Abstract
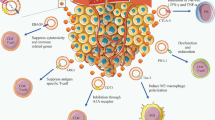
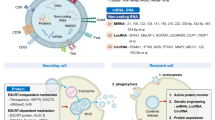
Cancer cells, both in vivo and in vitro, have been demonstrated to release membranous structures, defined as microvesicles or exosomes, consisting of an array of macromolecules derived from the originating cells, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. While only recently have the roles of these vesicular components in intercellular communication become elucidated, significant evidence has demonstrated that tumor exosomes can exert a broad array of detrimental effects on the immune system—ranging from apoptosis of activated cytotoxic T cells to impairment of monocyte differentiation into dendritic cells, to induction of myeloid-suppressive cells and T regulatory cells. Immunosuppressive exosomes of tumor origin can be found within neoplastic lesions and in biologic fluids from cancer patients, implying a potential role of these pathways in in vivo tumor progression and systemic paraneoplastic syndromes. Through the expression of molecules involved in angiogenesis promotion, stromal remodeling, signaling pathway activation through growth factor/receptor transfer, chemoresistance, and genetic intercellular exchange, tumor exosomes could represent a central mediator of the tumor microenvironment. By understanding the nature of these tumor-derived exosomes/microvesicles and their roles in mediating cancer progression and modulating the host immune response will significantly impact therapeutic approaches targeting exosomes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor DD, Doellgast GJ (1979) Quantitation of peroxidase-antibody binding to membrane fragments using column chromatography. Anal Biochem 98:53–59
Théry C, Ostrowski M, Segura E (2009) Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nature Rev Immunol 9:581–593
Trams EG, Lauter CJ, Salem C Jr, Heine U (1981) Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of microvesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 645:63–70
Pan BT, Blostein R, Johnstone RM (1983) Loss of the transferrin receptor during the maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: an immunological approach. Biochem J 210:37–47
Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P (1983) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol 97:329–339
Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, Orr L, Turbide C (1987) Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem 262:9412–9420
van Niel G, Porto-Carreiro I, Simoes S, Raposo G (2006) Exosomes: a common pathway for a specialized function. J Biochem 140:13–21
Taylor DD, Homesley HD, Doellgast GJ (1980) Binding of specific peroxidase-labeled antibody to placental-type phosphatase on tumor-derived membrane fragments. Cancer Res 40:4064–4069
Taylor DD, Homesley HD, Doellgast GJ (1983) Membrane-associated immunoglobulins in cyst and ascites fluids of ovarian cancer patients. Am J Reprod Immunol 3:7–11
Taylor DD, Levy EM, Black PH (1985) Shed membrane vesicles: a mechanism for tumor induced immunosuppression. In: Mitchell MS, Reif AE (eds) Immunity to cancer. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 369–373
Taylor DD, Black PH (1986) Shedding of plasma membrane fragments: neoplastic and developmental importance. In: Steinberg M (ed) Developmental Biology. Plenum Press, New York, vol 3., pp 33–57
Xie Y, Zhang H, Li W, Deng Y, Munegowda MA, Chibbar R, Qureshi M, Xiang J (2010) Dendritic cells recruit T cell exosomes via exosomal LFA-1 leading to inhibition of CD8+ CTL responses through downregulation of peptide/MHC class I and Fas ligand-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol 185:5268–5278
Zumaquero E, Muñoz P, Cobo M, Lucena G, Pavón EJ, Martín A, Navarro P, García-Pérez A, Ariza-Veguillas A, Malavasi F, Sancho J, Zubiaur M (2010) Exosomes from human lymphoblastoid B cells express enzymatically active CD38 that is associated with signaling complexes containing CD81, Hsc-70, and Lyn. Exp Cell Res 316:2692–2706
Anand PK (2010) Exosomal membrane molecules are potent immune response modulators. Commun Integr Biol 3:405–408
Montecalvo A, Shufesky WJ, Stolz DB, Sullivan MG, Wang Z, Divito SJ, Papworth GD, Watkins SC, Robbins PD, Larregina AT, Morelli AE (2008) Exosomes as a short-range mechanism to spread alloantigen between dendritic cells during T cell allorecognition. J Immunol 180:3081–3090
Prado N, Cañamero M, Villalba M, Rodríguez R, Batanero E (2010) Bystander suppression to unrelated allergen sensitization through intranasal administration of tolerogenic exosomes in mouse. Mol Immunol 47:2148–2151
Rak J (2010) Microparticles in cancer. Semin Thromb Hemost 36:888–906
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C (2005) Tumor-derived exosomes as mediates of T-cell signaling defects. Brit J Cancer 92:305–311
Kesimer M, Scull M, Brighton B, DeMaria G, Burns K, O'Neal W, Pickles RJ, Sheehan JK (2009) Characterization of exosome-like vesicles released from human tracheobronchial ciliated epithelium: a possible role in innate defense. FASEB J 23:1858–1868
Taylor DD, Bender DP, Gercel-Taylor C, Stanson J, Whiteside TL (2001) Modulation of TcR/CD3-zeta chain expression by a circulating factor derived from ovarian cancer patients. Br J Cancer 84:1624–1629
Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ (2010) Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics 73:1907–1920
Graner MW, Alzate O, Dechkovskaia AM, Keene JD, Sampson JH, Mitchell DA, Bigner DD (2009) Proteomic and immunologic analyses of brain tumor exosomes. FASEB J 23:1541–1557
Parsons TD, Lenzi D, Almers W, Roberts WM (1994) Calcium-triggered exocytosis and endocytosis in an isolated presynaptic cell: capacitance measurements in saccular hair cells. Neuron 13:875–883
Simons K, Gerl MJ (2010) Revitalizing membrane rafts: new tools and insights. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:688–699
Piper RC, Katzmann DJ (2007) Biogenesis and function of multivesicular bodies. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:519–547
Doring T, Gotthardt K, Stieler J, Prange R (2010) γ2-Adaptin is functioning in the late endosomal sorting pathway and interacts with ESCRT-I and -III subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803:1252–1264
DeGassart A, Geminard C, Hoekstra D, Vidal M (2004) Exosome secretion: the art of reutilizing non-recycled proteins? Traffic 5:896–903
Buschow SI, Liefhebber JM, Wubbolts R, Stoorvogel W (2005) Exosomes contain ubiquitinated proteins. Blood Cells Mol Dis 35:398–403
Qu JL, Qu XJ, Zhao MF, Teng YE, Zhang Y, Hou KZ, Jiang YH, Yang XH, Liu YP (2009) The role of cbl family of ubiquitin ligases in gastric cancer exosome-induced apoptosis of Jurkat T cells. Acta Oncol 15:1–8
Wollert T, Hurley JH (2010) Molecular mechanisms of multivesicular body biogenesis by ESCRT complexes. Nature 464:864–869
Katzmann DJ, Stefan CJ, Babst M, Emr SD (2003) Vps27 recruits ESCRT machinery to endosomes during MVB sorting. J Cell Biol 162:413–423
Skinner AM, O’Neill SL, Kurre P (2009) Cellular microvesicle pathways can be targeted to transfer genetic information between non-immune cells. PLoS One 4:e6219
Min CK, Bang SY, Cho BA, Choi YH, Yang JS, Lee SH, Seong SY, Kim KW, Kim S, Jung JU, Choi MS, Kim IS, Cho NH (2008) Role of amphipathic helix of a herpes viral protein in membrane deformation and T cell receptor downregulation. PLoS Pathog 4:e1000209
Chen J, Wang J, Meyers KR, Enns CA (2009) Transferrin-directed internalization and cycling of transferring receptor 2. Traffic 10:1488–1501
Simpson RJ, Jensen SS, Lim JW (2008) Proteomic profiling of exosomes: current perspectives. Proteomics 8:4083–4099
Mathivanan S, Simpson RJ (2009) ExoCarta: a compendium of exosomal proteins and RNA. Proteomics 9:4997–5000
Muntasell A, Berger AC, Roche PA (2007) T cell-induced secretion of MHC class II-peptide complexes on B cell exosomes. EMBO J 26:4263–4272
Janiszewski M, DoCarmo AO, Pedro MA, Silva E, Knobel E, Laurindo FR (2004) Platelet-derived exosomes of septic individuals possess proapoptotic NAD(P)H oxidase activity: a novel vascular redox pathway. Crit Care Med 32:818–825
Wolfers J, Lozier A, Raposo G, Regnault A, Thery C, Masurier C, Flament C, Pouzieux S, Faure F, Tursz T, Angevin E, Amigorena ZL (2001) Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of shared tumor rejection antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nat Med 7:297–303
Pfeffer SR (2010) Two Rabs for exosome release. Nat Cell Biol 12:3–4
McCready J, Sims JD, Chan D, Jay DG (2010) Secretion of extracellular hsp90alpha via exosomes increases cancer cell motility: a role for plasminogen activation. BMC Cancer 10:294
Lee HM, Choi EJ, Kim JH, Kim TD, Kim YK, Kang C, Gho YS (2010) A membranous for of ICAM-1 on exosomes efficiently blocks leukocyte adhesion to activated endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:251–256
Chairoungdua A, Smith DL, Pochard P, Hull M, Caplan MJ (2010) Exosome release of β-catenin: a novel mechanism that antagonizes Wnt signaling. J Cell Biol 190:1079–1091
Zöller M (2009) Tetraspanins: push and pull in suppressing and promoting metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 9:40–55
Stinton LM, Eystathioy T, Selak S, Chan EK, Fritzler MJ (2004) Autoantibodies to protein transport and messenger RNA pathways: endosomes, lysosomes, Golgi complex, proteasomes, assemblyosomes, exosomes, and GW bodies. Clin Immunol 110:30–44
Cheruvanky A, Zhou H, Pisitkun T, Kopp JB, Knepper MA, Yuen PS, Star RA (2007) Rapid isolation of urinary exosomal biomarkers using a nanomembrane ultrafiltration concentrator. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292:F1657–F1661
Viaud S, Théry C, Ploix S, Tursz T, Lapierre V, Lantz O, Zitvogel L, Chaput N (2010) Dendritic cell-derived exosomes for cancer immuntherapy: what's next? Cancer Res 70:1281–1285
Andre F, Schartz NE, Movassagh M, Flament C, Pautier P, Morice P, Pomel C, Lhomme C, Escudier B, Le Chevalier T, Tursz T, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Angevin E, Zitvogel L (2002) Malignant effusions and immunogenic tumour-derived exosomes. Lancet 360:295–305
Parolini I, Federici C, Raggi C, Lugini L, Palleschi S, De Milito A, Coscia C, Iessi E, Logozzi M, Molinari A, Colone M, Tatti M, Sargiacomo M, Fais S (2009) Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J Biol Chem 284:34211–34222
Simons M, Raposo G (2009) Exosomes: vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:575–581
Park JE, Tan HS, Datta A, Lai RC, Zhang H, Meng W, Lim SK, Sze SK (2010) Hypoxic tumor cell modulates its microenvironment to enhance angiogenic and metastatic potential by secretion of proteins and exosomes. Mol Cell Proteomics 9:1085–1099
Marhaba R, Klingbeil P, Nuebel T, Nazarenko I, Buechler MW, Zoeller M (2008) CD44 and EpCAM: cancer-initiating cell markers. Curr Mol Med 8:784–804
Xiang X, Poliakov A, Liu C, Liu Y, Deng ZB, Wang J, Cheng Z, Shah SV, Wang GJ, Zhang L, Grizzle WE, Mobley J, Zhang HG (2009) Induction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells by tumor exosomes. Int J Cancer 124:2621–2633
Hong BS, Cho JH, Kim H, Choi EJ, Rho S, Kim J, Kim JH, Choi DS, Kim YK, Hwang D, Gho YS (2009) Colorectal cancer cell-derived microvesicles are enriched in cell cycle-related mRNAs that promote proliferation of endothelial cells. BMC Genomics 10:556
Nazarenko I, Rana S, Baumann A, McAlear J, Hellwig A, Trendelenburg M, Lochnit G, Preissner KT, Zöller M (2010) Cell surface tetraspanin Tspan8 contributes to molecular pathways of exosome-induced endothelial cell activation. Cancer Res 70:1668–1678
Keller S, König AK, Marmé F, Runz S, Wolterink S, Koensgen D, Mustea A, Sehouli J, Altevogt P (2009) Systemic presence and tumor-growth promoting effect of ovarian carcinoma released exosomes. Cancer Lett 278:73–81
Dolo V, D'Ascenzo S, Violini S, Pompucci L, Festuccia C, Ginestra A, Vittorelli ML, Canevari S, Pavan A (1999) Matrix-degrading proteinases are shed in membrane vesicles by ovarian cancer cells in vivo and in vitro. Clin Exp Metastasis 17:131–140
Dolo V, Ginestra A, Cassara D, Ghersi G, Nagase H, Vittorelli ML (1999) Shed membrane vesicles and selective localization of gelatinases and MMP-9/TIMP-1 complexes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 878:497–499
Graves LE, Ariztia EV, Navari JR, Matzel HJ, Stack MS, Fishman DA (2004) Proinvasive properties of ovarian cancer ascites-derived membrane vesicles. Cancer Res 64:7045–7049
Lewis CE, Pollard JW (2006) Distinct role of macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res 66:605–612
McLellan AD (2009) Exosome release by primary B cells. Crit Rev Immunol 29:203–217
Ratajczak J, Wysoczynski M, Hayek F, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak MZ (2006) Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia 20:1487–1495
Ichim TE, Zhong Z, Kaushal S, Zheng X, Ren X, Hao X, Joyce JA, Hanley HH, Riordan NH, Koropatnick J, Bogin V, Minev BR, Min WP, Tullis RH (2008) Exosomes as a tumor immune escape mechanism: possible therapeutic implications. J Transl Med 6:37
Lenassi M, Cagney G, Liao M, Vaupotic T, Bartholomeeusen K, Cheng Y, Krogan NJ, Plemenitas A, Peterlin BM (2010) HIV Nef is secreted in exosomes and triggers apoptosis in bystander CD4+ T cells. Traffic 11:110–122
Izquierdo-Useros N, Naranjo-Gómez M, Archer J, Hatch SC, Erkizia I, Blanco J, Borràs FE, Puertas MC, Connor JH, Fernández-Figueras MT, Moore L, Clotet B, Gummuluru S, Martinez-Picado J (2009) Capture and transfer if HIV-1 particles by mature dendritic cells converges with the exosome-dissemination pathway. Blood 113:2732–2741
Izquierdo-Useros N, Naranjo-Gómez M, Erkizia I, Puertas MC, Borràs FE, Blanco J, Martinez-Picado J (2010) HIV and mature dendritic cells: Trojan exosomes riding the Trojan horse? PLoS Pathog 6:e1000740
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Rak J (2009) Microvesicles: messengers and mediators of tumor progression. Cell Cycle 8:2014–2018
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Micallef J, Lhotak V, May L, Guha A, Rak J (2008) Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 10:619–624
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Kerbel RS, Allison AC, Rak J (2009) Endothelial expression of autocrine VEGF upon the uptake of tumor-derived microvesicles containing oncogenic EGFR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:3794–3799
Viswanathan M, Sangiliyandi G, Vinod SS, Mohanprasad BK, Shanmugam G (2003) Genomic instability and tumor-specific alterations in oral squamous cell carcinomas assessed by inter-(simple sequence repeat) PCR. Clin Cancer Res 9:1057–1062
Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, Cantaluppi V, Biancone L (2010) Exosomes/microvesicles as a mechanism of cell-to-cell communication. Kidney Int 78:838–848
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky AM, Breakefield XO (2008) Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol 10:1470–1476
Janowska-Wieczorek A, Wysoczynski M, Kijowski J, Marquez-Curtis L, Machalinski B, Ratajczak J, Ratajczak MZ (2005) Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. Int J Cancer 113:752–760
Koh W, Sheng CT, Tan B, Lee QY, Kuznetsov V, Kiang LS, Tanavde V (2010) Analysis of deep sequencing microRNA expression profile from human embryonic stem cells derived mesenchymal stem cells reveals possible role of let-7 microRNA family in downstream targeting of hepatic nuclear factor 4 alpha. BMC Genomics 11(Suppl 1):S6
Yuan XL, Chen L, Li MX, Dong P, Xue J, Wang J, Zhang TT, Wang XA, Zhang FM, Ge HL, Shen LS, Xu D (2010) Elevated expression of Foxp3 in tumor-infiltrating Treg cells suppresses T-cell proliferation and contributes to gastric cancer progression in a COX-2-dependent manner. Clin Immunol 134:277–288
Whiteside TL (2005) Tumour-derived exosomes or microvesicles: another mechanism of tumour escape from the host immune system? Br J Cancer 92:209–211
Valenti R, Huber V, Iero M, Filipazzi P, Parmiani G, Rivoltini L (2007) Tumor-released microvesicles as vehicles of immunosuppression. Cancer Res 67:2912–2915
Cocucci E, Racchetti G, Meldolesi J (2009) Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol 19:43–51
Huber V, Fais S, Iero M, Lugini L, Canese P, Squarcina P, Zaccheddu A, Colone M, Arancia G, Gentile M, Seregni E, Valenti R, Ballabio G, Belli F, Leo E, Parmiani G, Rivoltini L (2005) Human colorectal cancer cells induce T-cell death through release of proapoptotic microvesicles: role in immune escape. Gastroenterol 128:1796–1804
Wieckowski EU, Visus C, Szajnik M, Szczepanski MJ, Storkus WJ, Whiteside TL (2009) Tumor-derived microvesicles promote regulatory T cell expansion and induce apoptosis in tumor-reactive activated CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol 183:3720–3730
Huber V, Filipazzi P, Iero M, Fais S, Rivoltini L (2008) More insights into the immunosuppressive potential of tumor exosomes. J Transl Med 6:63
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C, Lyons KS, Stanson J, Whiteside TL (2003) T-cell apoptosis and suppression of T-cell receptor/CD3-zeta by Fas ligand-containing membrane vesicles shed from ovarian tumors. Clin Cancer Res 9:5113–5119
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C, Weese JL (1989) Expression and shedding of mdr-1 antigen by variants of the murine B16 melanoma. Surg Forum 40:406–408
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C, Gall SA (1996) Expression and shedding of CD44 isoforms by gynecologic cancer patients. J Soc Gynecol Invest 3:289–294
Taylor DD, Lyons KS, Gercel-Taylor C (2002) Shed membrane fragment-associated markers for endometrial and ovarian cancers. Gynecol Oncol 84:443–448
Schorey JS, Bhatnagar S (2008) Exosome function: from tumor immunology to pathogen biology. Traffic 9:871–881
Zindl CL, Chaplin DD (2010) Immunology: tumor immune evasion. Science 328:697–698
Moserle L, Amadori A, Indraccolo S (2009) The angiogenic switch: implications in the regulation of tumor dormancy. Curr Mol Med 9:935–941
Gao D, Nolan D, McDonnell K, Vahdat L, Benezra R, Altorki N, Mittal V (2009) Bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells contribute to the angiogenic switch in tumor growth and metastatic progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1796:33–40
Zwirner NW, Croci DO, Domaica CI, Rabinovich GA (2010) Overcoming the hurdles of tumor immunity by targeting regulatory pathways in innate and adaptive immune cells. Curr Pharm Des 16:255–267
Soloski MJ (2001) Recognition of tumor cells by the innate immune system. Curr Opin Immunol 13:154–162
Ashiru O, Boutet P, Fernández-Messina L, Agüera-González S, Skepper JN, Valés-Gómez M, Reyburn HT (2010) Natural killer cell cytotoxicity is suppressed by exposure to the human NKG2D ligand MICA*008 that is shed by tumor cells in exosomes. Cancer Res 70:481–489
Groh V, Wu J, Yee C, Spies T (2002) Tumour-derived soluble MIC ligands impair expression of NKG2D and T-cell activation. Nature 419:734–738
Frey AB (2006) Myeloid suppressor cells regulate the adaptive immune response to cancer. J Clin Invest 116:2587–2590
Makarenkova VP, Bansal V, Matta BM, Perez LA, Ochoa JB (2006) CD11b+/Gr-1+ myeloid suppressor cells cause T cell dysfunction after traumatic stress. J Immunol 176:2085–2094
Yu S, Liu C, Su K, Wang J, Liu Y, Zhang L, Li C, Cong Y, Kimberly R, Grizzle WE, Falkson C, Zhang HG (2007) Tumor exosomes inhibit differentiation of bone marrow dendritic cells. J Immunol 178:6867–6875
Soderberg A, Barral AM, Soderstrom M, Sander B, Rosen A (2007) Redox-signaling transmitted in trans to neighboring cells by melanoma-derived TNF-containing exosomes. Free Radic Biol Med 43:90–99
Chalmin F, Ladoire S, Mignot G, Vincent J, Bruchard M, Remy-Martin JP, Boireau W, Rouleau A, Simon B, Lanneau D, De Thonel A, Multhoff G, Hamman A, Martin F, Chauffert B, Solary E, Zitvogel L, Garrido C, Ryffel B, Borg C, Apetoh L, Rébé C, Ghiringhelli F (2010) Membrane-associated Hsp72 from tumor-derived exosomes mediates STAT3-dependent immunosuppressive function of mouse and human myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Clin Invest 120:457–471
Liu Y, Xiang X, Zhuang X, Zhang S, Liu C, Cheng Z, Michalek S, Grizzle W, Zhang HG (2010) Contribution of MyD88 to the tumor exosome-mediated induction of myeloid derived suppressor cells. Am J Pathol 176:2490–2499
Iero M, Valenti R, Huber V, Filipazzi P, Parmiani G, Fais S, Rivoltini L (2008) Tumour-released exosomes and their implications in cancer immunity. Cell Death Differ 15:80–88
Wieckowski E, Whiteside TL (2006) Human tumor-derived vs dendritic cell derived exosomes have distinct biologic roles and molecular profiles. Immunol Res 36:247–254
Tomihari M, Chung JS, Akiyoshi H, Cruz PD Jr, Ariizumi K (2010) DC-HIL/glycoprotein Nmb promotes growth of melanoma in mice by inhibiting the activation of tumor-reactive T cells. Cancer Res 70:5778–5787
Kim JW, Wieckowski E, Taylor DD, Reichert TE, Watkins S, Whiteside TL (2005) Fas ligand-positive membranous vesicles isolated from sera of patients with oral cancer induce apoptosis of activated T lymphocytes. Clin Cancer Res 11:1010–1020
Laulagnier K, Grand D, Dujardin A, Hamdi S, Vincent-Schneider H, Lankar D, Salles JP, Bonnerot C, Perret B, Record M (2004) PLD2 is enriched on exosomes and its activity is correlated to the release of exosomes. FEBS Lett 572:11–14
Morelli AE (2006) The immune regulatory effect of apoptotic cells and exosomes on dendritic cells: its impact on transplantation. Am J Transplant 6:254–261
Abusamra AJ, Zhong Z, Zheng X, Li M, Ichim TE, Chin JL, Min WP (2005) Tumor exosomes expressing Fas ligand mediate CD8+ T cell apoptosis. Blood Cells Mol Dis 35:169–173
Wu JD, Higgins LM, Steinle A, Cosman D, Haugk K, Plymate SR (2004) Prevalent expression of the immunostimulatory MHC class I chain-related molecule is counteracted by shedding in prostate cancer. J Clin Invest 114:560–568
Clayton A, Tabi Z (2005) Exosomes and the MICA-NKG2D system in cancer. Blood Cells Mol Dis 34:206–213
Liu C, Yu S, Zinn K, Wang J, Zhang L, Jia Y, Kappes JC, Barnes S, Kimberly RP, Grizzle WT, Zhang HG (2006) Murine mammary carcinoma exosomes promote tumor growth by suppression of NK cell function. J Immunol 176:1375–1385
Clayton A, Mitchell JP, Court J, Linnane S, Mason MD, Tabi Z (2008) Human tumor-derived exosomes down-modulate NKG2D expression. J Immunol 180:7249–7258
Perone MJ, Larregina AT, Shufesky WJ, Papworth GD, Sullivan ML, Zahorchak AF, Stolz DB, Baum LG, Watkins SC, Thomson AW, Morelli AE (2006) Transgenic galectin-1 induces maturation of dendritic cells that elicit contrasting responses in naïve and activated T cells. J Immunol 176:7207–7220
Blanchard N, Lankar D, Faure F, Regnault A, Dumont C, Raposo G, Hivroz C (2002) TCR activation of human T cells induces the production of exosomes bearing TCR/CD3/zeta complex. J Immunol 168:3235–3241
Bamias A, Tsiatas ML, Kafantari E, Liakou C, Rodolakis A, Voulgaris Z, Vlahos G, Papageorgiou T, Tsitsilonis O, Bamia C, Papatheodoridis G, Politi E, Archimandritis A, Antsaklis A, Dimopoulos MA (2007) Significant differences of lymphocytes isolated from ascites of patients with ovarian cancer compared to blood and tumor lymphocytes. Association of CD3+ CD56+ cells with platinum resistance. Gynecol Oncol 106:75–81
Kalinski P, Okada H (2010) Polarized dendritic cells as cancer vaccines: directing effector-type T cells to tumors. Semin Immunol 22(3):173–182
Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, Charoentong P, Kirilovsky A, Bindea G, Berger A, Camus M, Gillard M, Bruneval P, Fridman WH, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z, Galon J (2010) Biomolecular network reconstruction identifies T cell homing factors associated with colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 138(4):1429–1440
Lee CH, Chiang YH, Chang SE, Chong CL, Cheng BM, Roffler SR (2009) Tumor-localized ligation of CD3 and CD28 with systemic regulatory T-cell depletion induces potent innate and adaptive antitumor responses. Clin Cancer Res 15:2756–2766
Maccalli C, Pisarra P, Vegetti C, Sensi M, Parmiani G, Anichini A (1999) Differential loss of T cell signaling molecules in metastatic melanoma patients' T lymphocyte subsets expressing distinct TCR variable regions. J Immunol 163:6912–6923
Nieuwland R, van der Post JA, Gemma CA, Kenter G, Sturk A (2010) Microparticles and exosomes in gynecologic neoplasias. Semin Thromb Hemost 36:925–929
Ristorcelli E, Beraud E, Verrando P, Villard C, Lafitte D, Sbarra V, Lombardo D, Verine A (2008) Human tumor nanoparticles induce apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. FASEB J 22:3358–3369
Khazaie K, von Boehmer H (2006) The impact of CD4+ CD25+ Treg on tumor specific CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 16:124–136
Shen LS, Wang J, Shen DF, Yuan XL, Dong P, Li MX, Xue J, Zhang FM, Ge HL, Xu D (2009) CD4+CD25+CD127low/- regulatory T cells express Foxp3 and suppress effector T cell proliferation and contribute to gastric cancers progression. Clin Immunol 131:109–118
Wada J, Onishi H, Suzuki H, Yamasaki A, Nagai S, Morisaki T, Katano M (2010) Surface-bound TGF-beta1 on effusion-derived exosomes participates in maintenance of number and suppressive function of regulatory T cells in malignant effusions. Anticancer Res 30:3747–3757
Gardella S, Gardella S, Andrei C, Lotti LV, Poggi A, Torrisi MR, Zocchi MR, Rubartelli A (2001) CD8+ T lymphocytes induce polarized exocytosis of secretory lysosomes by dendritic cells with release of interleukin-1B and cathepsin D. Blood 98:2152–2159
Xie Y, Bai O, Yuan J, Chibbar R, Slattery K, Wei Y, Deng Y, Xiang J (2009) Tumor apoptotic bodies inhibit CTL responses and antitumor immunity via membrane-bound transforming growth factor-beta-1 inducing CD8+ T-cell anergy and CD4+ Tr1 cell responses. Cancer Res 69:7756–7766
Szajnik M, Czystowska M, Szczepanski MJ, Mandapathil M, Whiteside TL (2010) Tumor-derived microvesicles induce, expand and up-regulate biological activities of human regulatory T cells (Treg). PLoS One 5:e11469
Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438:932–936
Anderson HC, Mulhall D, Garimella R (2010) Role of extracellular membrane vesicles in the pathogenesis of various diseases, including cancer, renal diseases, atherosclerosis, and arthritis. Lab Invest 90:1549–1557
Temme S, Eis-Hubinger AM, McLellan AD, Koch N (2010) The herpes simplex virus-1 encoded glycoprotein B diverts HLA-DR into the exosome pathway. J Immunol 184:236–243
Miguet L, Béchade G, Fornecker L, Zink E, Felden C, Gervais C, Herbrecht R, Van Dorsselaer A, Mauvieux L, Sanglier-Cianferani S (2009) Proteomic analysis of malignant B-cell derived microparticles reveals CD148 as a potentially useful antigenic biomarker for mantle cell lymphoma diagnosis. J Proteome Res 8:3346–3354
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C, Jiang CG, Black PH (1988) Characterization of plasma membrane shedding from murine melanoma cells. Int J Cancer 41:629–635
Taylor DD, Black PH (1985) Inhibition of macrophage Ia antigen expression by shed plasma membrane vesicles from metastatic murine melanoma lines. J Natl Cancer Inst 74:859–867
Poutsiaka DD, Schroder EW, Taylor DD, Levy EM, Black PH (1985) Membrane vesicles shed by murine melanoma cells selectively inhibit the expression of Ia antigen by macrophages. J Immunol 134:138–144
Pelton JJ, Taylor DD, Fowler WC, Gercel-Taylor C, Carp NZ, Weese JL (1991) Lymphokine-activated killer cell suppressor factor in malignant effusions. Arch Surg 126:476–480
Albanese J, Meterissian S, Kontogiannea M, Dubreuil C, Hand A, Sorba S, Dainiak N (1998) Biologically acive Fas antigen and its cognate ligand are expressed on plasma membrane-derived extracellular vesicles. Blood 91:3862–3874
Admyre C, Johansson SM, Qazi KR, Filén JJ, Lahesmaa R, Norman M, Neve EP, Scheynius A, Gabrielsson S (2007) Exosomes with immune modulatory features are present in human breast milk. J Immunol 179:1969–1978
Kim SH, Bianco NR, Shufesky WJ, Morelli AE, Robbins PD (2007) MHC class II + exosomes in plasma suppress inflammation in an antigen-specific and Fas ligand/Fas-dependent manner. J Immunol 179(4):2235–2241
Martinez FO, Sica A, Mantovani A, Locati M (2008) Macrophage activation and polarization. Front Biosci 13:453–461
Ehrt S, Schnappinger D, Bekiranov S, Drenkow J, Shi S, Gingeras TR, Gaasterland T, Schoolnik G, Nathan C (2001) Reprogramming of the macrophage transcriptome in response to interferon-gamma and Mycobacterium tuberculosis: signaling roles of nitric oxide synthase-2 and phagocyte oxidase. J Exp Med 194:1123–1140
Martinez FO, Gordon S, Locati M, Mantovani A (2006) Transcriptional profiling of the human monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and polarization: new molecules and patterns of gene expression. J Immunol 177:7303–7311
Gordon S (2003) Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol 3:23–35
Dinarello CA (1996) Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood 87:2095–2147
Scotton CJ, Martinez FO, Smelt MJ, Sironi M, Locati M, Mantovani A, Sozzani S (2005) Transcriptional profiling reveals complex regulation of the monocyte IL-1 beta system by IL-13. J Immunol 174:834–845
Roman J, Ritzenthaler JD, Fenton MJ, Roser S, Schuyler W (2000) Transcriptional regulation of the human interleukin 1beta gene by fibronectin: role of protein kinase C and activator protein 1 (AP-1). Cytokine 12:1581–1589
Roman J, McDonald JA (1997) Fibronectins and fibronectin receptors in lung development, injury and repair. In: Crystal RG, West JB, Barnes P, Weibel ER (eds) The lung: scientific foundations, 2nd edn. Raven, New York, pp 737–755
Graves K, Roman J (1996) Fibronectin modulates the expression of interleukin-1β and its receptor antagonist in human mononuclear cells. Am J Physiol 271:L61–L69
Pacifici R, Roman J, Kimble R, Civitelli R, Brownfield CM, Bizzarri C (1994) Ligand binding to monocyte alpha 5 beta 1 integrin activates the alpha 2 beta 1 receptor via the alpha 5 subunit cytoplasmic domain and protein kinase C. J Immunol 153:2222–2233
Takizawa T, Nishinarita S, Kitamura N, Hayakawa J, Kang H, Tomita Y, Mitamura K, Yamagami K, Horie T (1995) Interaction of the cell-binding domain of fibronectin with VLA-5 integrin induces monokine production in cultured human monocytes. Clin Exp Immunol 101:376–382
Ruoslahti E (1996) RGD and other recognition sequences for integrins. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 12:697–715
Ardoin SP, Shanahan JC, Pisetsky DS (2007) The role of microparticles in inflammation and thrombosis. Scan J Immunol 66:159–165
Distler JH, Distler O (2010) Inflammation: microparticles and their roles in inflammatory arthritides. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6(7):385–386
Eken C, Gasser O, Zenhaeusern G, Oehri I, Hess C, Schifferli JA (2008) Polymorphonuclear neutrophil-derived ectosomes interfere with the maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol 180:817–824
Gasser O, Schifferli JA (2004) Activated polymorphonuclear neutrophils disseminate anti-inflammatory microparticles by ectocytosis. Blood 104:2543–2548
Mack M, Kleinschmidt A, Brühl H, Klier C, Nelson PJ, Cihak J, Plachý J, Stangassinger M, Erfle V, Schlöndorff D (2000) Transfer of the chemokine receptor CCR5 between cells by membrane-derived microparticles: a mechanism for cellular human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection. Nat Med 6:769–775
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published as part of the Special Issue on Small Vesicles as Immune Modulators.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, D.D., Gercel-Taylor, C. Exosomes/microvesicles: mediators of cancer-associated immunosuppressive microenvironments. Semin Immunopathol 33, 441–454 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-010-0234-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-010-0234-8