Abstract
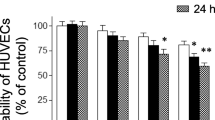
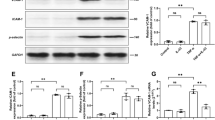
Expression of cell adhesion molecules by vascular endothelial cells (ECs) plays an important role in migration and adhesion of leukocytes into the surrounding tissues, which is a vital step in inflammation and atherogenesis. Estradiol (E2), a human sex hormone and steroid, has differential anti-inflammatory properties, increases arterial vasodilation, inhibits the cellular response to vascular injury, and prevents atherosclerosis. However, the related mechanisms are poorly understood. Here, we studied the effect of E2 on expression of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecules by cytokine-stimulated human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs). Pre-treatment of HAEC with E2 inhibited tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα)-induced expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intracellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in a time- and dose-dependent manner. E2 at 10 nmol/L inhibited interleukin-1 (IL-1)-stimulated expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1. The effect of E2 on cytokine-stimulated VCAM-1 expression was more prominent than that of ICAM-1. E2 reduced TNF-induced mRNA expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1. Repressed expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 was associated with decreased adherence of lymphocytes and monocytes to cytokine-stimulated HAEC. E2 suppressed TNF-induced activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) in HAEC. Importantly, E2 improved AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) expression in HAEC. Pharmaceutical inhibition of AMPK and PPARα blocks the effect of E2 on NF-κB, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1. These results indicate that E2 may have anti-inflammatory properties in ECs. The anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic properties of E2 may partly be ascribed to an effect on activation of AMPK and PPARα and subsequent inhibition of TNF-induced NF-κB activation, leading to the decreased expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1. Our findings support further investigations on the therapeutic benefits of E2 in several pathological events involving endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
19 October 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-022-01111-2
References
Alexiou, D., Karayiannakis, A. J., Syrigos, K. N., Zbar, A., Kremmyda, A., Bramis, I., et al. (2001). Serum levels of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in colorectal cancer patients: correlations with clinicopathological features, patient survival and tumour surgery. European Journal of Cancer, 37, 2392–2397.
Carling, D. (2005). AMP-activated protein kinase: Balancing the scales. Biochimie, 87, 87–91.
Chomczynski, P., & Sacchi, N. (1987). Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Analytical Biochemistry, 162, 156–159.
Collins, T. (1993). Endothelial nuclear factor-kappa B and the initiation of the atherosclerotic lesion. Laboratory Investigation; A Journal of Technical Methods and Pathology, 68, 499–508.
Fruchart, J. C., Duriez, P., & Staels, B. (1999). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha activators regulate genes governing lipoprotein metabolism, vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Current Opinion in Lipidology, 10, 245–257.
Ghisletti, S., Meda, C., Maggi, A., & Vegeto, E. (2005). 17beta-estradiol inhibits inflammatory gene expression by controlling NF-kappaB intracellular localization. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 25, 2957–2968.
Hardie, D. G., & Carling, D. (1997). The AMP-activated protein kinase–fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? European Journal of Biochemistry/FEBS, 246, 259–273.
Haubner, F., Lehle, K., Munzel, D., Schmid, C., Birnbaum, D. E., & Preuner, J. G. (2007). Hyperglycemia increases the levels of vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1 and monocyte-chemoattractant-protein-1 in the diabetic endothelial cell. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 360, 560–565.
Hawley, S. A., Davison, M., Woods, A., Davies, S. P., Beri, R. K., Carling, D., et al. (1996). Characterization of the AMP-activated protein kinase kinase from rat liver and identification of threonine 172 as the major site at which it phosphorylates AMP-activated protein kinase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 27879–27887.
Huo, Y., & Ley, K. (2001). Adhesion molecules and atherogenesis. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica, 173, 35–43.
Jang, Y., Lincoff, A. M., Plow, E. F., & Topol, E. J. (1994). Cell adhesion molecules in coronary artery disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 24, 1591–1601.
Kim, S. R., Bae, Y. H., Bae, S. K., Choi, K. S., Yoon, K. H., Koo, T. H., et al. (2008). Visfatin enhances ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression through ROS-dependent NF-kappaB activation in endothelial cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1783, 886–895.
Kume, N., Cybulsky, M. I., & Gimbrone, M. A, Jr. (1992). Lysophosphatidylcholine, a component of atherogenic lipoproteins, induces mononuclear leukocyte adhesion molecules in cultured human and rabbit arterial endothelial cells. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 90, 1138–1144.
Li, H., Cybulsky, M. I., Gimbrone, M. A, Jr, & Libby, P. (1993). An atherogenic diet rapidly induces VCAM-1, a cytokine-regulatable mononuclear leukocyte adhesion molecule, in rabbit aortic endothelium. Arteriosclerosis and Thrombosis : A Journal of Vascular Biology/American Heart Association, 13, 197–204.
Lidington, E. A., Moyes, D. L., McCormack, A. M., & Rose, M. L. (1999). A comparison of primary endothelial cells and endothelial cell lines for studies of immune interactions. Transplant Immunology, 7, 239–246.
Marx, N., Sukhova, G. K., Collins, T., Libby, P., & Plutzky, J. (1999). PPARalpha activators inhibit cytokine-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human endothelial cells. Circulation, 99, 3125–3131.
Mendelsohn, M. E., & Karas, R. H. (1999). The protective effects of estrogen on the cardiovascular system. The New England journal of Medicine, 340, 1801–1811.
Morrow, V. A., Foufelle, F., Connell, J. M., Petrie, J. R., Gould, G. W., & Salt, I. P. (2003). Direct activation of AMP-activated protein kinase stimulates nitric-oxide synthesis in human aortic endothelial cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 31629–31639.
Murphy, E. (2011). Estrogen signaling and cardiovascular disease. Circulation Research, 109, 687–696.
Murphy, A. J., Guyre, P. M., & Pioli, P. A. (2010). Estradiol suppresses NF-kappa B activation through coordinated regulation of let-7a and miR-125b in primary human macrophages. Journal of Immunology, 184, 5029–5037.
Nizamutdinova, I. T., Oh, H. M., Min, Y. N., Park, S. H., Lee, M. J., Kim, J. S., et al. (2007). Paeonol suppresses intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells by blocking p38, ERK and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathways. International Immunopharmacology, 7, 343–350.
Park, H., Kaushik, V. K., Constant, S., Prentki, M., Przybytkowski, E., Ruderman, N. B., et al. (2002). Coordinate regulation of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase, sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase by AMP-activated protein kinase in rat tissues in response to exercise. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 32571–32577.
Polte, T., Newman, W., & Gopal, T. V. (1990). Full length vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1). Nucleic Acids Research, 18, 5901.
Price, D. T., & Loscalzo, J. (1999). Cellular adhesion molecules and atherogenesis. The American Journal of Medicine, 107, 85–97.
Ruderman, N. B., Cacicedo, J. M., Itani, S., Yagihashi, N., Saha, A. K., Ye, J. M., et al. (2003). Malonyl-CoA and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK): Possible links between insulin resistance in muscle and early endothelial cell damage in diabetes. Biochemical Society Transactions, 31, 202–206.
Seguin, C., Abid, M. R., Spokes, K. C., Schoots, I. G., Brkovic, A., Sirois, M. G., et al. (2008). Priming effect of homocysteine on inducible vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in endothelial cells. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy =. Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, 62, 395–400.
Springer, T. A. (1994). Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: The multistep paradigm. Cell, 76, 301–314.
Vietor, I., Schwenger, P., Li, W., Schlessinger, J., & Vilcek, J. (1993). Tumor necrosis factor-induced activation and increased tyrosine phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in human fibroblasts. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 268, 18994–18999.
Weber, C., Erl, W., Pietsch, A., Strobel, M., Ziegler-Heitbrock, H. W., & Weber, P. C. (1994). Antioxidants inhibit monocyte adhesion by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa B mobilization and induction of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in endothelial cells stimulated to generate radicals. Arteriosclerosis and Thrombosis : A Journal of Vascular Biology/American Heart Association, 14, 1665–1673.
Winterbone, M. S., Tribolo, S., Needs, P. W., Kroon, P. A., & Hughes, D. A. (2009). Physiologically relevant metabolites of quercetin have no effect on adhesion molecule or chemokine expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis, 202, 431–438.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, X., Pei, F. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Estradiol Inhibits Cytokine-Induced Expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 in Cultured Human Endothelial Cells Via AMPK/PPARα Activation. Cell Biochem Biophys 72, 709–717 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0522-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0522-y