & Trotter, J. (2002). Process outgrowth of oligodendrocytes is promoted by interaction of fyn kinase with the cytoskeletal protein tau. Journal of Neuroscience, 22, 698–707.
Komori, T. (1999). Tau-positive glial inclusions in progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration and Pick’s disease. Brain Pathology, 9, 663–679.
Kopito, R. R. (2000). Aggresomes, inclusion bodies and protein aggregation. Trends in Cell Biology, 10, 524–530.
Kramer, E. M., Klein, C., Koch, T., Boytinck, M., & Trotter, J. (1999). Compartmentation of Fyn kinase with glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored molecules in oligodendrocytes facilitates kinase activation during myelination. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 29042–29049.
Laferriere, N. B., MacRae, T. H., & Brown, D. L. (1997). Tubulin synthesis and assembly in differentiating neurons. Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 75, 103–117.
Lantos, P. L. (1998). The definition of multiple system atrophy: a review of recent developments. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 57, 1099–1111.
Lee, V. M., Giasson, B. I., & Trojanowski, J. Q. (2004). More than just two peas in a pod: common amyloidogenic properties of tau and alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neuroscience, 27, 129–134.
Lee, V. M., Goedert, M., & Trojanowski, J. Q. (2001). Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 24, 1121–1159.
Lee, J., Gravel, M., Zhang, R., Thibault, P., & Braun, P. E. (2005). Process outgrowth in oligodendrocytes is mediated by CNP, a novel microtubule assembly myelin protein. Journal of Cell Biology, 170, 661–673.
Lee, J. C., Mayer-Proschel, M., & Rao, M. S. (2000). Gliogenesis in the central nervous system. Glia, 30, 105–121.
Liang, X., Draghi, N. A., & Resh, M. D. (2004). Signaling from integrins to Fyn to Rho family GTPases regulates morphologic differentiation of oligodendrocytes. Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 7140–7149.
Lin, W. L., Lewis, J., Yen, S. H., Hutton, M., & Dickson, D. W. (2003). Filamentous tau in oligodendrocytes and astrocytes of transgenic mice expressing the human tau isoform with the P301L mutation. American Journal of Pathology, 162, 213–218.
Liu, A., Muggironi, M., Marin-Husstege, M., & Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. (2003). Oligodendrocyte process outgrowth in vitro is modulated by epigenetic regulation of cytoskeletal severing proteins. Glia, 44, 264–274.
Liu, A., Stadelmann, C., Moscarello, M., Bruck, W., Sobel, A., Mastronardi, F. G. et al. (2005). Expression of stathmin, a developmentally controlled cytoskeleton-regulating molecule, in demyelinating disorders. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 737–747.
LoPresti, P., Szuchet, S., Papasozomenos, S. C., Zinkowski, R. P., & Binder, L. I. (1995). Functional implications for the microtubule-associated protein tau: localization in oligodendrocytes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 92, 10369–10373.
Lüders, J., & Stearns, T. (2007). Microtubule-organizing centres: a re-evaluation. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology, 8, 161–167.
Lunn, K. F., Baas, P. W., & Duncan, I. D. (1997). Microtubule organization and stability in the oligodendrocyte. Journal of Neuroscience, 17, 4921–4932.
Miller, D. W., Cookson, M. R., & Dickson, D. W. (2004). Glial cell inclusions and the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron Glia Biology, 1, 13–21.
Muller, R., Heinrich, M., Heck, S., Blohm, D., & Richter-Landsberg, C. (1997). Expression of microtubule-associated proteins MAP2 and tau in cultured rat brain oligodendrocytes. Cell & Tissue Research, 288, 239–249.
Nixon, R. A. (2006). Autophagy in neurodegenerative disease: friend, foe or turncoat? Trends in Neurosciences, 29, 528–535.
Osterhout, D. J., Wolven, A., Wolf, R. M., Resh, M. D., & Chao, M. V. (1999). Morphological differentiation of oligodendrocytes requires activation of Fyn tyrosine kinase. Journal of Cell Biology, 145, 1209–1218.
Ozon, S., Guichet, A., Gavet, O., Roth, S., & Sobel, A. (2002). Drosophila stathmin: a microtubule-destabilizing factor involved in nervous system formation. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 13, 698–710.
Pfeiffer, S. E., Warrington, A. E., & Bansal, R. (1993). The oligodendrocyte and its many cellular processes. Trends in Cell Biology, 3, 191–197.
Quarles R. H., Macklin W. B., & Morell P. (2006). Myelin formation, structure and biochemistry. In G. J. Siegel, R. W. Albers, S. T. Brady, & D. L. Price (Eds.), Basic Neurochemistry (7th ed., pp. 51–71). New York: Elsevier.
Raynaud-Messina, Merdes, A. (2007). γ-Tubulin complexes and microtubule organization. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 19, 24–30.
Richter-Landsberg C. (2000). The oligodendroglia cytoskeleton in health and disease. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 59, 11–18.
Richter-Landsberg C. (2007). Heat shock proteins: expression and functional roles in nerve cells and glia. In C. Richter-Landsberg (Ed.), Heat Shock Proteins in Neural Cells (pp 1–12). New York: Springer.
Richter-Landsberg, C., & Bauer, N. G. (2004). Tau-inclusion body formation in oligodendroglia: the role of stress proteins and proteasome inhibition. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 22, 443–451.
Richter-Landsberg, C., & Goldbaum, O. (2003). Stress proteins in neural cells: functional roles in health and disease. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 60, 337–349.
Richter-Landsberg, C., & Goldbaum, O. (2007). Small heat shock proteins and the cytoskeleton. In C. Richter-Landsberg (Ed.), Heat Shock Proteins in Neural Cells (pp. 13–24). New York: Springer.
Richter-Landsberg, C., & Gorath, M. (1999). Developmental regulation of alternatively spliced isoforms of mRNA encoding MAP2 and tau in rat brain oligodendrocytes during culture maturation. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 56, 259–270.
Richter-Landsberg, C., & Heinrich, M. (1996). OLN-93: a new permanent oligodendroglia cell line derived from primary rat brain glial cultures. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 45, 161–173.
Ross, C. A., & Poirier, M. A. (2005). Opinion: What is the role of protein aggregation in neurodegeneration? Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 6, 891–898.
Sherman, M. Y., & Goldberg, A. L. (2001). Cellular defenses against unfolded proteins: a cell biologist thinks about neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron, 29, 15–32.
Smith, R. (2004). Moving molecules: mRNA trafficking in Mammalian oligodendrocytes and neurons. Neuroscientist, 10, 495–500.
Song, J., Goetz, B. D., Baas, P. W., & Duncan, I. D. (2001). Cytoskeletal reorganization during the formation of oligodendrocyte processes and branches. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 17, 624–636.
Song, J., O’Connor L. T., Yu, W., Baas, P. W., & Duncan, I. D. (1999). Microtubule alterations in cultured taiep rat oligodendrocytes lead to deficits in myelin membrane formation. Journal of Neurocytology, 28, 671–683.
Sperber, B. R., Boyle-Walsh, E. A., Engleka, M. J., Gadue, P., Peterson, A. C., Stein, P. L. et al. (2001). A unique role for Fyn in CNS myelination. Journal of Neuroscience, 21, 2039–2047.
Sperber, B. R., & McMorris, F. A. (2001). Fyn tyrosine kinase regulates oligodendroglial cell development but is not required for morphological differentiation of oligodendrocytes. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 63, 303–312.
Takeda, A., Arai, N., Komori, T., Iseki, E., Kato, S., & Oda, M. (1997). Tau immunoreactivity in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy. Neuroscience Letters, 234, 63–66.
Terada, N., Kidd, G. J., Kinter, M., Bjartmar, C., Moran-Jones, K., & Trapp, B. D. (2005). Beta IV tubulin is selectively expressed by oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system. Glia, 50, 212–222.
Umemori, H., Sato, S., Yagi, T., Aizawa, S., & Yamamoto, T. (1994). Initial events of myelination involve Fyn tyrosine kinase signalling. Nature, 367, 572–576.
Vouyiouklis, D. A., & Brophy, P. J. (1993). Microtubule-associated protein MAP1B expression precedes the morphological differentiation of oligodendrocytes. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 35, 257–267.
Vouyiouklis, D. A., & Brophy, P. J. (1995). Microtubule-associated proteins in developing oligodendrocytes: transient expression of a MAP2c isoform in oligodendrocyte precursors. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 42, 803–817.
Wiese, C., & Zheng, Y. (2006). Microtubule nucleation: γ-tubulin and beyond. Journal of Cell Science, 119, 4143–4153.
Wilson, R., & Brophy, P. J. (1989). Role for the oligodendrocyte cytoskeleton in myelination. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 22, 439–448.
Zamora-Leon, S. P., Lee, G., Davies, P., & Shafit-Zagardo, B. (2001). Binding of Fyn to MAP-2c through an SH3 binding domain. Regulation of the interaction by ERK2. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 39950–39958.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Germany and the Society for Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (CurePSP), USA. I thank Dr. Olaf Goldbaum for the help with the graphic art and for providing Fig. 3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richter-Landsberg, C. The Cytoskeleton in Oligodendrocytes. J Mol Neurosci 35, 55–63 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-007-9017-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-007-9017-7