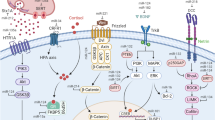
Abstract
Psychiatric illnesses are disabling disorders with poorly understood underlying pathophysiologies. However, it is becoming increasingly evident that these illnesses result from disruptions across whole cellular networks rather than any particular monoamine system. Recent evidence continues to support the hypothesis that these illnesses arise from impairments in cellular plasticity cascades, which lead to aberrant information processing in the circuits that regulate mood, cognition, and neurovegetative functions (sleep, appetite, energy, etc.). As a result, many have begun to consider future therapies that would be capable of affecting global changes in cellular plasticity to restore appropriate synaptic function and neuronal connectivity. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are non-coding RNAs that can repress the gene translation of hundreds of their targets and are therefore well-positioned to target a multitude of cellular mechanisms. Here, we review some properties of miRNAs and show they are altered by stress, glucocorticoids, mood stabilizers, and in a particular psychiatric disorder, schizophrenia. While this field is still in its infancy, we consider their potential for regulating behavioral phenotypes and targeting key predicted signaling cascades that are implicated in psychiatric illness. Clearly, considerable research is required to better determine any therapeutic potential of targeting miRNAs; however, these agents may provide the next generation of effective therapies for psychiatric illnesses.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belmaker, R. H., & Agam, G. (2008). Major depressive disorder. New England Journal of Medicine, 358(1), 55–68.
Beveridge, N. J., Tooney, P. A., Carroll, A. P., Gardiner, E., Bowden, N., Scott, R. J., et al. (2008). Dysregulation of miRNA 181b in the temporal cortex in schizophrenia. Human Molecular Genetics, 17(8), 1156–1168.
Bhattacharyya, S. N., Habermacher, R., Martine, U., Closs, E. I., & Filipowicz, W. (2006). Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell, 125(6), 1111–1124.
Bremner, J. D., Elzinga, B., Schmahl, C., & Vermetten, E. (2008). Structural and functional plasticity of the human brain in posttraumatic stress disorder. Progress in Brain Research, 167, 171–186.
Cerqueira, J. J., Pego, J. M., Taipa, R., Bessa, J. M., Almeida, O. F., & Sousa, N. (2005). Morphological correlates of corticosteroid-induced changes in prefrontal cortex-dependent behaviors. Journal of Neuroscience, 25(34), 7792–7800.
Chaudhuri, K., & Chatterjee, R. (2007). MicroRNA detection and target prediction: Integration of computational and experimental approaches. DNA and Cell Biology, 26(5), 321–337.
Chen, G., & Manji, H. K. (2006). The extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway: An emerging promising target for mood stabilizers. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 19(3), 313–323.
Cheng, H. Y., Papp, J. W., Varlamova, O., Dziema, H., Russell, B., Curfman, J. P., et al. (2007). MicroRNA modulation of circadian-clock period and entrainment. Neuron, 54(5), 813–829.
Coyle, J. T., & Duman, R. S. (2003). Finding the intracellular signaling pathways affected by mood disorder treatments. Neuron, 38(2), 157–160.
Crosby, M. E., Kulshreshtha, R., Ivan, M., & Glazer, P. M. (2009). MicroRNA regulation of DNA repair gene expression in hypoxic stress. Cancer Research, 69(3), 1221–1229.
Cryan, J. F., Kelly, P. H., Neijt, H. C., Sansig, G., Flor, P. J., & van Der Putten, H. (2003). Antidepressant and anxiolytic-like effects in mice lacking the group III metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR7. European Journal of Neuroscience, 17(11), 2409–2417.
Czeh, B., Perez-Cruz, C., Fuchs, E., & Flugge, G. (2008). Chronic stress-induced cellular changes in the medial prefrontal cortex and their potential clinical implications: Does hemisphere location matter? Behavioural Brain Research, 190(1), 1–13.
Diorio, D., Viau, V., & Meaney, M. J. (1993). The role of the medial prefrontal cortex (cingulate gyrus) in the regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress. Journal of Neuroscience, 13(9), 3839–3847.
Drevets, W. C. (2000). Functional anatomical abnormalities in limbic and prefrontal cortical structures in major depression. Progress in Brain Research, 126, 413–431.
Drevets, W. C., Ongur, D., & Price, J. L. (1998). Neuroimaging abnormalities in the subgenual prefrontal cortex: Implications for the pathophysiology of familial mood disorders. Molecular Psychiatry, 3(3), 220–226, 190–221.
Drevets, W. C., Price, J. L., Simpson, J. R., Jr., Todd, R. D., Reich, T., Vannier, M., et al. (1997). Subgenual prefrontal cortex abnormalities in mood disorders. Nature, 386(6627), 824–827.
Drevets, W. C., Savitz, J., & Trimble, M. (2008). The subgenual anterior cingulate cortex in mood disorders. CNS Spectrums, 13(8), 663–681.
Duman, R. S. (2004). Role of neurotrophic factors in the etiology and treatment of mood disorders. Neuromolecular Medicine, 5(1), 11–25.
Fish, E. W., Shahrokh, D., Bagot, R., Caldji, C., Bredy, T., Szyf, M., et al. (2004). Epigenetic programming of stress responses through variations in maternal care. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1036, 167–180.
Goodwin, F. K., & Jamison, K. R. (2007). Manic-depressive illness: Bipolar disorders and recurrent depression (2nd ed.). Oxford; New York: Oxford University Press.
Grippo, A. J., & Johnson, A. K. (2009). Stress, depression and cardiovascular dysregulation: A review of neurobiological mechanisms and the integration of research from preclinical disease models. Stress, 12(1), 1–21.
Hansen, T., Olsen, L., Lindow, M., Jakobsen, K. D., Ullum, H., Jonsson, E., et al. (2007). Brain expressed microRNAs implicated in schizophrenia etiology. PLoS ONE, 2(9), e873.
Hasler, G., Drevets, W. C., Gould, T. D., Gottesman, I. I., & Manji, H. K. (2006). Toward constructing an behaviroal phenotype strategy for bipolar disorders. Biological Psychiatry, 60(2), 93–105.
Kato, T. (2008). Molecular neurobiology of bipolar disorder: A disease of ‘mood-stabilizing neurons’? Trends in Neurosciences, 31(10), 495–503.
Keck, P. E., Jr., McElroy, S. L., Strakowski, S. M., Stanton, S. P., Kizer, D. L., Balistreri, T. M., et al. (1996). Factors associated with pharmacologic noncompliance in patients with mania. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 57(7), 292–297.
Kocerha, J., Faghihi, M. A., Lopez-Toledano, M. A., Huang, J., Ramsey, A. J., Caron, M. G., et al. (2009). MicroRNA-219 modulates NMDA receptor-mediated neurobehavioral dysfunction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science USA, 106, 3507–3512.
Kupfer, D. J. (2005). The increasing medical burden in bipolar disorder. JAMA, 293(20), 2528–2530.
Lang, U. E., Puls, I., Muller, D. J., Strutz-Seebohm, N., & Gallinat, J. (2007). Molecular mechanisms of schizophrenia. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 20(6), 687–702.
Leung, A. K., Calabrese, J. M., & Sharp, P. A. (2006). Quantitative analysis of Argonaute protein reveals microRNA-dependent localization to stress granules. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science USA, 103(48), 18125–18130.
Leung, A. K., & Sharp, P. A. (2007). microRNAs: A safeguard against turmoil? Cell, 130(4), 581–585.
Malleret, G., Haditsch, U., Genoux, D., Jones, M. W., Bliss, T. V., Vanhoose, A. M., et al. (2001). Inducible and reversible enhancement of learning, memory, and long-term potentiation by genetic inhibition of calcineurin. Cell, 104(5), 675–686.
Manji, H. K., Gottesman, I. I., & Gould, T. D. (2003). Signal transduction and genes-to-behaviors pathways in psychiatric diseases. Science STKE, 2003(207), pe49.
Marsit, C. J., Eddy, K., & Kelsey, K. T. (2006). MicroRNA responses to cellular stress. Cancer Research, 66(22), 10843–10848.
McGowan, P. O., Sasaki, A., D’Alessio, A. C., Dymov, S., Labonte, B., Szyf, M., et al. (2009). Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Nature Neuroscience, 12(3), 342–348.
Miller, M. M., & McEwen, B. S. (2006). Establishing an agenda for translational research on PTSD. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1071, 294–312.
Mitsukawa, K., Mombereau, C., Lotscher, E., Uzunov, D. P., van der Putten, H., Flor, P. J., et al. (2006). Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 7 ablation causes dysregulation of the HPA axis and increases hippocampal BDNF protein levels: Implications for stress-related psychiatric disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology, 31(6), 1112–1122.
Mulkey, R. M., Endo, S., Shenolikar, S., & Malenka, R. C. (1994). Involvement of a calcineurin/inhibitor-1 phosphatase cascade in hippocampal long-term depression. Nature, 369(6480), 486–488.
Neumeister, A., Wood, S., Bonne, O., Nugent, A. C., Luckenbaugh, D. A., Young, T., et al. (2005). Reduced hippocampal volume in unmedicated, remitted patients with major depression versus control subjects. Biological Psychiatry, 57(8), 935–937.
Perkins, D. O., Jeffries, C. D., Jarskog, L. F., Thomson, J. M., Woods, K., Newman, M. A., et al. (2007). microRNA expression in the prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Genome Biology, 8(2), R27.
Pittenger, C., & Duman, R. S. (2008). Stress, depression, and neuroplasticity: A convergence of mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology, 33(1), 88–109.
Pulkkinen, K., Malm, T., Turunen, M., Koistinaho, J., & Yla-Herttuala, S. (2008). Hypoxia induces microRNA miR-210 in vitro and in vivo ephrin-A3 and neuronal pentraxin 1 are potentially regulated by miR-210. FEBS Letters, 582(16), 2397–2401.
Rainer, J., Ploner, C., Jesacher, S., Ploner, A., Eduardoff, M., Mansha, M., et al. (2009). Glucocorticoid-regulated microRNAs and mirtrons in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia, 23, 746–752.
Rajewsky, N. (2006). microRNA target predictions in animals. Nature Genetics, 38(Suppl), S8–S13.
Sapolsky, R. M., Romero, L. M., & Munck, A. U. (2000). How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocrine Reviews, 21(1), 55–89.
Sethupathy, P., Megraw, M., & Hatzigeorgiou, A. G. (2006). A guide through present computational approaches for the identification of mammalian microRNA targets. Nature Methods, 3(11), 881–886.
Shaltiel, G., Chen, G., & Manji, H. K. (2007). Neurotrophic signaling cascades in the pathophysiology and treatment of bipolar disorder. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 7(1), 22–26.
Sklar, P., Smoller, J. W., Fan, J., Ferreira, M. A., Perlis, R. H., Chambert, K., et al. (2008). Whole-genome association study of bipolar disorder. Molecular Psychiatry, 13(6), 558–569.
Stark, K. L., Xu, B., Bagchi, A., Lai, W. S., Liu, H., Hsu, R., et al. (2008). Altered brain microRNA biogenesis contributes to phenotypic deficits in a 22q11-deletion mouse model. Nature Genetics, 40(6), 751–760.
Tabares-Seisdedos, R., & Rubenstein, J. L. (2009). Chromosome 8p as a potential hub for developmental neuropsychiatric disorders: Implications for schizophrenia, autism and cancer. Molecular Psychiatry, 14, 563–589.
Uchida, S., Nishida, A., Hara, K., Kamemoto, T., Suetsugi, M., Fujimoto, M., et al. (2008). Characterization of the vulnerability to repeated stress in Fischer 344 rats: Possible involvement of microRNA-mediated down-regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor. European Journal of Neuroscience, 27(9), 2250–2261.
Vreugdenhil, E., Verissimo, C. S., Mariman, R., Kamphorst, J. T., Barbosa, J. S., Zweers, T., et al. (2009). MicroRNAs miR-18 and miR-124a downregulate the glucocorticoid receptor: Implications for glucocorticoid responsiveness in the brain. Endocrinology, 150, 2220–2228.
Wang, J. H., & Kelly, P. T. (1997). Postsynaptic calcineurin activity downregulates synaptic transmission by weakening intracellular Ca2+ signaling mechanisms in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 17(12), 4600–4611.
Weaver, I. C., Cervoni, N., Champagne, F. A., D’Alessio, A. C., Sharma, S., Seckl, J. R., et al. (2004). Epigenetic programming by maternal behavior. Nature Neuroscience, 7(8), 847–854.
Wellman, C. L. (2001). Dendritic reorganization in pyramidal neurons in medial prefrontal cortex after chronic corticosterone administration. Journal of Neurobiology, 49(3), 245–253.
Winder, D. G., Mansuy, I. M., Osman, M., Moallem, T. M., & Kandel, E. R. (1998). Genetic and pharmacological evidence for a novel, intermediate phase of long-term potentiation suppressed by calcineurin. Cell, 92(1), 25–37.
Yang, M., Lee, J. E., Padgett, R. W., & Edery, I. (2008). Circadian regulation of a limited set of conserved microRNAs in Drosophila. BMC Genomics, 9, 83.
Zhou, R., Yuan, P., Wang, Y., Hunsberger, J. G., Elkahloun, A., Wei, Y., et al. (2008). Evidence for selective microRNAs and their effectors as common long-term targets for the actions of mood stabilizers. Neuropsychopharmacology, 34, 1395–1405.
Zhu, Y., Kalbfleisch, T., Brennan, M. D., & Li, Y. (2009). A microRNA gene is hosted in an intron of a schizophrenia-susceptibility gene. Schizophrenia Research, 109, 86–89.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hunsberger, J.G., Austin, D.R., Chen, G. et al. MicroRNAs in Mental Health: From Biological Underpinnings to Potential Therapies. Neuromol Med 11, 173–182 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-009-8070-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-009-8070-5