Abstract
Introduction
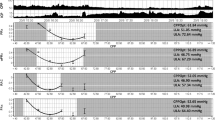
To examine hemispheric differences in cerebral autoregulation in children with traumatic brain injury (TBI). After IRB approval and consent, subjects underwent static cerebral autoregulation testing during the first 9 days after PICU admission. Cerebral autoregulation was quantified using the autoregulatory index (ARI).
Results
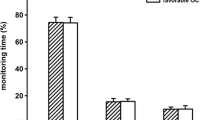
Forty-two (27 M:15 F) children (10 ± 5 years) with TBI and admission Glasgow coma scale score (5 ± 2) were enrolled. Seven (54%) of the 13 children with focal TBI and 8 (28%) of 29 children with diffuse TBI had impairment or absence of cerebral autoregulation of atleast one hemisphere. In patients with isolated focal TBI, ARI was lower (0.40 ± 0.40 vs. 0.67 ± 0.40; P = 0.03) in the side of TBI than in the unaffected hemisphere, but cerebral autoregulation was often impaired on the side without TBI or shift (5/13) on head CT. There was no difference in ARI between hemispheres in children with diffuse TBI, with or without superimposed focal lesions (P = 0.17). Patients with bilateral intact cerebral autoregulation tended to have higher 6 month Glasgow Outcome Score (GOS) than patients with either unilateral or bilateral cerebral autoregulation impairment (GOS 4.0 ± 0.60 vs. 3.6 ± 0.80; P = 0.08).
Conclusions
Hemispheric differences in cerebral autoregulation were common in children with isolated focal TBI. Absence of TBI on CT was not always associated with intact cerebral autoregulation. Patients with bilaterally intact cerebral autoregulation tended to have better outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paulson OB, Strandgaad S, Edvinsson L. Cerebral autoregulation. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 1990;2(2):162–92.
Novak V, Chowdhary A, Farrar B, Nagaraja H, Braun J, Kanard R, et al. Altered cerebral vasoregulation in hypertension and stroke. Neurology 2003;60:1657–63.
Tomura N, Kato T, Kanna I, Shishido F, Inugami A, Uemura K, et al. Increased blood flow in human brain tumor after administration of angiotensin II: demonstration by PET. Comput Med Imaging Graph 1993;17(6):443–9.
Kumar A, Schmidt A, Hiler M, Smielewski P, Pickard JD, Czosnyka M. Asymmetry of critical closing pressure following head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2005;76:1570–3.
Cold GE, Jensen FT. Cerebral autoregulation in unconscious patients with brain injury. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1978;22(3):270–80.
Lang EW, Yip K, Griffith J, Lagopoulos J, Mudaliar Y, Dorsch NW. Hemispheric asymmetry and temporal profiles of cerebral pressure autoregulation in head injury. J Clin Neurosci 2003;10(6):670–3.
Schmidt EA, Czosnyka M, Harris NG, Minhas PS, Pickard JD. Asymmetry of cerebral autoregulation following head injury. Acta Neuorochir Suppl 2002;81:133–4.
Vavilala MS, Muangman S, Tontisirin N, Fisk D, Roscigno C, Mitchell P, et al. Impaired cerebral autoregulation and 6-month outcome in children with severe traumatic brain injury: preliminary findings. Dev Neurosci 2006; 28(4–5):348–53.
Strebel S, Lam AM, Matta B, Mayberg TS, Aaslid R, Newell DW. Dynamic and static cerebral autoregulation during isoflurane, desflurane and propofol anesthesia. Anesthesiology 1995;83:66–76.
Lam AM. Intraoperative transcranial Doppler monitoring. Anesthesiology 1995;82:1536–7.
Tontisirin N, Muangman S, Suz P, Pihoker C, Fisk D, Moore A, et al. Early childhood gender differences in anterior and posterior cerebral blood flow velocity and autoregulaiton. Pediatrics 2007;119:610–5.
Vavilala MS, Kincaid MS, Muangman SL, Suz P, Rozet I, Lam AM. Gender difference in cerebral blood flow velocity and autoregulation between anterior and posterior circulation in healthy children. Pediatr Res 2005;58(3):574–8.
Bode H. Pediatric Applications of Transcranial Doppler Sonography. New York: Springer-Verlag Wein; 1988.
Jennett B, Teasdale G, Braakman R, Minderhoud J, Heiden J, Kurze T. Progonosis of patients with severe head injury. Neurosurgery 1979;4:283–9.
Sigmund GA, Tong KA, Nickerson JP, Wall CJ, Oyoyo U, Ashwal S. Multimodality comparison of neuroimaging in pediatric traumatic brain injury. Pediatr Neurol 2007;36(4):217–26.
Park CW, Strurzenegger M, Douville CM, Aaslid R, Newell DW. Autoregulation Response and CO2 reactivity of the basilar artery. Stroke 2003;34(1):34–9.
Kaps BR. Cerebral autoregulation in middle cerebral artery territory precedes that of posterior cerebral artery in human cortex. Cerebrovasc Dis 2002;13:21–5.
Hanbrich C, Wendet A, Diehl RR, Klotzsch C. Dynamic autoregulation testing in the posterior cerebral artery. Stroke 2004;35(4):848–52.
Hilz MJ, Axelrod FB, Haertl U, Brown CM, Stemper B. Transcranial Doppler Sonography during head up tilt suggests preserved central sympathetic activation in familial dysautonomia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2002;72:657–60.
Vavilala MS, Lee LA, Boddu K, Visco E, Newell DW, Zimmerman JJ, et al. Cerebral autoregulation in Pediatric traumatic brain injury. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2004;5(3):298.
Blaha M, Aaslid R, Douville CM, Correra R, Newell DW. Cerebral blood flow and dynamic cerebral autoreguation during ethanol intoxation and hypercapmia. J Clin Neuorsci 2003;10(2):195–8.
Cremer OL, Diephuis JC, Van Scest H, Vaessen PH, Bruens MG, Hennis PJ, et al. Cerebral oxygen extraction and autoregulation during extracorporeal whole body hyperthermia in humans. Anesthesiology 2004;100(5):1101–7.
Bakker SLM, Leeuw FE, Heijer T, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Breteler MM. Cerebral haemodynamics in the elderly: the Rotterdam study. Neuroepidemiology 2004;23(4):178–84.
Mandura M, Laryz D, Wojitacha M. Changes in cerebral hemodynamics assessed by transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography in children after head injury. Child Nerv Syst 2002;18:124–8.
Aldrich EF, Eisenberg HM, Daydijari C, Luerssen TG, Fouldes MA, Jane JA, et al. Diffuse brain swelling in severely head injured children. J Neurosurg 1992;76:450–4.
Bruce DA, Alavi A, Bilaniuk L, Dolinskad C, Obrist W, Uzzell B. Diffuse cerebral swelling following head injuries in children the syndrome of “malignant brain oedema”. J Neurosurg 1981;54:170–8.
Wintermark M, Chiolero R, Van Melle G, Revelly JP, Porcher F, Regli L, et al. Cerebral vascular autoregulation assessed by perfusion CT in severe head trauma patients. J Neuroradiol 2006;33(1):27–37.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Ms. Domonique Calhoun. This research was supported by National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Award K23HD044632-04.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vavilala, M.S., Tontisirin, N., Udomphorn, Y. et al. Hemispheric Differences in Cerebral Autoregulation in Children with Moderate and Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurocrit Care 9, 45–54 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-007-9036-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-007-9036-9