Abstract
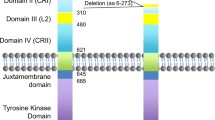
Glioblastoma represents one of the most challenging problems in neurooncology. Among key elements driving its behavior is the transmembrane epidermal growth factor receptor family, with the first member epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) centered in most studies. Engagement of the extracellular domain with a ligand activates the intracellular tyrosine kinase (TK) domain of EGFR, leading to autophosphorylation and signal transduction that controls proliferation, gene transcription, and apoptosis. Oncogenic missense mutations, deletions, and insertions in the EGFR gene are preferentially located in the extracellular domain in glioblastoma and cause constitutive activation of the receptor. The mutant EGFR may also transactivate other cell surface molecules, such as additional members of the EGFR family and the platelet-derived growth factor receptor, which ignite signaling cascades that synergize with the EGFR-initiated cascade. Because of the cell surface location and increased expression of the receptor along with its important biological function, EGFR has triggered much effort for designing targeted therapy. These approaches include TK inhibition, monoclonal antibody, vaccine, and RNA-based downregulation of the receptor. Treatment success requires that the drug penetrates the blood–brain barrier and has low systemic toxicity but high selectivity for the tumor. While the blockade of EGFR-dependent processes resulted in experimental and clinical treatment success, cells capable of using alternative signaling ultimately escape this strategy. A combination of interventions targeting tumor-specific cell surface regulators along with convergent downstream signaling pathways will likely enhance efficacy. Studies on EGFR in glioblastoma have revealed much information about the complexity of gliomagenesis and also facilitated the development of strategies for targeting drivers of tumor growth and combination therapies with increasing complexity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczyk, K. A., Klein-Scory, S., Tehrani, M. M., Warnken, U., Schmiegel, W., Schnölzer, M., et al. (2011). Characterization of soluble and exosomal forms of the EGFR released from pancreatic cancer cells. Life Sciences, 89(9–10), 304–312.
Agarwal, S., Sane, R., Oberoi, R., Ohlfest, J. R., & Elmquist, W. F. (2011). Delivery of molecularly targeted therapy to malignant glioma, a disease of the whole brain. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine, 13, e17.
Altaba, A. R. (1999). Gli proteins encode context-dependent positive and negative functions: Implications for development and disease. Development, 126(14), 3205–3216.
Amado, R. G., Wolf, M., Peeters, M., Van Cutsem, E., Siena, S., Freeman, D. J., et al. (2008). Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 26, 1626–1634.
Andersson, U., Guo, D., Malmer, B., Bergenheim, A. T., Brännström, T., Hedman, H., et al. (2004). Epidermal growth factor receptor family (EGFR, ErbB2-4) in gliomas and meningiomas. Acta Neuropathology (Berlin), 108(2), 135–142.
Assi, H., Candolfi, M., Baker, G., Mineharu, Y., Lowenstein, P. R., & Castro, M. G. (2012). Gene therapy for brain tumors: Basic developments and clinical implementation. Neuroscience Letters, 527(2), 71–77.
Babu, R., & Adamson, D. C. (2012). Rindopepimut an evidence-based review of its therapeutic potential in the treatment of EGFRvIII-positive glioblastoma. Core Evidence, 7, 93–103.
Berezowska, S., & Schlegel, J. (2011). Targeting ErbB receptors in high-grade glioma. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 17(23), 2468–2487.
Blesa, J. M., Mollá, S. B., Esparcia, M. F., Ortells, J. M., Godoy, M. P., Das, A. M., et al. (2012). Durable complete remission of a brainstem glioma treated with a combination of bevacizumab and cetuximab. Case Reports in Oncology, 5(3), 676–681.
Boerner, J. L., Demory, M. L., Silva, C., & Parsons, S. J. (2004). Phosphorylation of Y845 on the epidermal growth factor receptor mediates binding to the mitochondrial protein cytochrome c oxidase subunit II. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 24, 7059–7071.
Bonavia, R., Inda, M. M., Vandenberg, S., Cheng, S. Y., Nagane, M., Hadwiger, P., et al. (2012). EGFRvIII promotes glioma angiogenesis and growth through the NF-κB, interleukin-8 pathway. Oncogene, 31(36), 4054–4066.
Bora, R. S., Gupta, D., Mukkur, T. K., & Saini, K. S. (2012). RNA interference therapeutics for cancer: Challenges and opportunities (review). Molecular Medicine Report, 6(1), 9–15.
Brand, T. M., Iida, M., & Wheeler, D. L. (2011). Molecular mechanisms of resistance to the EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 11(9), 777–792.
Bu, N., Wu, H., Sun, B., Zhang, G., Zhan, S., Zhang, R., et al. (2011). Exosome-loaded dendritic cells elicit tumor-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T cells in patients with glioma. Journal of Neuro-oncology, 104(3), 659–667.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. (2008). Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature, 455(7216), 1061–1068.
Castro, A. S., Parente, B., Gonçalves, I., Antunes, A., Barroso, A., Conde, S., et al. (2013). Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation study for 5 years, in a population of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia, 19(1), 7–12.
Clark, P. A., Iida, M., Treisman, D. M., Kalluri, H., Ezhilan, S., Zorniak, M., et al. (2012). Activation of multiple ERBB family receptors mediates glioblastoma cancer stem-like cell resistance to EGFR-targeted inhibition. Neoplasia, 14(5), 420–428.
Colman, H., Li, Z., Sulman, E. P., McDonald, J. M., Shooshtari, N. L., Rivera, A., et al. (2010). A multigene predictor of outcome in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology, 12(1), 49–57.
Combs, S. E., Heeger, S., Haselmann, R., Edler, L., Debus, J., & Schulz-Ertner, D. (2006). Treatment of primary glioblastoma multiforme with cetuximab, radiotherapy and temozolomide (GERT)–phase I/II trial: Study protocol. BMC Cancer, 6, 133.
Cunningham, D., Humblet, Y., Siena, S., Khayat, D., Bleiberg, H., Santoro, A., et al. (2004). Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 351, 337–345.
de Almeida Sassi, S. F., Lunardi Brunetto, A., Schwartsmann, G., Roesler, R., & Abujamra, A. L. (2012). Glioma revisited: From neurogenesis and cancer stem cells to the epigenetic regulation of the niche. Journal of Oncology, 2012, 537861.
De Bacco, F., Casanova, E., Medico, E., Pellegatta, S., Orzan, F., Albano, R., et al. (2012). The MET oncogene is a functional marker of a glioblastoma stem cell subtype. Cancer Research, 72(17), 4537–4550.
Del Vecchio, C. A., Giacomini, C. P., Vogel, H., Jensen, K. C., Florio, T., Merlo, A., Pollack, J. R., Wong, A. J. (2012) EGFRvIII gene rearrangement is an early event in glioblastoma tumorigenesis and expression defines a hierarchy modulated by epigenetic mechanisms. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.280 [Epub ahead of print].
Del Vecchio, C. A., & Wong, A. J. (2010). Rindopepimut, a 14-mer injectable peptide vaccine against EGFRvIII for the potential treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Current Opinion in Molecular Therapeutics, 12(6), 741–754.
Dunn, G. P., Rinne, M. L., Wykosky, J., Genovese, G., Quayle, S. N., Dunn, I. F., et al. (2012). Emerging insights into the molecular and cellular basis of glioblastoma. Genes & Development, 26(8), 756–784.
Eller, J. L., Longo, S. L., Kyle, M. M., Bassano, D., Hicklin, D. J., & Canute, G. W. (2005). Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab augments radiation effects in glioblastoma multiforme in vitro and in vivo. Neurosurgery, 56(1), 155–162.
Emrich, J. G., Brady, L. W., Quang, T. S., Class, R., Miyamoto, C., Black, P., et al. (2002). Radioiodinated (I-125) monoclonal antibody 425 in the treatment of high grade glioma patients: Ten-year synopsis of a novel treatment. American Journal of Clinical Oncology, 25(6), 541–546.
Fan, Q. W., & Weiss, W. A. (2010). Targeting the RTK-PI3K-mTOR axis in malignant glioma: Overcoming resistance. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, 347, 279–296.
Feng, H., Hu, B., Jarzynka, M. J., Li, Y., Keezer, S., Johns, T. G., et al. (2012). Phosphorylation of dedicator of cytokinesis 1 (Dock180) at tyrosine residue Y722 by Src family kinases mediates EGFRvIII-driven glioblastoma tumorigenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(8), 3018–3023.
Fenton, T. R., Nathanson, D., Ponte de Albuquerque, C., Kuga, D., Iwanami, A., Dang, J., et al. (2012). Resistance to EGF receptor inhibitors in glioblastoma mediated by phosphorylation of the PTEN tumor suppressor at tyrosine 240. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(35), 14164–14169.
Forbes, S. A., Tang, G., Bindal, N., Bamford, S., Dawson, E., Cole, C., et al. (2010). COSMIC (the Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer): A resource to investigate acquired mutations in human cancer. Nucleic Acids Research, 38(Database issue):D652-D657. PMCID:PMC2808858.
Gan, H. K., Lappas, M., Cao, D. X., Cvrljevdic, A., Scott, A. M., & Johns, T. G. (2009). Targeting a unique EGFR epitope with monoclonal antibody 806 activates NF-kappaB and initiates tumour vascular normalization. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 13(9), 3993–4001.
Graner, M. W., Alzate, O., Dechkovskaia, A. M., Keene, J. D., Sampson, J. H., Mitchell, D. A., et al. (2009). Proteomic and immunologic analyses of brain tumor exosomes. FASEB Journal, 23(5), 1541–1557.
Guo, D., Wang, B., Han, F., & Lei, T. (2010). RNA interference therapy for glioblastoma. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 10(6), 927–936.
Guryanova, O. A., Wu, Q., Cheng, L., Lathia, J. D., Huang, Z., Yang, J., et al. (2011). Nonreceptor tyrosine kinase BMX maintains self-renewal and tumorigenic potential of glioblastoma stem cells by activating STAT3. Cancer Cell, 19(4), 498–511.
Halatsch, M. E., Gehrke, E. E., Vougioukas, V. I., Bötefür, I. C., A-Borhani, F., Efferth, T., et al. (2004). Inverse correlation of epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA induction and suppression of anchorage-independent growth by OSI-774, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in glioblastoma multiforme cell lines. Journal of Neurosurgery, 100(3), 523–533.
Halatsch, M. E., Löw, S., Mursch, K., Hielscher, T., Schmidt, U., Unterberg, A., et al. (2009). Candidate genes for sensitivity and resistance of human glioblastoma multiforme cell lines to erlotinib. Laboratory investigation. Journal of Neurosurgery, 111(2), 211–218.
Halatsch, M. E., Schmidt, U., Bötefür, I. C., Holland, J. F., & Ohnuma, T. (2000). Marked inhibition of glioblastoma target cell tumorigenicity in vitro by retrovirus-mediated transfer of a hairpin ribozyme against deletion-mutant epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA. Journal of Neurosurgery, 92(2), 297–305.
Hasselbalch, B., Lassen, U., Hansen, S., Holmberg, M., Sørensen, M., Kosteljanetz, M., et al. (2010). Cetuximab, bevacizumab, and irinotecan for patients with primary glioblastoma and progression after radiation therapy and temozolomide: A phase II trial. Neuro-Oncology, 12(5), 508–516.
Hau, P., Jachimczak, P., Schlaier, J., & Bogdahn, U. (2011). TGF-β2 signaling in high-grade gliomas. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, 12(12), 2150–2157.
Hegi, M. E., Diserens, A. C., Gorlia, T., Hamou, M. F., de Tribolet, N., Weller, M., et al. (2005). MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. New England Journal of Medicine, 352(10), 997–1003.
Hegi, M. E., Rajakannu, P., & Weller, M. (2012). Epidermal growth factor receptor: A re-emerging target in glioblastoma. Current Opinion in Neurology, 25(6), 774–779.
Huang, P. H., Mukasa, A., Bonavia, R., Flynn, R. A., Brewer, Z. E., Cavenee, W. K., et al. (2007). Quantitative analysis of EGFRvIII cellular signaling networks reveals a combinatorial therapeutic strategy for glioblastoma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104, 12867–12872.
Hynes, N. E., & Lane, H. A. (2005). ERBB receptors and cancer: The complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nature Reviews Cancer, 5, 341–354.
Idbaih, A., Aimard, J., Boisselier, B., Marie, Y., Paris, S., Criniere, E., et al. (2009). Epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular domain mutations in primary glioblastoma. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology, 35(2), 208–213.
Inda, M. M., Bonavia, R., Mukasa, A., Narita, Y., Sah, D. W., Vandenberg, S., et al. (2010). Tumor heterogeneity is an active process maintained by a mutant EGFR-induced cytokine circuit in glioblastoma. Genes & Development, 24, 1731–1745.
Jarboe, J. S., Dutta, S., Velu, S. E., Willey, C. D. (2012). Mini-review: Bmx Kinase Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Recent Patents on Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery, 29 [Epub ahead of print].
Ji, H., Sharpless, N. E., & Wong, K. K. (2006). EGFR targeted therapy: View from biological standpoint. Cell Cycle, 5(18), 2072–2076.
Jin, X., Jin, X., Sohn, Y. W., Yin, J., Kim, S. H., Joshi, K., et al. (2013). Blockade of EGFR signaling promotes glioma stem-like cell invasiveness by abolishing ID3-mediated inhibition of p27(KIP1) and MMP3 expression. Cancer Letters, 328(2), 235–242.
Johns, T. G., Perera, R. M., Vernes, S. C., Vitali, A. A., Cao, D. X., Cavenee, W. K., et al. (2007). The efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor-specific antibodies against glioma xenografts is influenced by receptor levels, activation status, and heterodimerization. Clinical Cancer Research, 13, 1911–1925.
Johnson, H., Del Rosario, A. M., Bryson, B. D., Schroeder, M. A., Sarkaria, J. N., & White, F. M. (2012). Molecular characterization of EGFR and EGFRvIII signaling networks in human glioblastoma tumor xenografts. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 11(12), 1724–1740.
Kang, C. S., Zhang, Z. Y., Jia, Z. F., Wang, G. X., Qiu, M. Z., Zhou, H. X., et al. (2006). Suppression of EGFR expression by antisense or small interference RNA inhibits U251 glioma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Gene Therapy, 13(5), 530–538.
Karapetis, C. S., Khambata-Ford, S., Jonker, D. J., O’Callaghan, C. J., Tu, D., Tebbutt, N. C., et al. (2008). K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 359, 1757–1765.
Karpel-Massler, G., Schmidt, U., Unterberg, A., & Halatsch, M. E. (2009). Therapeutic inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor in high-grade gliomas: Where do we stand? Molecular Cancer Research, 7(7), 1000–1012.
Kim, C., Shah, B. P., Subramaniam, P., & Lee, K. B. (2011). Synergistic induction of apoptosis in brain cancer cells by targeted codelivery of siRNA and anticancer drugs. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 8(5), 1955–1961.
Kohno, M., Horibe, T., Haramoto, M., Yano, Y., Ohara, K., Nakajima, O., et al. (2011). A novel hybrid peptide targeting EGFR-expressing cancers. European Journal of Cancer, 47(5), 773–783.
Le Mercier, M., Hastir, D., Lopez, X. M., De Néve, N., Maris, C., Trepant, A. L., et al. (2012). A simplified approach for the molecular classification of glioblastomas. PLoS ONE, 7(9), e45475.
Lee, J. C., Vivanco, I., Beroukhim, R., Huang, J. H., Feng, W. L., DeBiasi, R. M. et al., (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor activation in glioblastoma through novel missense mutations in the extracellular domain. PLoS Med 3(12),e485.
Li, M., Mukasa, A., Inda, M. M., Zhang, J., Chin, L., Cavenee, W., et al. (2011). Guanylate binding protein 1 is a novel effector of EGFR-driven invasion in glioblastoma. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 208(13), 2657–2673.
Li, L., Quang, T. S., Gracely, E. J., Kim, J. H., Emrich, J. G., Yaeger, T. E., et al. (2010). A phase II study of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor radioimmunotherapy in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Journal of Neurosurgery, 113(2), 192–198.
Liu, T. F., Hall, P. D., Cohen, K. A., Willingham, M. C., Cai, J., Thorburn, A., et al. (2005). Interstitial diphtheria toxin epidermal growth factor fusion protein therapy produces regressions of subcutaneous human glioblastoma multiforme tumors in athymic nude mice. Clinical Cancer Research, 11(1), 329–334.
Liu, Y., Li, C., & Lin, J. (2010). STAT3 as a therapeutic target for glioblastoma. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 10(7), 512–519.
Loew, S., Schmidt, U., Unterberg, A., & Halatsch, M. E. (2009). The epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma multiforme and other malignant neoplasms. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 9(6), 703–715.
Longo, S. L., Padalino, D. J., McGillis, S., Petersen, K., Schirok, H., Politz, O., et al. (2012). Bay846, a new irreversible small molecule inhibitor of EGFR and Her2, is highly effective against malignant brain tumor models. Investigational New Drugs, 30(6), 2161–2172.
Luwor, R. B., Johns, T. G., Murone, C., Huang, H. J., Cavenee, W. K., Ritter, G., et al. (2001). Monoclonal antibody 806 inhibits the growth of tumor xenografts expressing either the de2-7 or amplified epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) but not wild-type EGFR. Cancer Research, 61(14), 5355–5361.
Marsh, J. C., Goldfarb, J., Shafman, T. D., & Aidnag, Z. D. (2012). Current status of immunotherapy and gene therapy for high-grade gliomas. Cancer Control, 20(1), 43–48.
Mellinghoff, I. K., Wang, M. Y., Vivanco, I., Haas-Kogan, D. A., Zhu, S. J., Dia, E. Q., et al. (2005). Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. New England Journal of Medicine, 353, 2012–2024.
Meng, W., Jiang, L., Lu, L., Hu, H., Yu, H., Ding, D., et al. (2012). Anti-miR-155 oligonucleotide enhances chemosensitivity of U251 cell to taxol by inducing apoptosis. Cell Biology International, 36(7), 653–659.
Mengelberger, D., Kern, D., Loipetzberger, A., Eberl, M., & Aberger, F. (2012). Cooperative hedgehog-EGFR signaling. Frontiers in Bioscience, 17, 90–99.
Mineo, J. F., Bordron, A., Baroncini, M., Maurage, C. A., Ramirez, C., Siminski, R. M., et al. (2007). Low HER2-expressing glioblastomas are more often secondary to anaplastic transformation of low-grade glioma. Journal of Neuro-oncology, 85(3), 281–287.
Moyer, J. D., Barbacci, E. G., Iwata, K. K., Arnold, L., Boman, B., Cunningham, A., et al. (1997). Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Research, 57(21), 4838–4848.
Noerholm, M., Balaj, L., Limperg, T., Salehi, A., Zhu, L. D., Hochberg, F. H., et al. (2012). RNA expression patterns in serum microvesicles from patients with glioblastoma multiforme and controls. BMC Cancer, 17(12), 22.
Ou, S. H. (2012). Second-generation irreversible epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs): A better mousetrap? A review of the clinical evidence. Critical Reviews in Oncology Hematology, 83(3), 407–421.
Peereboom, D. M., Shepard, D. R., Ahluwalia, M. S., Brewer, C. J., Agarwal, N., Stevens, G. H., et al. (2010). Phase II trial of erlotinib with temozolomide and radiation in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Journal of Neuro-oncology, 98(1), 93–99.
Prayson, R. A. (2009). Lipomatous supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumor with glioblastomatous differentiation. Annals of Diagnostic Pathology, 13, 36–40.
Quang, T. S., & Brady, L. W. (2004). Radioimmunotherapy as a novel treatment regimen: 125I-labeled monoclonal antibody 425 in the treatment of high-grade brain gliomas. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics, 58(3), 972–975.
Quatrale, A. E., Porcelli, L., Silvestris, N., Colucci, G., Angelo, A., & Azzariti, A. (2011). EGFR tyrosine kinases inhibitors in cancer treatment: In vitro and in vivo evidence. Frontiers in Bioscience, 16, 1962–1972.
Raizer, J. J., Abrey, L. E., Lassman, A. B., Chang, S. M., Lamborn, K. R., Kuhn, J. G., et al. (2010). A phase II trial of erlotinib in patients with recurrent malignant gliomas and nonprogressive glioblastoma multiforme postradiation therapy. Neuro-Oncology, 12(1), 95–103.
Rich, J. N., Rasheed, B. K., & Yan, H. (2004). EGFR mutations and sensitivity to gefitinib. New England Journal of Medicine, 351(12), 1260–1261.
Rivera, F., Vega-Villegas, M. E., & Lopez-Brea, M. F. (2008). Cetuximab, its clinical use and future perspectives. Anti-Cancer Drugs, 19(2), 99–113.
Sai, K., Wang, S., Balasubramaniyan, V., Conrad, C., Lang, F. F., Aldape, K., et al. (2012). Induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in glioblastoma stem-like cells by WP1193, a novel small molecule inhibitor of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Journal of Neuro-oncology, 107(3), 487–501.
Sampson, J. H., Archer, G. E., Mitchell, D. A., Heimberger, A. B., Herndon, J. E., 2nd, Lally-Goss, D., et al. (2009). An epidermal growth factor receptor variant III-targeted vaccine is safe and immunogenic in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 8(10), 2773–2779.
Schneider, T., Becker, A., Ringe, K., Reinhold, A., Firsching, R., & Sabel, B. A. (2008). Brain tumor therapy by combined vaccination and antisense oligonucleotide delivery with nanoparticles. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 195(1–2), 21–27.
Scott, A. M., Lee, F. T., Tebbutt, N., Herbertson, R., Gill, S. S., Liu, Z., et al. (2007). A phase I clinical trial with monoclonal antibody ch806 targeting transitional state and mutant epidermal growth factor receptors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(10), 4071–4076.
Shao, H., Chung, J., Balaj, L., Charest, A., Bigner, D. D., Carter, B. S., et al. (2012). Protein typing of circulating microvesicles allows real-time monitoring of glioblastoma therapy. Nature Medicine, 18(12), 1835–1840.
Shin, B. J., Burkhardt, J. K., Riina, H. A., & Boockvar, J. A. (2012). Superselective intra-arterial cerebral infusion of novel agents after blood-brain disruption for the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: A technical case series. Neurosurgery Clinics of North America, 23(2), 323–329.
Shinojima, N., Tada, K., Shiraishi, S., Kamiryo, T., Kochi, M., Nakamura, H., et al. (2003). Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Research, 63, 6962–6970.
Shir, A., & Levitzki, A. (2002). Inhibition of glioma growth by tumor-specific activation of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR. Nature Biotechnology, 20(9), 895–900.
Singh, A. B., & Harris, R. C. (2005). Autocrine, paracrine and juxtacrine signaling by EGFR ligands. Cellular Signalling, 17, 1183–1193.
Skog, J., Würdinger, T., van Rijn, S., Meijer, D. H., Gainche, L., Sena-Esteves, M., et al. (2008). Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nature Cell Biology, 10(12), 1470–1476.
Stechishin, O. D., Luchman, H. A., Ruan, Y., Blough, M. D., Nguyen, S. A., Kelly, J. J., et al. (2013). On-target JAK2/STAT3 inhibition slows disease progression in orthotopic xenografts of human glioblastoma brain tumor stem cells. Neuro-Oncology, 15(2), 198–207.
Stockhausen, M. T., Broholm, H., Villingshoj, M., Kirchhoff, M., Gerdes, T., Kristoffersen, K., et al. (2011). Maintenance of EGFR and EGFRvIII expressions in an in vivo and in vitro model of human glioblastoma multiforme. Experimental Cell Research, 317, 1513–1526.
Stommel, J. M., Kimmelman, A. C., Ying, H., Nabioullin, R., Ponugoti, A. H., Wiedemeyer, R., et al. (2007). Coactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases affects the response of tumor cells to targeted therapies. Science, 318, 287–290.
Stupp, R., Hegi, M. E., Mason, W. P., van den Bent, M. J., Taphoorn, M. J., Janzer, R. C., et al. (2009). Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. The lancet Oncology, 10(5), 459–466.
Stupp, R., Mason, W. P., van den Bent, M. J., Weller, M., Fisher, B., Taphoorn, M. J., et al. (2005). Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. New England Journal of Medicine, 352(10), 987–996.
Tanaka, K., Babic, I., Nathanson, D., Akhavan, D., Guo, D., Gini, B., et al. (2011). Oncogenic EGFR signaling activates an mTORC2-NF-κB pathway that promotes chemotherapy resistance. Cancer Discovery, 1(6), 524–538.
Tanaka, S., Louis, D. N., Curry, W. T., Batchelor, T. T., & Dietrich, J. (2012). Diagnostic and therapeutic avenues for glioblastoma: No longer a dead end? Natural Review of Clinical Oncology, 10(1), 14–26.
Taylor, T. E., Furnari, F. B., & Cavenee, W. K. (2012). Targeting EGFR for treatment of glioblastoma: Molecular basis to overcome resistance. Current Cancer Drug Targets, 12(3), 197–209.
Taylor, D. D., & Gercel-Taylor, C. (2011). Exosomes/microvesicles: Mediators of cancer-associated immunosuppressive microenvironments. Seminars in Immunopathology, 33(5), 441–454.
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Research Network. (2008). Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature, 455, 1061–1068.
Thiessen, B., Stewart, C., Tsao, M., Kamel-Reid, S., Schaiquevich, P., Mason, W., et al. (2010). A phase I/II trial of GW572016 (lapatinib) in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: Clinical outcomes, pharmacokinetics and molecular correlation. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, 65(2), 353–361.
Thomas, C. Y., Chouinard, M., Cox, M., Parsons, S., Stallings-Mann, M., Garcia, R., et al. (2003). Spontaneous activation and signaling by overexpressed epidermal growth factor receptors in glioblastoma cells. International Journal of Cancer, 104(1), 19–27.
Torp, S. H., Gulati, S., Johannessen, E., & Dalen, A. (2007). Coexpression of c-erbB 1–4 receptor proteins in human glioblastomas. An immunohistochemical study. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 26(3), 353–359.
Ullrich, A., Coussens, L., Hayflick, J. S., Dull, T. J., Gray, A., Tam, A. W., et al. (1984). Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Nature, 309, 418–425.
van den Bent, M. J., Brandes, A. A., Rampling, R., Kouwenhoven, M. C., Kros, J. M., Carpentier, A. F., et al. (2009a). Randomized phase II trial of erlotinib versus temozolomide or carmustine in recurrent glioblastoma: EORTC brain tumor group study 26034. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27(8), 1268–1274.
van den Bent, M. J., Vogelbaum, M. A., Wen, P. Y., Macdonald, D. R., & Chang, S. M. (2009b). End point assessment in gliomas: Novel treatments limit usefulness of classical Macdonald’s Criteria. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27(18), 2905–2908.
Verhaak, R. G. W., Hoadley, K. A., Purdom, E., Wang, V., & The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. (2010). An integrated analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastome characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR and NF1. Cancer Cell, 17(1), 98.
Vivanco, I., Robins, H. I., Rohle, D., Campos, C., Grommes, C., Nghiemphu, P. L., et al. (2012). Differential sensitivity of glioma- versus lung cancer-specific EGFR mutations to EGFR kinase inhibitors. Cancer Discovery, 2(5), 458–471.
Wang, S. C., & Hung, M. C. (2009). Nuclear translocation of the epidermal growth factor receptor family membrane tyrosine kinase receptors. Clinical Cancer Research, 15(21), 6484–6489.
Watanabe, K., Tachibana, O., Sata, K., Yonekawa, Y., Kleihues, P., & Ohgaki, H. (1996). Overexpression of the EGF receptor and p53 mutations are mutually exclusive in the evolution of primary and secondary glioblastomas. Brain Pathology, 6(3), 217–223.
Wells, A. (1999). EGF receptor. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 31(6), 637–643.
Wissner, A., & Mansour, T. S. (2008). The development of HKI-272 and related compounds for the treatment of cancer. Archiv der Pharmazie (Weinheim), 341(8), 465–477.
Wong, S. T., Zhang, X. Q., Zhuang, J. T., Chan, H. L., Li, C. H., & Leung, G. K. (2012). MicroRNA-21 inhibition enhances in vitro chemosensitivity of temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma cells. Anticancer Research, 32(7), 2835–2841.
Yamazaki, H., Kijima, H., Ohnishi, Y., Abe, Y., Oshika, Y., Tsuchida, T., et al. (1998). Inhibition of tumor growth by ribozyme-mediated suppression of aberrant epidermal growth factor. JNCI Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 90(8), 581.
Yan, H., Parsons, D. W., Jin, G., McLendon, R., Rasheed, B. A., Yuan, W., et al. (2009). IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. New England Journal of Medicine, 360(8), 765–773.
Yang, X. D., Jia, X. C., Corvalan, J. R. F., Wang, P., & Davis, C. G. (2001). Development of ABX-EGF, a fully human anti-EGF receptor monoclonal antibody, for cancer therapy. Critical Reviews in Oncology and Hematology, 38, 17–23.
Yang, Y., Jiang, H., Gao, H., Kong, J., Zhang, P., Hu, S., et al. (2012). The monoclonal antibody CH12 enhances the sorafenib-mediated growth inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts expressing epidermal growth factor receptor variant III. Neoplasia, 14(6), 509–518.
Yoon, H., Kim, D. J., Ahn, E. H., Gellert, G. C., Shay, J. W., Ahn, C. H., et al. (2009). Antitumor activity of a novel antisense oligonucleotide against Akt1. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 108(4), 832–838.
Yung, W. K., Vredenburgh, J. J., Cloughesy, T. F., Nghiemphu, P., Klencke, B., Gilbert, M. R., et al. (2010). Safety and efficacy of erlotinib in first-relapse glioblastoma: A phase II open-label study. Neuro-Oncology, 12(10), 1061–1070.
Zaczek, A., Brandt, B., & Bielawski, K. P. (2005). The diverse signaling network of EGFR, HER2, HER3 and HER4 tyrosine kinase receptors and the consequences for therapeutic approaches. Histology and Histopathology, 20(3), 1005–1015.
Zeineldin, R., Ning, Y., & Hudson, L. G. (2010). The constitutive activity of epidermal growth factor receptor vIII leads to activation and differential trafficking of wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor and erbB2. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 58(6), 529–541.
Zhou, X., Ren, Y., Moore, L., Mei, M., You, Y., Xu, P., et al. (2010). Downregulation of miR-21 inhibits EGFR pathway and suppresses the growth of human glioblastoma cells independent of PTEN status. Laboratory Investigation, 90(2), 144–155.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank to Katalin Kovago for the electronic preparation of figures. Grant support to DEP was provided by the Carol M. Baldwin Breast Cancer Research Fund, the Upstate Golisano Children’s Hospital/Children’s Miracle Network, and the George W. Perkins III endowment for Neurosurgery at SUNY Upstate Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalman, B., Szep, E., Garzuly, F. et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor as a Therapeutic Target in Glioblastoma. Neuromol Med 15, 420–434 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8229-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8229-y