Abstract
Background
Numerous molecules have been introduced to participate in the formation of breast cancer, the most common malignancy in women. Among them, neuropeptide substance P (SP) and its related receptor neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) have attracted unprecedented attention in tumorigenesis processes. In this study, we investigated the effect of the SP/NK1R pathway on the induction of oxidative stress in breast cancer and examine the therapeutic potential of NK1R inhibition in this malignancy.
Methods
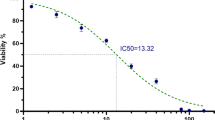
MCF-7 cells were treated with varying concentrations of SP and aprepitant, an FDA-approved NK1R antagonist, either as a single drug or in a combined modality. Resazurin assay was used to evaluate the anti-cancer ability of aprepitant. The alteration in the intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and gene expression were determined using ROS assay and the qRT-PCR analysis, respectively.
Results
The stimulation of the SP/NK1R axis in the MCF-7 cells was coupled with the accumulation of ROS as well as upregulation of NF-κB and its related pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and IL-6. In contrast, the suppression of NK1R by aprepitant halted the viability of MCF-7 cells, at least partly due to p53-mediated upregulation of p21. Moreover, aprepitant attenuated the oncogenic properties of SP by preventing the oxidative property of this neuropeptide.
Conclusion
Overall, our results suggest that the SP/NK1R pathway might play a critical role in breast cancer pathogenesis, probably through inducing ROS/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses. Moreover, it seems that blockage of the axis has promising therapeutic value against breast cancer cells.
Graphical Abstract

Schematic representation proposed for the plausible mechanism by which the stimulation of the SP/NK1R might induce oxidative stress in breast cancer-derived MCF-7 cells. Once SP interacts with NK1R, this signaling axis could disturb the balance between the expression of p53 and NF-κB, an event that leads to the accumulation of ROS within MCF-7 cells. The produced ROS, in turn, elevates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) and downregulates the expression of p21. On the other hand, aprepitant, an antagonist of NK1R, could reduce the survival of proliferative capacity of MCF-7 cells by decreasing the intracellular levels of ROS and p53-mediated up-regulation of p21. Along with the effect on p53, aprepitant could also reduce the expression of NF-κB and its related pro-inflammatory cytokines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A., & Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 68, 394–424.
Caughran, J., Braun, T. M., Breslin, T. M., Smith, D. R., Kreinbrink, J. L., Parish, G. K., Davis, A. T., Bacon‐Baguley, T. A., Silver, S. M., & Henry, N. L. (2018). The Effect of the 2009 USPSTF breast cancer screening recommendations on breast cancer in Michigan: A longitudinal study. The Breast Journal, 24, 730–737.
Waks, A. G., & Winer, E. P. (2019). Breast cancer treatment: a review. Jama, 321, 288–300.
He, F., & Zuo, L. (2015). Redox roles of reactive oxygen species in cardiovascular diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16, 27770–27780.
Salmaninejad, A., Kangari, P., & Shakoori, A. (2017). Oxidative stress: development and progression of breast cancer. Tehran University Medical Journal TUMS Publications, 75, 1–9.
Tong, L., Chuang, C.-C., Wu, S., & Zuo, L. (2015). Reactive oxygen species in redox cancer therapy. Cancer Letters, 367, 18–25.
Schieber, M. S., & Chandel, N. S. (2013). ROS links glucose metabolism to breast cancer stem cell and EMT phenotype. Cancer Cell, 23, 265–267.
Yip, N., Fombon, I., Liu, P., Brown, S., Kannappan, V., Armesilla, A., Xu, B., Cassidy, J., Darling, J., & Wang, W. (2011). Disulfiram modulated ROS–MAPK and NF κ B pathways and targeted breast cancer cells with cancer stem cell-like properties. British Journal of Cancer, 104, 1564–1574.
Ghahremani, F., Sabbaghzadeh, R., Ebrahimi, S., Javid, H., Ghahremani, J., & Hashemy, S. I. (2021). Pathogenic role of the SP/NK1R system in GBM cells through inhibiting the thioredoxin system. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 24, 499.
Suvas, S. (2017). Role of substance P neuropeptide in inflammation, wound healing, and tissue homeostasis. The Journal of Immunology, 199, 1543–1552.
Mozafari, M., Ebrahimi, S., Darban, R. A., & Hashemy, S. I. (2022). Potential in vitro therapeutic effects of targeting SP/NK1R system in cervical cancer. Molecular Biology Reports, 49, 1067–1076.
Wang, L., Wang, N., Zhang, R., Dong, D., Liu, R., Zhang, L., Ji, W., Yu, M., Zhang, F., & Niu, R. (2020). TGFβ regulates NK1R-Tr to affect the proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Life Sciences, 256, 117674.
Zhou, Y., Zhao, L., Xiong, T., Chen, X., Zhang, Y., Yu, M., Yang, J., & Yao, Z. (2013). Roles of full-length and truncated neurokinin-1 receptors on tumor progression and distant metastasis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 140, 49–61.
Davoodian, M., Boroumand, N., Bahar, M. M., Jafarian, A. H., Asadi, M., & Hashemy, S. I. (2019). Evaluation of serum level of substance P and tissue distribution of NK-1 receptor in breast cancer. Molecular Biology Reports, 46, 1285–93.
Hesketh, P. J., Grunberg, S. M., Gralla, R. J., Warr, D. G., Roila, F., de Wit, R., Chawla, S. P., Carides, A. D., Ianus, J., & Elmer, M. E. (2003). The oral neurokinin-1 antagonist aprepitant for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: a multinational, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients receiving high-dose cisplatin—the Aprepitant Protocol 052 Study Group. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 21, 4112–4119.
Bashash, D., Safaroghli-Azar, A., Bayati, S., Razani, E., Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A., Gharehbaghian, A., Momeny, M., Sanjadi, M., Rezaie-Tavirani, M., & Ghaffari, S. H. (2018). Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) inhibition sensitizes APL cells to anti-tumor effect of arsenic trioxide via restriction of NF-κB axis: Shedding new light on resistance to Aprepitant. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 103, 105–114.
Oyama, K., Fushida, S., Kaji, M., Takeda, T., Kinami, S., Hirono, Y., Yoshimoto, K., Yabushita, K., Hirosawa, H., & Takai, Y. (2013). Aprepitant plus granisetron and dexamethasone for prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in patients with gastric cancer treated with S-1 plus cisplatin. Journal of Gastroenterology, 48, 1234–1241.
Garnier, A., Vykoukal, J., Hubertus, J., Alt, E., Von Schweinitz, D., Kappler, R., Berger, M., & Ilmer, M. (2015). Targeting the neurokinin-1 receptor inhibits growth of human colon cancer cells. International Journal of Oncology, 47, 151–160.
Zhou, Y., Wang, M., Tong, Y., Liu, X., Dong, D., & Shao, J. (2015). Expression of neurokinin receptors and the effect of their antago-nists on human breast cancer. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 24, 1167–1173.
Korfi, F., Javid, H., Assaran Darban, R., & Hashemy, S. I. (2021). The Effect of SP/NK1R on the Expression and Activity of Catalase and Superoxide Dismutase in Glioblastoma Cancer Cells. Biochemistry Research International, 2021, 6620708.
Blaser, H., Dostert, C., Mak, T. W., & Brenner, D. (2016). TNF and ROS crosstalk in inflammation. Trends in Cell Biology, 26, 249–261.
Ko, E.-Y., Heo, S.-J., Cho, S.-H., Lee, W., Kim, S.-Y., Yang, H.-W., Ahn, G., Cha, S.-H., Kwon, S.-H., & Jeong, M. S. (2019). 3‑Bromo‑5‑(ethoxymethyl)‑1, 2‑benzenediol inhibits LPS-induced pro-inflammatory responses by preventing ROS production and downregulating NF-κB in vitro and in a zebrafish model. International Immunopharmacology, 67, 98–105.
Yang, C.-R., Wilson-Van Patten, C., Planchon, S. M., Wuerzberger-Davis, S. M., Davis, T. W., Cuthill, S., Miyamoto, S., & Boothman, D. A. (2000). Coordinate modulation of Sp1, NF‐kappa B, and p53 in confluent human malignant melanoma cells after ionizing radiation. The FASEB Journal, 14, 379–390.
Reddy, B. Y., Trzaska, K. A., Murthy, R. G., Navarro, P., & Rameshwar, P. (2008). Neurokinin receptors as potential targets in breast cancer treatment. Current Drug Discovery Technologies, 5, 15–19.
Singh, D., Joshi, D. D., Hameed, M., Qian, J., Gascon, P., Maloof, P. B., Mosenthal, A., & Rameshwar, P. (2000). Increased expression of preprotachykinin-I and neurokinin receptors in human breast cancer cells: implications for bone marrow metastasis. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 388–393.
Mayuri, M., & Vijayakumar, T. M. (2021). A comprehensive review on neurokinin-1 receptor antagonism in breast cancer. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 11, 009–014.
Sosa, V., Moline, T., Somoza, R., Paciucci, R., Kondoh, H., & Lleonart, M. E. (2013). Oxidative stress and cancer: an overview. Ageing Research Reviews, 12, 376–390.
Liu, B., Chen, Y., & Clair, D. K. S. (2008). ROS and p53: a versatile partnership. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 44, 1529–1535.
Papa, S., Bubici, C., Pham, C., Zazzeroni, F., & Franzoso, G. (2005). NF-kB meets ROS: an “iron-ic” encounter. Cell Death Differ, 12, 1259–1262.
Ghahremanloo, A., Javid, H., Afshari, A. R., & Hashemy, S. I. (2021). Investigation of the Role of Neurokinin-1 Receptor Inhibition Using Aprepitant in the Apoptotic Cell Death through PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signal Transduction Pathways in Colon Cancer Cells. BioMed Research International, 2021, 1383878.
Bayati, S., Bashash, D., Ahmadian, S., Safaroghli-Azar, A., Alimoghaddam, K., Ghavamzadeh, A., & Ghaffari, S. H. (2016). Inhibition of tachykinin NK1 receptor using aprepitant induces apoptotic cell death and G1 arrest through Akt/p53 axis in pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. European Journal of Pharmacology, 791, 274–283.
Bragado, P., Armesilla, A., Silva, A., & Porras, A. (2007). Apoptosis by cisplatin requires p53 mediated p38α MAPK activation through ROS generation. Apoptosis,, 12, 1733–1742.
Ozben, T. (2007). Oxidative stress and apoptosis: impact on cancer therapy. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 96, 2181–2196.
Kim, E. M., Jung, C.-H., Kim, J., Hwang, S.-G., Park, J. K., & Um, H.-D. (2017). The p53/p21 complex regulates cancer cell invasion and apoptosis by targeting Bcl-2 family proteins. Cancer Research, 77, 3092–3100.
Luo, J.-L., Kamata, H., & Karin, M. (2005). IKK/NF-κB signaling: balancing life and death–a new approach to cancer therapy. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 115, 2625–2632.
Maolake, A., Izumi, K., Natsagdorj, A., Iwamoto, H., Kadomoto, S., Makino, T., Naito, R., Shigehara, K., Kadono, Y., & Hiratsuka, K. (2018). Tumor necrosis factor‐α induces prostate cancer cell migration in lymphatic metastasis through CCR 7 upregulation. Cancer Science, 109, 1524–1531.
Chung, S. S., Wu, Y., Okobi, Q., Adekoya, D., Atefi, M., Clarke, O., Dutta, P., & Vadgama, J. V. (2017). Proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α increased telomerase activity through NF-κB/STAT1/STAT3 activation, and withaferin A inhibited the signaling in colorectal cancer cells. Mediators of Inflammation, 2017, 5958429.
Munoz, M., Gonzalez-Ortega, A., Salinas-Martín, M. V., Carranza, A., Garcia-Recio, S., Almendro, V., & Covenas, R. (2014). The neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant is a promising candidate for the treatment of breast cancer. International Journal of Oncology, 45, 1658–1672.
Author contributions
RAD and SIH contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by SJ and HJ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SJ and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jafarinezhad, S., Assaran Darban, R., Javid, H. et al. The SP/NK1R system promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells through NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses. Cell Biochem Biophys 81, 787–794 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-023-01171-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-023-01171-y