Abstract
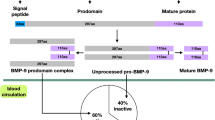
Bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP7), also known as osteogenic protein-1 (OP-1) is a member of Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) family of proteins. Bone morphogenetic proteins were discovered in 1965 by Marshal Urist, of which BMP7 is of particular interest in this review being a leptin-independent anorexinogen and having role in energy expenditure in the brown adipose tissue, which makes it a potential target for preventing/treating obesity. As it has been established that Obesity displays a state of leptin-resistance, thus a protein-like BMP7 which acts through a leptin-independent pathway could give new therapeutic directions. This review will also discuss the synthesis and action of BMP7, along with its receptors and signal transduction. A brief note about BMP7-mediated brown fat development and energy balance is also discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Bottcher et al., Adipose tissue expression and genetic variants of the bone morphogenetic protein receptor 1A gene (BMPR1A) are associated with human obesity. Diabetes. 58(9), 2119–2128 (2009)
D. Schleinitz et al., Genetic and evolutionary analyses of the human bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2 (BMPR2) in the pathophysiology of obesity. PLoS. ONE. 6(2), e16155 (2011)
S. Kishigami, Y. Mishina, BMP signaling and early embryonic patterning. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16(3), 265–278 (2005)
Y. Yamamoto, M. Oelgeschlager, Regulation of bone morphogenetic proteins in early embryonic development. Naturwissenschaften. 91(11), 519–534 (2004)
N. Zamani, C.W. Brown, Emerging roles for the transforming growth factor-{beta} superfamily in regulating adiposity and energy expenditure. Endocr. Rev. 32(3), 387–403 (2011)
Y.H. Tseng et al., New role of bone morphogenetic protein 7 in brown adipogenesis and energy expenditure. Nature. 454(7207), 1000–1004 (2008)
E. Ozkaynak et al., OP-1 cDNA encodes an osteogenic protein in the TGF-beta family. EMBO J. 9(7), 2085–2093 (1990)
M. Tanaka et al., Expression of BMP-7 and USAG-1 (a BMP antagonist) in kidney development and injury. Kidney Int. 73(2), 181–191 (2008)
A.M. Cypess, C.R. Kahn, Brown fat as a therapy for obesity and diabetes. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 17(2), 143–149 (2010)
B. Cannon, J. Nedergaard, Brown adipose tissue: function and physiological significance. Physiol. Rev. 84(1), 277–359 (2004)
C.M. Vacher et al., A putative physiological role of hypothalamic CNTF in the control of energy homeostasis. FEBS Lett. 582(27), 3832–3838 (2008)
G. Perides et al., Neuroprotective effect of human osteogenic protein-1 in a rat model of cerebral hypoxia/ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 187(1), 21–24 (1995)
J.K. Sabo, T.J. Kilpatrick, H.S. Cate, Effects of bone morphogenic proteins on neural precursor cells and regulation during central nervous system injury. Neurosignals. 17(4), 255–264 (2009)
B. Lebrun et al., Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and food intake regulation: a minireview. Auton. Neurosci. 126–127, 30–38 (2006)
J.W. Cordeira et al., Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates hedonic feeding by acting on the mesolimbic dopamine system. J. Neurosci. 30(7), 2533–2541 (2010)
K.L. Townsend et al., Bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP7) reverses obesity and regulates appetite through a central mTOR pathway. FASEB J. 26(5), 2187–2196 (2012)
K.L. Townsend et al., Increased mitochondrial activity in BMP7-treated brown adipocytes, due to increased CPT1- and CD36-mediated fatty acid uptake. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 19(3), 243–257 (2013)
M.R. Boon et al., BMP7 activates brown adipose tissue and reduces diet-induced obesity only at subthermoneutrality. PLoS. ONE. 8(9), e74083 (2013)
M. Bluher, Adipokines-removing road blocks to obesity and diabetes therapy. Mol. Metab. 3(3), 230–240 (2014)
K.L. Ong et al., Off-label use of bone morphogenetic proteins in the United States using administrative data. Spine. 35(19), 1794–1800 (2010)
A.P. White et al., Clinical applications of BMP-7/OP-1 in fractures, nonunions and spinal fusion. Int. Orthop. 31(6), 735–741 (2007)
S. Vukicevic, M.N. Helder, F.P. Luyten, Developing human lung and kidney are major sites for synthesis of bone morphogenetic protein-3 (osteogenin). J. Histochem. Cytochem. 42(7), 869–875 (1994)
M. Zeisberg, Bone morphogenic protein-7 and the kidney: current concepts and open questions. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 21(3), 568–573 (2006)
A. Divoux, K. Clement, Architecture and the extracellular matrix: the still unappreciated components of the adipose tissue. Obes. Rev. 12(5), e494–e503 (2011)
T.J. Schulz, Y.H. Tseng, Systemic control of brown fat thermogenesis: integration of peripheral and central signals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1302, 35–41 (2013)
T.J. Schulz et al., Identification of inducible brown adipocyte progenitors residing in skeletal muscle and white fat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 108(1), 143–148 (2011)
B. Dattatreyamurty et al., Cerebrospinal fluid contains biologically active bone morphogenetic protein-7. Exp. Neurol. 172(2), 273–281 (2001)
M.N. Helder et al., Expression pattern of osteogenic protein-1 (bone morphogenetic protein-7) in human and mouse development. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 43(10), 1035–1044 (1995)
C.E. Johanson et al., Choroid plexus recovery after transient forebrain ischemia: role of growth factors and other repair mechanisms. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 20(2), 197–216 (2000)
S. Soderstrom, T. Ebendal, Localized expression of BMP and GDF mRNA in the rodent brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 56(5), 482–492 (1999)
A.P. Coll, I.S. Farooqi, S. O’Rahilly, The hormonal control of food intake. Cell. 129(2), 251–262 (2007)
M.W. Schwartz, D. Porte Jr, Diabetes, obesity, and the brain. Science. 307(5708), 375–379 (2005)
K. Ohyama, R. Das, M. Placzek, Temporal progression of hypothalamic patterning by a dual action of BMP. Development. 135(20), 3325–3331 (2008)
J.L. Wrana et al., Mechanism of activation of the TGF-beta receptor. Nature. 370(6488), 341–347 (1994)
J. Massague, F. Weis-Garcia, Serine/threonine kinase receptors: mediators of transforming growth factor beta family signals. Cancer Surv. 27, 41–64 (1996)
B.L. Hogan, Bone morphogenetic proteins: multifunctional regulators of vertebrate development. Genes Dev. 10(13), 1580–1594 (1996)
D.M. Kingsley, The TGF-beta superfamily: new members, new receptors, and new genetic tests of function in different organisms. Genes Dev. 8(2), 133–146 (1994)
A. Nohe et al., The mode of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor oligomerization determines different BMP-2 signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 277(7), 5330–5338 (2002)
E.D. Rosen, B.M. Spiegelman, Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature. 444(7121), 847–853 (2006)
N. Hosogai et al., Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine dysregulation. Diabetes. 56(4), 901–911 (2007)
B.M. Spiegelman, J.S. Flier, Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell. 104(4), 531–543 (2001)
K. Townsend, Y.H. Tseng, Brown adipose tissue: Recent insights into development, metabolic function and therapeutic potential. Adipocyte. 1(1), 13–24 (2012)
K.I. Stanford et al., Brown adipose tissue regulates glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Invest. 123(1), 215–223 (2013)
S. Gesta, Y.H. Tseng, C.R. Kahn, Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell. 131(2), 242–256 (2007)
H.E. Young et al., Mesenchymal stem cells reside within the connective tissues of many organs. Dev. Dyn. 202(2), 137–144 (1995)
M. Harms, P. Seale, Brown and beige fat: development, function and therapeutic potential. Nat. Med. 19(10), 1252–1263 (2013)
M. Ghorbani, T.H. Claus, J. Himms-Hagen, Hypertrophy of brown adipocytes in brown and white adipose tissues and reversal of diet-induced obesity in rats treated with a beta3-adrenoceptor agonist. Biochem. Pharmacol. 54(1), 121–131 (1997)
D. Richard, F. Picard, Brown fat biology and thermogenesis. Front. Biosci. 16, 1233–1260 (2011)
D. Richard et al., Determinants of brown adipocyte development and thermogenesis. Int. J. Obes. 34(Suppl 2), S59–S66 (2010)
S. Cinti, The adipose organ. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids. 73(1), 9–15 (2005)
D. Sellayah, P. Bharaj, D. Sikder, Orexin is required for brown adipose tissue development, differentiation, and function. Cell Metab. 14(4), 478–490 (2011)
J.N. Artaza et al., Myostatin inhibits myogenesis and promotes adipogenesis in C3H 10T(1/2) mesenchymal multipotent cells. Endocrinology. 146(8), 3547–3557 (2005)
A. Rebbapragada et al., Myostatin signals through a transforming growth factor beta-like signaling pathway to block adipogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23(20), 7230–7242 (2003)
B.J. Feldman et al., Myostatin modulates adipogenesis to generate adipocytes with favorable metabolic effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 103(42), 15675–15680 (2006)
V. Gilsanz, H.H. Hu, S. Kajimura, Relevance of brown adipose tissue in infancy and adolescence. Pediatr. Res. 73(1), 3–9 (2013)
J.M. Heaton, The distribution of brown adipose tissue in the human. J. Anat. 112(Pt 1), 35–39 (1972)
J. Nedergaard, T. Bengtsson, B. Cannon, Three years with adult human brown adipose tissue. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1212, E20–E36 (2010)
B.B. Lowell, B.M. Spiegelman, Towards a molecular understanding of adaptive thermogenesis. Nature. 404(6778), 652–660 (2000)
P. Bostrom et al., A PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 481(7382), 463–468 (2012)
E. Canalis, A.N. Economides, E. Gazzerro, Bone morphogenetic proteins, their antagonists, and the skeleton. Endocr. Rev. 24(2), 218–235 (2003)
A. Voss-Andreae et al., Role of the central melanocortin circuitry in adaptive thermogenesis of brown adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 148(4), 1550–1560 (2007)
A.N. Verty, A.M. Allen, B.J. Oldfield, The endogenous actions of hypothalamic peptides on brown adipose tissue thermogenesis in the rat. Endocrinology. 151(9), 4236–4246 (2010)
J.F. Tobin, A.J. Celeste, Bone morphogenetic proteins and growth differentiation factors as drug targets in cardiovascular and metabolic disease. Drug Discov. Today. 11(9–10), 405–411 (2006)
I.S. Farooqi et al., Leptin regulates striatal regions and human eating behavior. Science. 317(5843), 1355 (2007)
D. Cota et al., Hypothalamic mTOR signaling regulates food intake. Science. 312(5775), 927–930 (2006)
H. Mori et al., Critical role for hypothalamic mTOR activity in energy balance. Cell Metab. 9(4), 362–374 (2009)
E.C. Villanueva et al., Complex regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 in the basomedial hypothalamus by leptin and nutritional status. Endocrinology. 150(10), 4541–4551 (2009)
D. Benjamin et al., Rapamycin passes the torch: a new generation of mTOR inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 10(11), 868–880 (2011)
A. Koncarevic et al., A novel therapeutic approach to treating obesity through modulation of TGFbeta signaling. Endocrinology. 153(7), 3133–3146 (2012)
C. Zhang et al., Inhibition of myostatin protects against diet-induced obesity by enhancing fatty acid oxidation and promoting a brown adipose phenotype in mice. Diabetologia. 55(1), 183–193 (2012)
B. Fournier et al., Blockade of the activin receptor IIb activates functional brown adipogenesis and thermogenesis by inducing mitochondrial oxidative metabolism. Mol. Cell. Biol. 32(14), 2871–2879 (2012)
A.C. McPherron et al., Increasing muscle mass to improve metabolism. Adipocyte. 2(2), 92–98 (2013)
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saini, S., Duraisamy, A.J., Bayen, S. et al. Role of BMP7 in appetite regulation, adipogenesis, and energy expenditure. Endocrine 48, 405–409 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0406-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0406-8