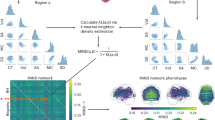
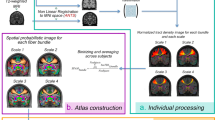
Abstract
Mapping brain structure in relation to neurological development, function, plasticity, and disease is widely considered to be one of the most essential challenges for opening new lines of neuro-scientific inquiry. Recent developments with MRI analysis of structural connectivity, anatomical brain segmentation, cortical surface parcellation, and functional imaging have yielded fantastic advances in our ability to probe the neurological structure-function relationship in vivo. To date, the image analysis efforts in each of these areas have typically focused on a single modality. Here, we extend the cortical reconstruction using implicit surface evolution (CRUISE) methodology to perform efficient, consistent, and topologically correct analyses in a natively multi-parametric manner. This effort combines and extends state-of-the-art techniques to simultaneously consider and analyze structural and diffusion information alongside quantitative and functional imaging data. Robust and consistent estimates of the cortical surface extraction, cortical labeling, diffusion-inferred contrasts, diffusion tractography, and subcortical parcellation are demonstrated in a scan-rescan paradigm. Accompanying this demonstration, we present a fully automated software system complete with validation data.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, J. L. R., Skare, S., & Ashburner, J. (2003). How to correct susceptibility distortions in spin-echo echo-planar images: application to diffusion tensor imaging. NeuroImage, 20, 870–888.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2000). Voxel-based morphometry–the methods. NeuroImage, 11(6 Pt 1), 805–821.
Awate, S.P. and Gee, J.C. (2007). A fuzzy, nonparametric segmentation framework for DTI and MRI analysis, In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging 2007 (IPMI’07). Kerkrade.
Bazin, P. L., & Pham, D. L. (2007a). Topology-preserving tissue classification of magnetic resonance brain images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 26(4), 487–496.
Bazin, P. L., & Pham, D. L. (2007b). Topology correction of segmented medical images using a fast marching algorithm. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 88(2), 182–190.
Bazin, P.-L., & Pham, D. L. (2008). Homeomorphic brain image segmentation with topological and statistical atlases. Medical Image Analysis, 12, 616–625.
Bazin, P. L., et al. (2011). Direct segmentation of the major white matter tracts in diffusion tensor images. NeuroImage, 58(2), 458–468.
Beg, F., Miller, M., Trouve, A., & Younes. (2005). Computing large deformation metric mappings via geodesic flows of diffeomorphisms. International Journal of Computer Vision, 23(2), 108–118.
Bogovic, J., et al. (2010). Statistical fusion of surface labels provided by multiple raters, over-complete, and ancillary data. In SPIE Medical Imaging Conference. San Diego, CA.
Brain Innovation B.V. (2007) BrainVoyager. Available from: http://www.brainvoyager.com/.
Carass, A., et al. (2011). Simple paradigm for extra-cerebral tissue removal: algorithm and analysis. NeuroImage, 56(4), 1982–1992.
Chen, M., et al. (2010). Multi-channel enhancement of the adaptive bases algorithm, In Organization for Human Brain Mapping. Barcelona, Spain.
Cointepas, Y., et al. (2001). BrainVISA: Software platform for visualization and analysis of multi-modality brain data. NeuroImage, 13(6), S98.
Covington, K. et al. (2010). Interfaces and integration of medical image analysis frameworks: Challenges and Opportunities. In Biomedical Science and Engineering Conference. Oak Ridge, TN.
Covington, K., Welch, E.B. and Landman, B.A. (2011). Integrating medical imaging analyses through a high-throughput bundled resource imaging system. In SPIE Medical Imaging Conference. Lake Buena Vista, Florida.
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage, 9(2), 179–194.
Desikan, R. S., et al. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage, 31(3), 968–980.
Eckstein, I., et al. (2009). Active fibers: Matching deformable tract templates to diffusion tensor images. Neuroimage, 47(Supplement 2), T82–T89.
El Kouby, V., et al. (2005). MR Diffusion-based inference of a fiber bundle model from a population of subjects, In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI’05). Palm Springs.
Fischl, B., Sereno, M. I., & Dale, A. M. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. II: Inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage, 9(2), 195–207.
Friston, K., (2006) Statistical parametric mapping: The analysis of functional brain images (p. 656). Academic Press.
Han, X., et al. (2001). Cortical surface reconstruction using a topology preserving geometric deformable model. In 5th IEEE Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis (MMBIA2001). Kauai, Hawaii.
Han, X., Xu, C., & Prince, J. L. (2003). A topology preserving level set method for geometric deformable models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 25, 755–768.
Han, X., et al. (2004). CRUISE: cortical reconstruction using implicit surface evolution. NeuroImage, 23(3), 997–1012.
Jezzard, P., & Balaban, R. S. (1995). Correction for geometric distortion in echo planar images from B0 field variations. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 34, 65–73.
Jezzard, P., Barnett, A. S., & Pierpaoli, C. (1998). Characterization and correction for Eddy current artifacts in echo planar diffusion imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 39, 801–812.
Jones, D. K. (2008). Studying connections in the living human brain with diffusion MRI. Cortex, 44(8), 936–952.
Koenderink, J. J., & van Doorn, A. J. (1992). Surface shape and curvature scales. Image and Vision Computing, 10(8), 557–565.
Landman, B. A., et al. (2007). Effects of diffusion weighting schemes on the reproducibility of DTI-derived fractional anisotropy, mean diffusivity, and principal eigenvector measurements at 1.5T. Neuroimage, 36(4), 1123–1138.
Landman, B., et al. (2011). Multi-parametric neuroimaging reproducibility: A 3T resource study. NeuroImage, 4(14), 2854–2866.
Lawes, I. N. C., et al. (2008). Atlas-based segmentation of white matter tracts of the human brain using diffusion tensor tractography and comparison with classical dissection. NeuroImage, 39, 62–79.
Lenglet, C., Rousson, M., & Deriche, R. (2006). DTI segmentation by statistical surface evolution. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 25(6), 685–700.
Lucas, B. C., et al. (2010). The Java Image Science Toolkit (JIST) for rapid prototyping and publishing of neuroimaging software. Neuroinformatics, 8(1), 5–17.
MacDonald, D., et al. (2000). Automated 3-D extraction of inner and outer surfaces of cerebral cortex from MRI. NeuroImage, 12(3), 340–356.
Maddah, M., et al. (2007). Probabilistic clustering and quantitative analysis of white matter fiber tracts, In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging 2007 (IPMI’07). Kerkrade.
Maddah, M. et al. (2008). A mathematical framework for incorporating anatomical knowledge in DT-MRI analysis, In Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, 2008. ISBI 2008. 5th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (p. 105–108). Paris, France.
Maes, F., et al. (1997). Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 16(2), 187–198.
Mangin, J.-F., et al. (1995). From 3D magnetic resonance images to structural representations of the cortex topography using topology preserving deformations. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 5, 297–318.
Marcus, D., et al. (2007). Open Access Series of Imaging Studies (OASIS): cross-sectional MRI data in young, middle aged, nondemented, and demented older adults. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19(9), 1498–1507.
Mori, S., et al. (1999). Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Annals of Neurology, 45(2), 265–269.
Mori, S. et al. (2005). MRI Atlas of human white matter. Elsevier.
Mueller, S. G., et al. (2005). Ways toward an early diagnosis in Alzheimer’s disease: the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI). Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 1(1), 55–66.
Pechura, C.M. and Martin, J.B. (1991). Mapping the brain and its functions. integrating enabling technologies into neuroscience research. National Academy Press.
Pham, D. L., & Prince, J. L. (1999). Adaptive fuzzy segmentation of magnetic resonance images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(9), 737–752.
Pieper, S., et al. (2006). The NA-MIC Kit: ITK, VTK, pipelines, grids and 3D slicer as an open platform for the medical image computing community. in 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: Nano to Macro.
Riviere, D., et al. (2002). Automatic recognition of cortical sulci of the human brain using a congregation of neural networks. Medical Image Analysis, 6(2), 77–92.
Rohde, G. K., Aldroubi, A., & Dawant, B. M. (2003). The adaptive bases algorithm for intensity-based nonrigid image registration. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 22(11), 1470–1479.
Rohde, G. K., et al. (2004). Comprehensive approach for correction of motion and distortion in diffusion-weighted MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 51, 103–114.
Sethian, J. A. (1999). Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods. Vol. second ed. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press.
Shattuck, D. W., & Leahy, R. M. (2000). BrainSuite: An automated corticalsurface identification tool. in Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention MICCAI. Berlin: Springer.
Shiee, N., et al. (2008). Automated reconstruction of the cerebral cortex in multiple. In Sixth IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI).
Shiee, N., et al. (2010). A Topology-preserving approach to the segmentation of brain images with multiple sclerosis lesions. NeuroImage, 1524–1535.
Smith, S. M., et al. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage, 23(Suppl 1), S208–S219.
Sporns, O., et al. (2004). Organization, development and function of complex brain networks. Trends in Cognitive Science, 8(9), 418–425.
Thambisetty, M., et al. (2010). Longitudinal changes in cortical thickness associated with normal aging. NeuroImage, 52(4), 1215–1223.
Thompson, P. M., & Toga, A. W. (2002). A framework for computational anatomy. Computing and Visualization in Science, 5, 1–12.
Tosun, D., Rettmann, M.E. and Prince, J.L. (2003). Mapping techniques for aligning sulci across multiple brains, in Proceedings of The Sixth Annual International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Interventions(MICCAI). Montréal.
Tosun, D., Rettmann, M., & Prince, J. (2004). Mapping techniques for aligning sulci across multiple brains. Medical Image Analysis, 8(3), 295–309.
Van Essen, D. C., et al. (2001). An integrated software suite for surface-based analyses of cerebral cortex. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 8(5), 443–459.
van Leemput, K., et al. (1999). Automated model-based tissue classification of MR images of the brain. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(10), 897–908.
Viola, P. and Wells, W.M. (1995). Alignment by maximization of mutual information. In Proc. 5th Int. Conf. on Computer Vision.
Wakana, S., et al. (2007). Reproducibility of quantitative tractography methods applied to cerebral white matter. NeuroImage, 36, 630–644.
Warfield, S. K., Zou, K. H., & Wells, W. M. (2004). Simultaneous truth and performance level estimation (STAPLE): an algorithm for the validation of image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 23(7), 903–921.
Xu, C., et al. (1999). Reconstruction of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(6), 467–480.
Zeng, X., et al. (1999). Segmentation and measurement of the cortex from 3-D MR images using coupled-surfaces propagation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(10), 927–937.
Acknowledgments
The authors are appreciative of the careful feedback from the anonymous reviewers and editor (Dr. David Kennedy). This research was supported by NIH/NIA N01-AG-4-0012, NINDS 5R01NS070906, 1R03EB012461, 1R01NS056307, NIH/NIDAK25DA025356 (Bazin), and NIH/NINDSR01NS054255 (Pham).
Grant Support
J. L. Prince/B. A. Landman (subcontract): NIH/NIA N01-AG-4-0012, J. Prince: 1R01NS056307, B. Landman 1R03EB012461.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix A
Appendix A
The regions indicated in Fig. 6 are as defined by (Desikan et al. 2006) and indexed as follows. 1 : L-Subcortical Region, 2 : L-Banks of Superior Temporal Sulcus, 3 : L-Caudal Anterior Cingulate, 4 : L-Caudal Middle Frontal, 5 : L-Corpus Callosum, 6 : L-Cuneus, 7 : L-Entorhinal 8 : L-Fusiform, 9 : L-Inferior Parietal, 10 : L-Inferior Temporal, 11 : L-Isthmus, 12 : L-Lateral Occipital, 13 : L-Lateral Orbitofrontal, 14 : L-Lingual, 15 : L-Medial Orbitofrontal, 16 : L-Middle Temporal, 17 : L-Parahippocampal, 18 : L-Paracentral, 19 : L-Pars Opercularis, 20 : L-Pars Orbitalis, 21 : L-Pars Triangularis, 22 : L-Pericalcarine, 23 : L-Postcentral, 24 : L-Posterior Cingulate, 25 : L-Precentral, 26 : L-Precuneus, 27 : L-Rostral Anterior Cingulate, 28 : L-Rostral Middle Frontal, 29 : L-Superior Frontal, 30 : L-Superior Parietal, 31 : L-Superior Temporal, 32 : L-Supramarginal, 33 : L-Frontal Pole, 34 : L-Temporal Pole, 35 : L-Transverse Temporal, 36 : R-Subcortical Region, 37 : R-Banks of the Superior Temporal Sulcus, 38 : R-Caudal Anterior Cingulate, 39 : R-Caudal Middle Frontal, 40 : R-Corpus Callosum, 41 : R-Cuneus, 42 : R-Entorhinal, 43 : R-Fusiform, 44 : R-Inferior Parietal, 45 : R-Inferior Temporal, 46 : R-Isthmus, 47 : R-Lateral Occipital, 48 : R-Lateral Orbitofrontal, 49 : R-Lingual, 50 : R-Medial Orbitofrontal, 51 : R-Middle Temporal, 52 : R-Parahippocampal, 53 : R-Paracentral, 54 : R-Pars Opercularis, 55 : R-Pars Orbitalis, 56 : R-Pars Triangularis, 57 : R-Pericalcarine, 58 : R-Postcentral, 59 : R-Posterior Cingulate, 60 : R-Precentral, 61 : R-Precuneus, 62 : R-Rostral Anterior Cingulate, 63 : R-Rostral Middle Frontal,64 : R-Superior Frontal, 65 : R-Superior Parietal, 66 : R-Superior Temporal, 67 : R-Supramarginal, 68 : R-Frontal Pole, 69 : R-Temporal Pole, 70 : R-Transverse Temporal
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Landman, B.A., Bogovic, J.A., Carass, A. et al. System for Integrated Neuroimaging Analysis and Processing of Structure. Neuroinform 11, 91–103 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-012-9159-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-012-9159-9