Abstract
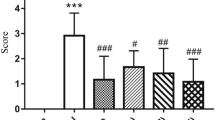
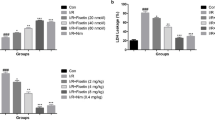
Oxysophoridine (OSR) is a bioactive alkaloid extracted from the Sophora alopecuroides Linn. Our aim is to explore the potential anti-inflammation mechanism of OSR in cerebral ischemic injury. Mice were intraperitoneally pretreated with OSR (62.5, 125, and 250 mg/kg) or nimodipine (Nim) (6 mg/kg) for 7 days followed by cerebral ischemia. The inflammatory-related cytokines in cerebral ischemic hemisphere tissue were determined by immunohistochemistry staining, Western blot and enzyme-like immunosorbent assay (ELISA). OSR-treated groups observably suppressed the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). OSR-treated group (250 mg/kg) markedly reduced the inflammatory-related protein prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-8 (IL-8). Meanwhile, it dramatically increased the interleukin-10 (IL-10). Our study revealed that OSR protected neurons from ischemia-induced injury in mice by downregulating the proinflammatory cytokines and blocking the NF-κB pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodríguez Cruz, Y., T. Yuneidys Mengana, A. Muñoz Cernuda, et al. 2010. Treatment with nasal neuro-EPO improves the neurological, cognitive, and histological state in a gerbil model of focal ischemia. The Scientific World Journal 10: 2288–2300.
Feigin, V.L. 2005. Stroke epidemiology in the developing world. The Lancet 365: 2160–2161.
Wang, Q., T.J. Kalogeris, M. Wang, A.W. Jones, and R.J. Korthuis. 2010. Antecedent ethanol attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced leukocyte-endothelial adhesive interactions and delayed neuronal death: Role of large conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Microcirculation 17: 427–438.
Mehta, S.L., N. Manhas, and R. Raghubir. 2007. Molecular targets in cerebral ischemia for developing novel therapeutics. Brain Research Reviews 54: 34–66.
Cai, F., C.R. Li, J.L. Wu, et al. 2006. Theaflavin ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats through its anti-inflammatory effect and modulation of STAT-1. Mediators of Inflammation 2006: 1–9.
Lo, E.H., T. Dalkara, and M.A. Moskowitz. 2003. Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 4: 399–414.
Nurmi, A., P.J. Lindsberg, M. Koistinaho, et al. 2004. Nuclear factor-κB contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 35: 987–991.
Sugama, Y., C. Tiruppathi, T. Andersen, J. Fenton, and A. Malik. 1992. Thrombin-induced expression of endothelial P-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1: a mechanism for stabilizing neutrophil adhesion. The Journal of Cell Biology 119: 935–944.
Kułdo, J.M., J. Westra, S.A. Ásgeirsdóttir, et al. 2005. Differential effects of NF-κB and p38 MAPK inhibitors and combinations thereof on TNF-α-and IL-1β-induced proinflammatory status of endothelial cells in vitro. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 289: 1229–1239.
Ridet, J., A. Privat, S. Malhotra, and F. Gage. 1997. Reactive astrocytes: cellular and molecular cues to biological function. Trends in Neurosciences 20: 570–577.
Nomoto, Y., M. Yamamoto, T. Fukushima, et al. 2001. Expression of nuclear factor κB and tumor necrosis factor α in the mouse brain after experimental thermal ablation injury. Neurosurgery 48: 158–166.
Swanson, R.A., W. Ying, and T.M. Kauppinen. 2004. Astrocyte influences on ischemic neuronal death. Current Molecular Medicine 4: 193–205.
Sofroniew, M.V. 2005. Reactive astrocytes in neural repair and protection. The Neuroscientist 11: 400–407.
Bethea, J.R., M. Castro, R.W. Keane, et al. 1998. Traumatic spinal cord injury induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation. The Journal of Neuroscience 18: 3251–3260.
Brambilla, R., V. Bracchi-Ricard, W.H. Hu, et al. 2005. Inhibition of astroglial nuclear factor κB reduces inflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 202: 145–156.
Alderton, W., C. Cooper, and R. Knowles. 2001. Nitric oxide synthases: structure, function and inhibition. Biochemical Journal 357: 593–615.
Liu, Y., W. Li, L. Hu, et al. 2015. Downregulation of nitric oxide by electroacupuncture against hypoxic‑ischemic brain damage in rats via nuclear factor‑κB/neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Molecular Medicine Reports 11: 837–842.
Ovize, M., G.F. Baxter, F. Di Lisa, et al. 2010. Postconditioning and protection from reperfusion injury: where do we stand? Position paper from the Working Group of Cellular Biology of the Heart of the European Society of Cardiology. Cardiovascular Research 87: 406–423.
Wang, T.F., Z. Lei, Y.X. Li, et al. 2013. Oxysophoridine protects against focal cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice. Neurochemical Research 38: 2408–2417.
Wang, H., Y. Li, N. Jiang, et al. 2013. Protective effect of oxysophoridine on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Neural Regeneration Research 8: 1349–1359.
Zhao, J., Y.X. Li, Y.J. Hao, et al. 2013. Effects of oxysophoridine on rat hippocampal neurons sustained oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion. CNS Neuroscience and Therapeutics 19: 138–141.
Longa, E.Z., P.R. Weinstein, S. Carlson, and R. Cummins. 1989. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20: 84–91.
Macrae, I. 1992. New models of focal cerebral-ischemia. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 34: 302–308.
Guo, Y., X. Xu, Q. Li, Z. Li, and F. Du. 2010. Anti-inflammation effects of picroside 2 in cerebral ischemic injury rats. Behavioral and Brain Functions 6: 1–7.
Scheller, C. 2014. Pharmacological perioperative brain neuroprotection: nimodipine? British Journal of Anaesthesia 112: 178–179.
Ghosh, S., and M.S. Hayden. 2008. New regulators of NF-κB in inflammation. Nature Reviews Immunology 8: 837–848.
Zhang, S. Y., L. T. Xu, A. X. Li, and S. M. Wang. 2015. Effects of ergosterol, isolated from scleroderma polyrhizum pers., on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in acute lung injury. Inflammation.
Rahman, A., and F. Fazal. 2011. Blocking NF-κB: an inflammatory issue. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 8: 497–503.
Wang, C., D. Zhang, G. Li, et al. 2007. Neuroprotective effects of safflor yellow B on brain ischemic injury. Experimental Brain Research 177: 533–539.
Zhu, Y., K. Saito, Y. Murakami, et al. 2006. Early increase in mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and their interactions in the mouse hippocampus after transient global ischemia. Neuroscience Letters 393: 122–126.
Xiang, Z., S. Thomas, and G. Pasinetti. 2007. Increased neuronal injury in transgenic mice with neuronal overexpression of human cyclooxygenase-2 is reversed by hypothermia and rofecoxib treatment. Current Neurovascular Research 4: 274–279.
Tabassum, R., K. Vaibhav, P. Shrivastava, et al. 2015. Perillyl alcohol improves functional and histological outcomes against ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuation of oxidative stress and repression of COX-2, NOS-2 and NF-κB in middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. European Journal of Pharmacology 747: 190–199.
Cheng, O., R.P. Ostrowski, W. Liu, and J.H. Zhang. 2010. Activation of liver X receptor reduces global ischemic brain injury by reduction of nuclear factor-κB. Neuroscience 166: 1101–1109.
Sasaki, T., K. Kitagawa, K. Yamagata, et al. 2004. Amelioration of hippocampal neuronal damage after transient forebrain ischemia in cyclooxygenase-2-deficient mice. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 24: 107–113.
Mukhopadhyay, P., B. Horváth, Z. Zsengellėr, et al. 2012. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation triggers inflammatory response and tissue injury associated with hepatic ischemia-reperfusion: therapeutic potential of mitochondrially targeted antioxidants. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 53: 1123–1138.
Maddahi, A., L.S. Kruse, Q.W. Chen, and L. Edvinsson. 2011. The role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and TNF-alpha receptors in cerebral arteries following cerebral ischemia in rat. Journal of Neuroinflammation 8: 1–13.
Jean, W.C., S.R. Spellman, E.S. Nussbaum, and W.C. Low. 1998. Reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia: the role of inflammation and the therapeutic horizon. Neurosurgery 43: 1382–1396.
Barone, F., B. Arvin, R. White, et al. 1997. Tumor necrosis factor-α A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke 28: 1233–1244.
Zhang, R.L., Z.G. Zhang, and M. Chopp. 2013. Targeting nitric oxide in the subacute restorative treatment of ischemic stroke. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 22: 843–851.
Hallenbeck, J.M., and A.J. Dutka. 1990. Background review and current concepts of reperfusion injury. Archives of Neurology 47: 1245–1254.
Aronowski, J., R. Strong, and J.C. Grotta. 1997. Reperfusion injury: demonstration of brain damage produced by reperfusion after transient focal ischemia in rats. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 17: 1048–1056.
Kuroda, S., and B. Siesjö. 1996. Reperfusion damage following focal ischemia: pathophysiology and therapeutic windows. Clinical Neuroscience 4: 199–212.
Ye, Y., Y. Lin, S. Manickavasagam, et al. 2008. Pioglitazone protects the myocardium against ischemia-reperfusion injury in eNOS and iNOS knockout mice. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology 295: 2436–2446.
Radak, D., I. Resanovic, and E.R. Isenovic. 2014. Link between oxidative stress and acute brain ischemia. Angiology 65: 667–676.
Iadecola, C., F. Zhang, R. Casey, H.B. Clark, and M.E. Ross. 1996. Inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in vascular cells after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 27: 1373–1380.
Choi, J.S., S.J. Kim, J.A. Shin, K.E. Lee, and E.M. Park. 2008. Effects of estrogen on temporal expressions of IL-1β and IL-1ra in rat organotypic hippocampal slices exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neuroscience Letters 438: 233–237.
Tukhovskaya, E. A., E. A. Turovsky, M. V. Turovskaya, et al. Anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 increases resistance to brain ischemia through modulation of ischemia-induced intracellular Ca2+ response. Neuroscience Letters 571: 55–60.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Margaret for editing and polishing the manuscript. The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 309605060) and the Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia (Grant No. NZ11212).
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yong-Sheng Wang and Yu-Xiang Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YS., Li, YX., Zhao, P. et al. Anti-inflammation Effects of Oxysophoridine on Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Inflammation 38, 2259–2268 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0211-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0211-4