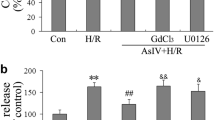
Abstract
Anisodamine is an ancient Chinese medicine derived from Tibet as a belladonna alkaloid, which is usually used for improvement of blood circulation in patients with organ phosphorus poisoning or shock. In this study, for the first time, we report its cardioprotective effects on preventing ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury of patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), and decreasing the myocardial infarction area and severity in heart of Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats. Our results suggest a potential molecular mechanism of anisodamine against the I/R injury in cardiomyocytes is associated with its anti-apoptotic effect. Anisodamine treatment decreases the expression of caspase-3 and caspase-8, and increases Bcl-2/Bax ratio in cardiomyocytes. Our data suggest that anisodamine can provide significant cardioprotection against I/R injury, potentially through the suppression of cardiomyocytes apoptosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boersma, E. (2006). Does time matter? A pooled analysis of randomized clinical trials comparing primary percutaneous coronary intervention and in-hospital fibrinolysis in acute myocardial infarction patients. European Heart Journal, 27, 779–788.
Buja, L. M. (2005). Myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cardiovascular Pathology, 14, 170–175.
Chen, L., Ling, Y. S., Lin, C. H., & Guan, T. J. (2013). Combined use of heparin and anisodamine reduces the risk of early thrombosis in native arteriovenous fistula. Vascular, 21(6), 369–374.
Esumi, K., Nishida, M., Shaw, D., Smith, T. W., & Marsh, J. D. (1991). NADH measurements in adult rat myocytes during simulated ischemia. American Journal of Physiology, 260, H1743–H1752.
Foadoddini, M., Esmailidehaj, M., Mehrani, H., Sadraei, S. H., Golmanesh, L., Wahhabaghai, H., et al. (2011). Pretreatment with hyperoxia reduces in vivo infarct size and cell death by apoptosis with an early and delayed phase of protection. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, 39, 233–240.
Fu, X. H., Fan, W. Z., Gu, X. S., Wei, Y. Y., Jiang, Y. F., Wu, W. L., et al. (2007). Effect of intracoronary administration of anisodamine on slow reflow phenomenon following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Chinese Medical Journal, 120, 1226–1231.
Fu, X. H., Fan, W. Z., Gu, X. S., Wei, Y. Y., Jiang, Y. F., Wu, W. L., et al. (2007). Effect of intracoronary administration of anisodamine on slow reflow phenomenon following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Chinese Medical Journal, 120, 1226–1231.
Klug, G., Mayr, A., Mair, J., Schocke, M., Nocker, M., Trieb, T., et al. (2011). Role of biomarkers in assessment of early infarct size after successful p-PCI for STEMI. Clinical Research in Cardiology, 100, 501–510.
Kondo-Nakamura, M., Shintani-Ishida, K., Uemura, K., & Yoshida, K. (2010). Brief exposure to carbon monoxide preconditions cardiomyogenic cells against apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 393, 449–454.
Liu, Y., Huo, Z., Yan, B., Lin, X., Zhou, Z. N., Liang, X., et al. (2010). Prolyl hydroxylase 3 interacts with Bcl-2 to regulate doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 401, 231–237.
Ludwig, L. M., Weihrauch, D., Kersten, J. R., Pagel, P. S., & Warltier, D. C. (2004). Protein kinase C translocation and Src protein tyrosine kinase activation mediate isoflurane-induced preconditioning in vivo: potential downstream targets of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels and reactive oxygen species. Anesthesiology, 100, 532–539.
Nunez, G., & Clarke, M. F. (1994). The Bcl-2 family of proteins: Regulators of cell death and survival. Trends in Cell Biology, 4, 399–403.
Olivetti, G., Quaini, F., Sala, R., Lagrasta, C., Corradi, D., Bonacina, E., et al. (1996). Acute myocardial infarction in humans is associated with activation of programmed myocyte cell death in the surviving portion of the heart. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 28, 2005–2016.
Poupko, J. M., Baskin, S. I., & Moore, E. (2007). The pharmacological properties of anisodamine. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 27, 116–121.
Silambarasan, T., Manivannan, J., Priya, M. K., Suganya, N., Chatterjee, S., & Raja, B. (2015). Sinapic acid protects heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury and H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells against oxidative stress. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 456, 853–859.
Soriano, M. E., & Scorrano, L. (2011). Traveling Bax and forth from mitochondria to control apoptosis. Cell, 145, 15–17.
Turer, A. T., Mahaffey, K. W., Gallup, D., Weaver, W. D., Christenson, R. H., Every, N. R., & Ohman, E. M. (2005). Enzyme estimates of infarct size correlate with functional and clinical outcomes in the setting of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Current Controlled Trials in Cardiovascular Medicine, 6, 12.
Xiu, R. J., Hammerschmidt, D. E., Coppo, P. A., & Jacob, H. S. (1982). Anisodamine inhibits thromboxane synthesis, granulocyte aggregation, and platelet aggregation. A possible mechanism for its efficacy in bacteremic shock. JAMA, 247, 1458–1460.
Xiu, R. J., Hammerschmidt, D. E., Coppo, P. A., & Jacob, H. S. (1982). Anisodamine inhibits thromboxane synthesis, granulocyte aggregation, and platelet aggregation: A possible mechanism for its efficacy in bacteremic shock. JAMA, 247, 1458–1460.
Yang, P., Zhang, B. H., & Hong, N. (1991). Anti-arrhythmia and vegetative nervous system effects of Anisodamine. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 12, 173–176.
Zhang, Z. X., Wang, P., Zhang, Q. S., Pan, X., Zhao, Q. X., & Wang, X. K. (2012). Effects of anisodamine on the expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 in experimental infusion phlebitis. Chinese Medical Journal, 125, 300–305.
Zhang, Z. X., Wang, P., Zhang, Q. S., Pan, X., Zhao, Q. X., & Wang, X. K. (2012). Effects of anisodamine on the expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 in experimental infusion phlebitis. Chinese Medical Journal, 125, 300–305.
Zhao, Z. Q., Nakamura, M., Wang, N. P., Wilcox, J. N., Shearer, S., Ronson, R. S., et al. (2000). Reperfusion induces myocardial apoptotic cell death. Cardiovascular Research, 45, 651–660.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, K., Fu, X., Jiang, L. et al. Cardioprotective Effect of Anisodamine Against Myocardial Ischemia Injury and its Influence on Cardiomyocytes Apoptosis. Cell Biochem Biophys 73, 707–716 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0642-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0642-4