Abstract
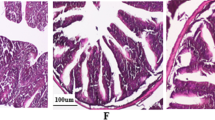
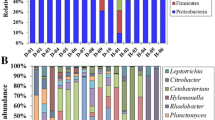
Fluorine is an environmental toxicant and exposure of fluorine could induce various health disorders. Gut microbiota has been known to be involved in maintaining animal or human health. Therefore, in the present study, we aimed to evaluate the relationship between fluorine exposure and gut microbiota in common carp. Gut microbiota composition was detected by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Intestinal structural integrity was assessed by hematoxylin-eosin staining and tight junction protection detection. The results showed that exposure of carp to fluorine led to the injury of intestinal tissues. And compared to the control group, the expression of tight junction protein ZO-1 and occludin was decreased. Meanwhile, the gut microbial diversity and composition were changed by fluorine exposure. At the phylum level, the abundance of Fusobacteria and Firmicutes increased significantly, and the abundance of Actinobacteria decreased markedly after treatment of fluorine. At the genus level, interestingly, we found the abundance of Plesiomonas, an important pathogenic bacteria, increased significantly by the treatment of fluorine. And the abundance of Akkermansia, a critical probiotics, was markedly inhibited by the treatment of fluorine. In conclusion, the results suggested fluorine exposure changed the gut microbiome composition and led to the damage of intestinal structural integrity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dhar V, Bhatnagar M (2009) Physiology and toxicity of fluoride. Indian J Dent Res 20(3):350–355
Chu S, Letcher RJ (2017) Side-chain fluorinated polymer surfactants in aquatic sediment and biosolid-augmented agricultural soil from the Great Lakes basin of North America. Sci Total Environ 607-608:262–270
Gao X, Hu Y, Li C, Dai C, Li L, Ou X, Wang Y (2016) Evaluation of fluorine release from air deposited coal spoil piles: a case study at Yangquan city, Northern China. Sci Total Environ 545-546:1–10
Song GH, Huang FB, Gao JP, Liu ML, Pang WB, Li W, Yan XY, Huo MJ, Yang X (2015) Effects of fluoride on DNA damage and caspase-mediated apoptosis in the liver of rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 166(2):173–182
Tian X, Feng J, Dong N, Lyu Y, Wei C, Li B, Ma Y, Xie J, Qiu Y, Song G, Ren X, Yan X (2019) Subchronic exposure to arsenite and fluoride from gestation to puberty induces oxidative stress and disrupts ultrastructure in the kidneys of rat offspring. Sci Total Environ 686:1229–1237
Zhou Q, Zhang J, Fu J, Shi J, Jiang G (2008) Biomonitoring: an appealing tool for assessment of metal pollution in the aquatic ecosystem. Anal Chim Acta 606(2):135–150
Butt CM, Berger U, Bossi R, Tomy GT (2010) Levels and trends of poly- and perfluorinated compounds in the arctic environment. Sci Total Environ 408(15):2936–2965
Chen J, Cao J, Luo Y, Xie L, Song J, Xue W, Jia R, Song J (2014) Expression of ERK and p-ERK proteins of ERK signaling pathway in the kidneys of fluoride-exposed carp (Cyprinus carpio). Acta Histochem 116(8):1337–1341
Chattopadhyay A, Podder S, Agarwal S, Bhattacharya S (2011) Fluoride-induced histopathology and synthesis of stress protein in liver and kidney of mice. Arch Toxicol 85(4):327–335
Gomis MI, Wang Z, Scheringer M, Cousins IT (2015) A modeling assessment of the physicochemical properties and environmental fate of emerging and novel per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Sci Total Environ 505:981–991
Cao J, Chen J, Wang J, Jia R, Xue W, Luo Y, Gan X (2013) Effects of fluoride on liver apoptosis and Bcl-2, Bax protein expression in freshwater teleost, Cyprinus carpio. Chemosphere 91(8):1203–1212
Sommer F, Backhed F (2013) The gut microbiota--masters of host development and physiology. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(4):227–238
Round JL, Mazmanian SK (2009) The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9(5):313–323
Putignani L, Del Chierico F, Petrucca A, Vernocchi P, Dallapiccola B (2014) The human gut microbiota: a dynamic interplay with the host from birth to senescence settled during childhood. Pediatr Res 76(1):2–10
Ba Q, Li M, Chen P, Huang C, Duan X, Lu L, Li J, Chu R, Xie D, Song H, Wu Y, Ying H, Jia X, Wang H (2017) Sex-dependent effects of cadmium exposure in early life on gut microbiota and fat accumulation in mice. Environ Health Perspect 125(3):437–446
Meng XL, Li S, Qin CB, Zhu ZX, Hu WP, Yang LP, Lu RH, Li WJ, Nie GX (2018) Intestinal microbiota and lipid metabolism responses in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) following copper exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 160:257–264
Rothenberg SE, Keiser S, Ajami NJ, Wong MC, Gesell J, Petrosino JF, Johs A (2016) The role of gut microbiota in fetal methylmercury exposure: insights from a pilot study. Toxicol Lett 242:60–67
Cao J, Chen J, Xie L, Wang J, Feng C, Song J (2015) Protective properties of sesamin against fluoride-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in kidney of carp (Cyprinus carpio) via JNK signaling pathway. Aquat Toxicol 167:180–190
Cao J, Chen J, Wang J, Wu X, Li Y, Xie L (2013) Tissue distributions of fluoride and its toxicity in the gills of a freshwater teleost, Cyprinus carpio. Aquat Toxicol 130-131:68–76
Claus SP, Guillou H, Ellero-Simatos S (2016) The gut microbiota: a major player in the toxicity of environmental pollutants? NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2:16003
Salim SY, Soderholm JD (2011) Importance of disrupted intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17(1):362–381
Modina SC, Polito U, Rossi R, Corino C, Di Giancamillo A (2019) Nutritional regulation of gut barrier integrity in weaning piglets. Animals (Basel) 9(12):1045
Konig J, Wells J, Cani PD, Garcia-Rodenas CL, MacDonald T, Mercenier A, Whyte J, Troost F, Brummer RJ (2016) Human intestinal barrier function in health and disease. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 7(10):e196
Wang L, Llorente C, Hartmann P, Yang AM, Chen P, Schnabl B (2015) Methods to determine intestinal permeability and bacterial translocation during liver disease. J Immunol Methods 421:44–53
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J, Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W, Pettersson S (2012) Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 336(6086):1262–1267
Rawls JF, Samuel BS, Gordon JI (2004) Gnotobiotic zebrafish reveal evolutionarily conserved responses to the gut microbiota. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(13):4596–4601
Holmes E, Li JV, Marchesi JR, Nicholson JK (2012) Gut microbiota composition and activity in relation to host metabolic phenotype and disease risk. Cell Metab 16(5):559–564
Li T, Long M, Gatesoupe FJ, Zhang Q, Li A, Gong X (2015) Comparative analysis of the intestinal bacterial communities in different species of carp by pyrosequencing. Microb Ecol 69(1):25–36
Tahara T, Yamamoto E, Suzuki H, Maruyama R, Chung W, Garriga J, Jelinek J, Yamano HO, Sugai T, An B, Shureiqi I, Toyota M, Kondo Y, Estecio MR, Issa JP (2014) Fusobacterium in colonic flora and molecular features of colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res 74(5):1311–1318
Kostic AD, Chun E, Robertson L, Glickman JN, Gallini CA, Michaud M, Clancy TE, Chung DC, Lochhead P, Hold GL, El-Omar EM, Brenner D, Fuchs CS, Meyerson M, Garrett WS (2013) Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 14(2):207–215
Li X, Yan Q, Xie S, Hu W, Yu Y, Hu Z (2013) Gut microbiota contributes to the growth of fast-growing transgenic common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). PLoS One 8(5):e64577
Abdallah Ismail N, Ragab SH, Abd Elbaky A, Shoeib AR, Alhosary Y, Fekry D (2011) Frequency of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in gut microbiota in obese and normal weight Egyptian children and adults. Arch Med Sci 7(3):501–507
Azman AS, Othman I, Fang CM, Chan KG, Goh BH, Lee LH (2017) Antibacterial, anticancer and neuroprotective activities of rare actinobacteria from mangrove forest soils. Indian J Microbiol 57(2):177–187
Alvarez A, Saez JM, Davila Costa JS, Colin VL, Fuentes MS, Cuozzo SA, Benimeli CS, Polti MA, Amoroso MJ (2017) Actinobacteria: current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere 166:41–62
Van Damme LR, Vandepitte J (1984) Isolation of Edwardsiella tarda and Plesiomonas shigelloides from mammals and birds in Zaire. Rev Elev Med Vet Pays Trop 37(2):145–151
Sack DA, Chowdhury KA, Huq A, Kay BA, Sayeed S (1988) Epidemiology of Aeromonas and Plesiomonas diarrhoea. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res 6(2):107–112
Dingemanse C, Belzer C, van Hijum SA, Gunthel M, Salvatori D, den Dunnen JT, Kuijper EJ, Devilee P, de Vos WM, van Ommen GB, Robanus-Maandag EC (2015) Akkermansia muciniphila and Helicobacter typhlonius modulate intestinal tumor development in mice. Carcinogenesis 36(11):1388–1396
Dao MC, Everard A, Aron-Wisnewsky J, Sokolovska N, Prifti E, Verger EO, Kayser BD, Levenez F, Chilloux J, Hoyles L, Consortium MI-O, Dumas ME, Rizkalla SW, Dore J, Cani PD, Clement K (2016) Akkermansia muciniphila and improved metabolic health during a dietary intervention in obesity: relationship with gut microbiome richness and ecology. Gut 65(3):426–436
Zhang Z, Wu X, Cao S, Cromie M, Shen Y, Feng Y, Yang H, Li L (2017) Chlorogenic acid ameliorates experimental colitis by promoting growth of Akkermansia in mice. Nutrients 9(7):677
Ottman N, Reunanen J, Meijerink M, Pietila TE, Kainulainen V, Klievink J, Huuskonen L, Aalvink S, Skurnik M, Boeren S, Satokari R, Mercenier A, Palva A, Smidt H, de Vos WM, Belzer C (2017) Pili-like proteins of Akkermansia muciniphila modulate host immune responses and gut barrier function. PLoS One 12(3):e0173004
Funding
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30972191), Jilin Province Industrial Technology Research and Development Special Project (no. 2019C059-5), and Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan Project (no. 20190201179JC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All authors have read the manuscript and agreed to submit it in its current form for consideration for publication in the journal.
The experiments were according to the Chinese regulation for Experimental Animals and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Jilin Agricultural University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Zhang, Y., Zhang, P. et al. Effects of Fluorine on Intestinal Structural Integrity and Microbiota Composition of Common Carp. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 3489–3496 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02456-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02456-6