Abstract
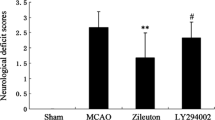
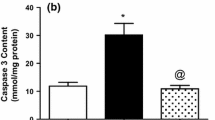
Systemic administration of kainic acid causes inflammation and apoptosis in the brain, resulting in neuronal loss. Dual cyclooxygenase/5-lipoxygenase (COX/5-LOX) inhibitors could represent a possible neuroprotective approach in preventing glutamate excitotoxicity. Consequently, we investigated the effects of a dual inhibitor of COX/5-LOX following intraperitoneal administration of kainic acid (KA, 10 mg/kg) in rats. Animals were randomized to receive either the dual inhibitor of COX/5-LOX (flavocoxid, 20 mg/kg i.p.) or its vehicle (1 ml/kg i.p.) 30 min after KA administration. Sham brain injury rats were used as controls. We evaluated protein expression of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK1/2) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) as well as levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and leukotriene B4 (LTB4) in the hippocampus. Animals were also observed for monitoring behavioral changes according to Racine Scale. Finally, histological analysis and brain edema evaluation were carried out. Treatment with the dual inhibitor of COX/5-LOX decreased protein expression of p-ERK1/2 and TNF-α in hippocampus, markedly reduced MDA, LTB4 and PGE2 hippocampal levels, and also ameliorated brain edema. Histological analysis showed a reduction in cell damage in rats treated with the dual inhibitor of COX/5-LOX, particularly in hippocampal subregion CA3c. Moreover, flavocoxid significantly improved behavioral signs following kainic acid administration. Our results suggest that dual inhibition of COX/5-LOX by flavocoxid has neuroprotective effects during kainic acid-induced excitotoxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altavilla, D., Minutoli, L., Polito, F., Irrera, N., Arena, S., Magno, C., et al. (2012). Effects of flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of COX and 5-lipoxygenase enzymes, on benign prostatic hyperplasia. British Journal Pharmacology, 167, 95–108.
Altavilla, D., Squadrito, F., Bitto, A., Polito, F., Burnett, B. P., Di Stefano, V., et al. (2009). Flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase, blunts pro-inflammatory phenotype activation in endotoxin-stimulated macrophages. British Journal Pharmacology, 157, 1410–1418.
Baik, E. J., Kim, E. J., Lee, S. H., & Moon, C. (1999). Cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors aggravate kainic acid induced seizure and neuronal cell death in the hippocampus. Brain Research, 843, 118–129.
Ben-Ari, Y. (1985). Limbic seizure and brain damage produced by kainic acid: Mechanisms and relevance to human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience, 14, 375–403.
Bishnoi, M., Patil, C. S., Kumar, A., & Kulkarni, S. K. (2007). Co-administration of acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid, a specific 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, potentiates the protective effect of COX-2 inhibitors in kainic acid-induced neurotoxicity in mice. Pharmacology, 79, 34–41.
Bitto, A., Minutoli, L., David, A., Irrera, N., Rinaldi, M., et al. (2012). Flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of COX-2 and 5-LOX of natural origin, attenuates the inflammatory response and protects mice from sepsis. Critical Care, 16, R32.
Burnett, B. P., Bitto, A., Altavilla, D., Squadrito, F., Levy, R. M., & Pillai, L. (2011). Flavocoxid inhibits phospholipase A2, peroxidase moieties of the cyclooxygenases (COX), and 5-lipoxygenase, modifies COX-2 gene expression, and acts as an antioxidant. Mediators of Inflammation, 2011, 385780.
Burnett, B. P., Jia, Q., Zhao, Y., & Levy, R. M. (2007a). A medicinal extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and Acacia catechu acts as a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase to reduce inflammation. Journal of Medicinal Food, 10, 442–451.
Burnett, B. P., & Levy, R. M. (2012). Flavocoxid (Limbrel®) manages osteoarthritis through modification of multiple inflammatory pathways: A review. Functional Foods in Health and Disease, 2, 379–413.
Burnett, B. P., Silva, S., Mesches, M. H., Wilson, S., & Jia, Q. (2007b). Safety evaluation of a combination, defined extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and Acacia catechu. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 31, 797–825.
Calapai, G., Squadrito, F., Rizzo, A., Marciano, M. C., Campo, G. M., & Caputi, A. P. (1995). Multiple actions of the coumarine derivative cloricromene and its protective effects on ischemic brain injury. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s archives of pharmacology, 351, 209–215.
Chen, B. C., Chang, Y. S., Kang, J. C., Hsu, M. J., Sheu, J. R., Chen, T. L., et al. (2004). Peptidoglycan induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression via Ras, Raf-1, and ERK in RAW 264.7 macrophages. The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 20889–20897.
Chou, T. C., Chang, L. P., Li, C. Y., Wong, C. S., & Yang, S. P. (2003). The antiinflammatory and analgesic effects of baicalin in carrageenan evoked thermal hyperalgesia. Anesthesia & Analgesia Journal, 97, 1724–1729.
Chu, J., & Praticò, D. (2009). The 5-lipoxygenase as a common pathway for pathological brain and vascular aging. Cardiovascular Psychiatry and Neurology, 2009, 174657.
De Clerq, E. (2005). Current lead natural products for the chemotherapy of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Medicinal Research Reviews, 20, 323–349.
Farooqui, A. A. (2011). Neurochemical aspects of inflammation in brain. In A. A. Farooqui & T. Farooqui (Eds.), Molecular aspects of neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Bentham Science.
Farooqui, A. A., Ong, W. Y., & Horrocks, L. A. (2006). Inhibitors of brain phospholipase A2 activity: Their neuropharmacological effects and therapeutic importance for the treatment of neurologic disorders. Pharmacological Reviews, 58, 591–620.
Gobbo, O. L., & O’Mara, S. M. (2004). Post-treatment, but not pre-treatment, with the selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib markedly enhances functional recovery from kainic acid-induced neurodegeneration. Neuroscience, 125, 317–327.
Holtman, L., van Vliet, E. A., van Schaik, R., Queiroz, C. M., Aronica, E., & Gorter, J. A. (2009). Effects of SC58236, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, on epileptogenesis and spontaneous seizures in a rat model for temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Research, 84, 56–66.
Huang, Y., Tsang, S. Y., Tao, X., & Chen, Z. Y. (2005). Biological properties of baicalein in cardiovascular system. Current Drug Targets - Cardiovascular & Hematological Disorders, 5, 177–184.
Jeong, E. A., Jeon, B. T., Shin, H. J., Kim, N., Lee, D. H., Kim, H. J., et al. (2011). Ketogenic diet-induced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activation decreases neuroinflammation in the mouse hippocampus after kainic acid-induced seizures. Experimental Neurology, 232, 195–202.
Jung, K. H., Chu, K., Lee, S. T., Kim, J., Sinn, D. I., Kim, J. M., et al. (2006). Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, inhibits the altered hippocampal neurogenesis with attenuation of spontaneous recurrent seizures following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Neurobiology of Disease, 23, 237–246.
Kawaguchi, K., Hickey, R. W., Rose, M. E., Zhu, L., Chen, J., & Graham, S. H. (2005). Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is induced in rat brain after kainate-induced seizures and promotes neuronal death in CA3 hippocampus. Brain Research, 1050, 130–137.
Kumar, A., Prakash, A., Pahwa, D., & Mishra, J. (2012). Montelukast potentiates the protective effect of rofecoxib against kainic acid-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 103, 43–52.
Kunz, T., & Oliw, E. H. (2001). The selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor rofecoxib reduces kainate-induced cell death in the rat hippocampus. European Journal of Neuroscience, 13, 569–575.
Leone, S., Ottani, A., & Bertolini, A. (2007). Dual acting anti-inflammatory drugs. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 7, 265–275.
Levy, R. M., Khokhlov, A., Kopenkin, S., Bart, B., Ermolova, T., Kantemirova, R., et al. (2010). Efficacy and safety of flavocoxid, a novel therapeutic, compared with naproxen: A randomized multicenter controlled trial in subjects with osteoarthritis of the knee. Advances in Therapy, 27, 731–742.
Lubin, F. D., Johnston, L. D., Sweatt, J. D., & Anderson, A. E. (2005). Kainate mediates nuclear factor-kappa B activation in hippocampus via phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase. Neuroscience, 133, 969–981.
Manev, H., Uz, T., & Qu, T. (2000). 5-Lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase mRNA expression in rat hippocampus: Early response to glutamate receptor activation by kainate. Experimental Gerontology, 35, 1201–1209.
Marini, H., Altavilla, D., Bellomo, M., Adamo, E. B., Marini, R., Laureanti, F., et al. (2004a). Modulation of IL-1 beta gene expression by lipid peroxidation inhibition after kainic acid-induced rat brain injury. Experimental Neurology, 188, 178–186.
Marini, H., Costa, C., Passaniti, M., Esposito, M., Campo, G. M., Ientile, R., et al. (2004b). Levetiracetam protects against kainic acid-induced toxicity. Life Sciences, 74, 1253–1264.
Mehta, A., Prabhakar, M., Kumar, P., Deshmukh, R., & Sharma, P. L. (2013). Excitotoxicity: Bridge to various triggers in neurodegenerative disorders. European Journal of Pharmacology, 698, 6–18.
Messina, S., Bitto, A., Aguennouz, M., Mazzeo, A., Migliorato, A., Polito, F., et al. (2009). Flavocoxid counteracts muscle necrosis and improves functional properties in MDX mice: A comparison study with methylprednisolone. Experimental Neurology, 220, 349–358.
Paxinos, G., & Watson, C. (1986). The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Sydney: Academic Press.
Polito, F., Bitto, A., Irrera, N., Squadrito, F., Fazzari, C., Minutoli, L., et al. (2010). Flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase, reduces pancreatic damage in an experimental model of acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Pharmacology, 161, 1002–1011.
Racine, R. J. (1972). Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation: Motor seizure. EEG. Clinical Neurophysiology, 32, 281–294.
Rojas, A., & Dingledine, R. (2013). Ionotropic glutamate receptors: Regulation by G-protein-coupled receptors. Molecular Pharmacology, 83, 746–752.
Singh, D. P., & Chopra, K. (2014). Flavocoxid, dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase, exhibits neuroprotection in rat model of ischaemic stroke. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 120, 33–42.
Takemiya, T., Maehara, M., Matsumura, K., Yasuda, S., Sugiura, H., & Yamagata, K. (2006). Prostaglandin E2 produced by late induced COX-2 stimulates hippocampal neuron loss after seizure in the CA3 region. Neuroscience Research, 56, 103–110.
Takemiya, T., Matsumura, K., & Yamagata, K. (2007). Roles of prostaglandin synthesis in excitotoxic brain diseases. Neurochemistry International, 51, 112–120.
Takemiya, T., & Yamagata, K. (2013). Intercellular signaling pathway among endothelia, astrocytes and neurons in excitatory neuronal damage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14, 8345–8357.
Van Loon, I. M. (1997). The golden root: Clinical applications of Scutellaria baicalensis GEORGI flavonoids as modulators of the inflammatory response. Alternative Medicine Review, 2, 472–480.
Vincent, P., & Mulle, C. (2009). Kainate receptors in epilepsy and excitotoxicity. Neuroscience, 158, 309–323.
Wang, Y., Liu, P. P., Li, L. Y., Zhang, H. M., & Li, T. (2011). Hypothermia reduces brain edema, spontaneous recurrent seizure attack, and learning memory deficits in the kainic acid treated rats. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 17, 271–280.
Wang, Q., Yu, S., Simonyi, A., Sun, G. Y., & Sun, A. Y. (2005). Kainic acid-mediated excitotoxicity as a model for neurodegeneration. Molecular Neurobiology, 31, 3–16.
Zhang, X. M., & Zhu, J. (2011). Kainic Acid-induced neurotoxicity: Targeting glial responses and glia-derived cytokines. Current Neuropharmacology, 9, 388–398.
Zheng, X. Y., Zhang, H. L., Luo, Q., & Zhu, J. (2011). Kainic acid-induced neurodegenerative model: Potentials and limitations. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, 2011, 457079.
Acknowledgments
This study was granted by a departmental funding.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Letteria Minutoli and Herbert Marini have equally contributed to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minutoli, L., Marini, H., Rinaldi, M. et al. A Dual Inhibitor of Cyclooxygenase and 5-Lipoxygenase Protects Against Kainic Acid-Induced Brain Injury. Neuromol Med 17, 192–201 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-015-8351-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-015-8351-0