Abstract
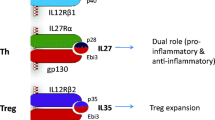
Interleukin 35 (IL-35) is the most recently identified member of the IL-12 family of cytokines and offers the potential to be a target for new therapies for autoimmune, inflammatory, and infectious diseases. Similar to other members of the IL-12 family including IL-12, IL-23, and IL-27, IL-35 is composed of a heterodimer of α and β chains, which in the case of IL-35 are the p35 and Epstein–Barr virus-induced gene 3 (EBI3) proteins. However, unlike its proinflammatory relatives, IL-35 has immunosuppressive effects that are mediated through regulatory T and B cells. Although there are limited data available regarding the role of IL-35 in human autoimmunity, several murine models of autoimmunity suggest that IL-35 may have potent effects in regulating immunoreactivity via IL-10-dependent mechanisms. We suggest that similar effects are operational in human disease and IL-35-directed therapies hold significant promise. In particular, we emphasize that IL-35 has immunosuppressive ability that are mediated via regulatory T and B cells that are IL-10 dependent. Further, although deletion of IL-35 does not result in spontaneous breach of tolerance, recombinant IL-35 can improve autoimmune responses in several experimental models.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collison LW, Vignali DA (2008) Interleukin-35: odd one out or part of the family? Immunol Rev 226:248–262
Yoshida K, Yang GX, Zhang W et al (2009) Deletion of interleukin-12p40 suppresses autoimmune cholangitis in dominant negative transforming growth factor beta receptor type II mice. Hepatology 50:1494–1500
Langrish CL, McKenzie BS, Wilson NJ, de Waal Malefyt R, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ (2004) IL-12 and IL-23: master regulators of innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev 202:96–105
Kastelein RA, Hunter CA, Cua DJ (2007) Discovery and biology of IL-23 and IL-27: related but functionally distinct regulators of inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol 25:221–242
Murugaiyan G, Mittal A, Lopez-Diego R, Maier LM, Anderson DE, Weiner HL (2009) IL-27 is a key regulator of IL-10 and IL-17 production by human CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 183:2435–2443
Goriely S, Molle C, Nguyen M et al (2006) Interferon regulatory factor 3 is involved in toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)- and TLR3-induced IL-12p35 gene activation. Blood 107:1078–1084
Wirtz S, Becker C, Fantini MC et al (2005) EBV-induced gene 3 transcription is induced by TLR signaling in primary dendritic cells via NF-kappa B activation. J Immunol 174:2814–2824
Collison LW, Workman CJ, Kuo TT et al (2007) The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function. Nature 450:566–569
Tedder TF, Leonard WJ (2014) Autoimmunity: regulatory B cells—IL-35 and IL-21 regulate the regulators. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10:452–453
Banchereau J, Pascual V, O'Garra A (2012) From IL-2 to IL-37: the expanding spectrum of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Nat Immunol 13:925–931
Shen P, Roch T, Lampropoulou V et al (2014) IL-35-producing B cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature 507:366–370
Terayama H, Yoshimoto T, Hirai S et al (2014) Contribution of IL-12/IL-35 common subunit p35 to maintaining the testicular immune privilege. PLoS One 9:e96120
Collison LW, Chaturvedi V, Henderson AL et al (2010) IL-35-mediated induction of a potent regulatory T cell population. Nat Immunol 11:1093–1101
Pankratz S, Bittner S, Herrmann AM et al (2014) Human CD4+ HLA-G+ regulatory T cells are potent suppressors of graft-versus-host disease in vivo. FASEB J 28:3435–3445
Nieuwenhuis EE, Neurath MF, Corazza N et al (2002) Disruption of T helper 2-immune responses in Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:16951–16956
Mattner F, Magram J, Ferrante J et al (1996) Genetically resistant mice lacking interleukin-12 are susceptible to infection with Leishmania major and mount a polarized Th2 cell response. Eur J Immunol 26:1553–1559
Zheng SG, Gray JD, Ohtsuka K, Yamagiwa S, Horwitz DA (2002) Generation ex vivo of TGF-beta-producing regulatory T cells from CD4 + CD25- precursors. J Immunol 169:4183–4189
Cua DJ, Sherlock J, Chen Y et al (2003) Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature 421:744–748
Murphy CA, Langrish CL, Chen Y et al (2003) Divergent pro- and antiinflammatory roles for IL-23 and IL-12 in joint autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 198:1951–1957
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM et al (2005) IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 201:233–240
Jonuleit H, Schmitt E, Kakirman H, Stassen M, Knop J, Enk AH (2002) Infectious tolerance: human CD25(+) regulatory T cells convey suppressor activity to conventional CD4(+) T helper cells. J Exp Med 196:255–260
Collison LW, Delgoffe GM, Guy CS et al (2012) The composition and signaling of the IL-35 receptor are unconventional. Nat Immunol 13:290–299
Grohmann U, Belladonna ML, Bianchi R et al (1998) IL-12 acts directly on DC to promote nuclear localization of NF-kappaB and primes DC for IL-12 production. Immunity 9:315–323
Wang RX, Yu CR, Dambuza IM et al (2014) Interleukin-35 induces regulatory B cells that suppress autoimmune disease. Nat Med 20:633–641
Wu CY, Gadina M, Wang K, O'Shea J, Seder RA (2000) Cytokine regulation of IL-12 receptor beta2 expression: differential effects on human T and NK cells. Eur J Immunol 30:1364–1374
Koch MA, Thomas KR, Perdue NR, Smigiel KS, Srivastava S, Campbell DJ (2012) T-bet(+) Treg cells undergo abortive Th1 cell differentiation due to impaired expression of IL-12 receptor beta2. Immunity 37:501–510
Saito M, Yoshida K, Hibi M, Taga T, Kishimoto T (1992) Molecular cloning of a murine IL-6 receptor-associated signal transducer, gp130, and its regulated expression in vivo. J Immunol 148:4066–4071
Presky DH, Yang H, Minetti LJ et al (1996) A functional interleukin 12 receptor complex is composed of two beta-type cytokine receptor subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:14002–14007
Yoshida K, Taga T, Saito M et al (1996) Targeted disruption of gp130, a common signal transducer for the interleukin 6 family of cytokines, leads to myocardial and hematological disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:407–411
Airoldi I, Di Carlo E, Cocco C et al (2005) Lack of Il12rb2 signaling predisposes to spontaneous autoimmunity and malignancy. Blood 106:3846–3853
Hirschfield GM, Liu X, Xu C et al (2009) Primary biliary cirrhosis associated with HLA, IL12A, and IL12RB2 variants. N Engl J Med 360:2544–2555
Matsui E, Kaneko H, Fukao T et al (1999) Mutations of the IL-12 receptor beta2 chain gene in atopic subjects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 266:551–555
Remmers EF, Cosan F, Kirino Y et al (2010) Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the MHC class I, IL10, and IL23R-IL12RB2 regions associated with Behcet's disease. Nat Genet 42:698–702
Bettini M, Castellaw AH, Lennon GP, Burton AR, Vignali DA (2012) Prevention of autoimmune diabetes by ectopic pancreatic beta-cell expression of interleukin-35. Diabetes 61:1519–1526
Cargill M, Schrodi SJ, Chang M et al (2007) A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes. Am J Hum Genet 80:273–290
Bossini-Castillo L, Martin JE, Broen J et al (2012) A GWAS follow-up study reveals the association of the IL12RB2 gene with systemic sclerosis in Caucasian populations. Hum Mol Genet 21:926–933
McGovern DP, Rotter JI, Mei L et al (2009) Genetic epistasis of IL23/IL17 pathway genes in Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15:883–889
Olson BM, Jankowska-Gan E, Becker JT, Vignali DA, Burlingham WJ, McNeel DG (2012) Human prostate tumor antigen-specific CD8+ regulatory T cells are inhibited by CTLA-4 or IL-35 blockade. J Immunol 189:5590–5601
Liu JQ, Liu Z, Zhang X et al (2012) Increased Th17 and regulatory T cell responses in EBV-induced gene 3-deficient mice lead to marginally enhanced development of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 188:3099–3106
Jafarzadeh, A., Jamali, M., Mahdavi, R., et al. (2014), Circulating levels of interleukin-35 in patients with multiple sclerosis: evaluation of the influences of FOXP3 gene polymorphism and treatment program. J Mol Neurosci
Niedbala W, Wei XQ, Cai B et al (2007) IL-35 is a novel cytokine with therapeutic effects against collagen-induced arthritis through the expansion of regulatory T cells and suppression of Th17 cells. Eur J Immunol 37:3021–3029
Kochetkova I, Golden S, Holderness K, Callis G, Pascual DW (2010) IL-35 stimulation of CD39+ regulatory T cells confers protection against collagen II-induced arthritis via the production of IL-10. J Immunol 184:7144–7153
Wirtz S, Billmeier U, McHedlidze T, Blumberg RS, Neurath MF (2011) Interleukin-35 mediates mucosal immune responses that protect against T-cell-dependent colitis. Gastroenterology 141:1875–1886
Gershwin ME, Mackay IR, Sturgess A, Coppel RL (1987) Identification and specificity of a cDNA encoding the 70 kd mitochondrial antigen recognized in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Immunol 138:3525–3531
Liaskou E, Hirschfield GM, Gershwin ME (2014) Mechanisms of tissue injury in autoimmune liver diseases. Semin Immunopathol 36:553–568
Wang L, Wang FS, Chang C, Gershwin ME (2014) Breach of tolerance: primary biliary cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis 34:297–317
Zhang J, Zhang W, Leung PS et al (2014) Ongoing activation of autoantigen-specific B cells in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 60:1708–1716
Lleo A, Zhang W, McDonald WH et al (2014) Shotgun proteomics: identification of unique protein profiles of apoptotic bodies from biliary epithelial cells. Hepatology 60:1314–1323
Chen RC, Naiyanetr P, Shu SA et al (2013) Antimitochondrial antibody heterogeneity and the xenobiotic etiology of primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 57:1498–1508
Yang CY, Ma X, Tsuneyama K et al (2014) IL-12/Th1 and IL-23/Th17 biliary microenvironment in primary biliary cirrhosis: implications for therapy. Hepatology 59:1944–1953
Hudspeth K, Pontarini E, Tentorio P et al (2013) The role of natural killer cells in autoimmune liver disease: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun 46:55–65
Huang W, Kachapati K, Adams D et al (2014) Murine autoimmune cholangitis requires two hits: cytotoxic KLRG1(+) CD8 effector cells and defective T regulatory cells. J Autoimmun 50:123–134
Yao Y, Yang W, Yang YQ et al (2014) Distinct from its canonical effects, deletion of IL-12p40 induces cholangitis and fibrosis in interleukin-2Ralpha(-/-) mice. J Autoimmun 51:99–108
Kawata K, Yang GX, Ando Y et al (2013) Clonality, activated antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells, and development of autoimmune cholangitis in dnTGFbetaRII mice. Hepatology 58:1094–1104
Ando Y, Yang GX, Kenny TP et al (2013) Overexpression of microRNA-21 is associated with elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines in dominant-negative TGF-beta receptor type II mouse. J Autoimmun 41:111–119
Oertelt S, Lian ZX, Cheng CM et al (2006) Anti-mitochondrial antibodies and primary biliary cirrhosis in TGF-beta receptor II dominant-negative mice. J Immunol 177:1655–1660
Tsuda M, Zhang W, Yang GX et al (2013) Deletion of interleukin (IL)-12p35 induces liver fibrosis in dominant-negative TGFbeta receptor type II mice. Hepatology 57:806–816
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J., Leung, P.S.C., Bowlus, C. et al. IL-35 and Autoimmunity: a Comprehensive Perspective. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 49, 327–332 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-015-8468-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-015-8468-9